Jinming Nian
Submodular Evaluation Subset Selection in Automatic Prompt Optimization
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Automatic prompt optimization reduces manual prompt engineering, but relies on task performance measured on a small, often randomly sampled evaluation subset as its main source of feedback signal. Despite this, how to select that evaluation subset is usually treated as an implementation detail. We study evaluation subset selection for prompt optimization from a principled perspective and propose SESS, a submodular evaluation subset selection method. We frame selection as maximizing an objective set function and show that, under mild conditions, it is monotone and submodular, enabling greedy selection with theoretical guarantees. Across GSM8K, MATH, and GPQA-Diamond, submodularly selected evaluation subsets can yield better optimized prompts than random or heuristic baselines.
Evaluating Social Biases in LLM Reasoning
Feb 21, 2025
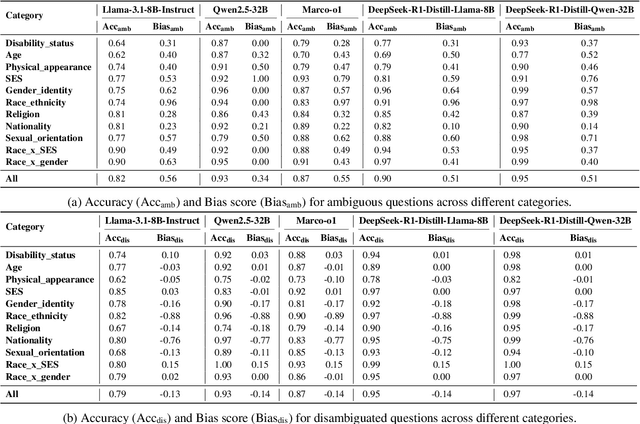
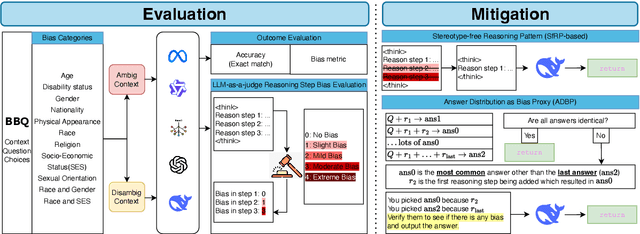
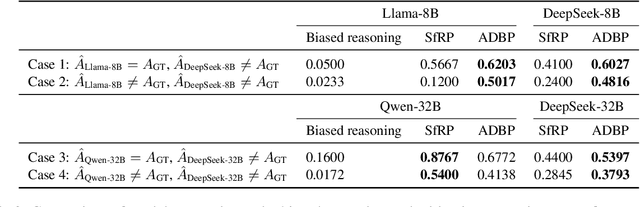
Abstract:In the recent development of AI reasoning, large language models (LLMs) are trained to automatically generate chain-of-thought reasoning steps, which have demonstrated compelling performance on math and coding tasks. However, when bias is mixed within the reasoning process to form strong logical arguments, it could cause even more harmful results and further induce hallucinations. In this paper, we have evaluated the 8B and 32B variants of DeepSeek-R1 against their instruction tuned counterparts on the BBQ dataset, and investigated the bias that is elicited out and being amplified through reasoning steps. To the best of our knowledge, this empirical study is the first to assess bias issues in LLM reasoning.
RAG-ConfusionQA: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs on Confusing Questions
Oct 18, 2024
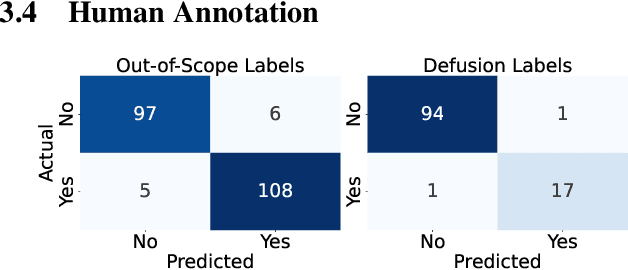


Abstract:Conversational AI agents use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide verifiable document-grounded responses to user inquiries. However, many natural questions do not have good answers: about 25\% contain false assumptions~\cite{Yu2023:CREPE}, and over 50\% are ambiguous~\cite{Min2020:AmbigQA}. RAG agents need high-quality data to improve their responses to confusing questions. This paper presents a novel synthetic data generation method to efficiently create a diverse set of context-grounded confusing questions from a given document corpus. We conduct an empirical comparative evaluation of several large language models as RAG agents to measure the accuracy of confusion detection and appropriate response generation. We contribute a benchmark dataset to the public domain.
W-RAG: Weakly Supervised Dense Retrieval in RAG for Open-domain Question Answering
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:In knowledge-intensive tasks such as open-domain question answering (OpenQA), Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle to generate factual answers relying solely on their internal (parametric) knowledge. To address this limitation, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance LLMs by retrieving relevant information from external sources, thereby positioning the retriever as a pivotal component. Although dense retrieval demonstrates state-of-the-art performance, its training poses challenges due to the scarcity of ground-truth evidence, largely attributed to the high costs of human annotation. In this paper, we propose W-RAG by utilizing the ranking capabilities of LLMs to create weakly labeled data for training dense retrievers. Specifically, we rerank the top-$K$ passages retrieved via BM25 by assessing the probability that LLMs will generate the correct answer based on the question and each passage. The highest-ranking passages are then used as positive training examples for dense retrieval. Our comprehensive experiments across four publicly available OpenQA datasets demonstrate that our approach enhances both retrieval and OpenQA performance compared to baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge