Jingzhi Tu
An Efficient Deep Learning Approach Using Improved Generative Adversarial Networks for Incomplete Information Completion of Self-driving
Sep 01, 2021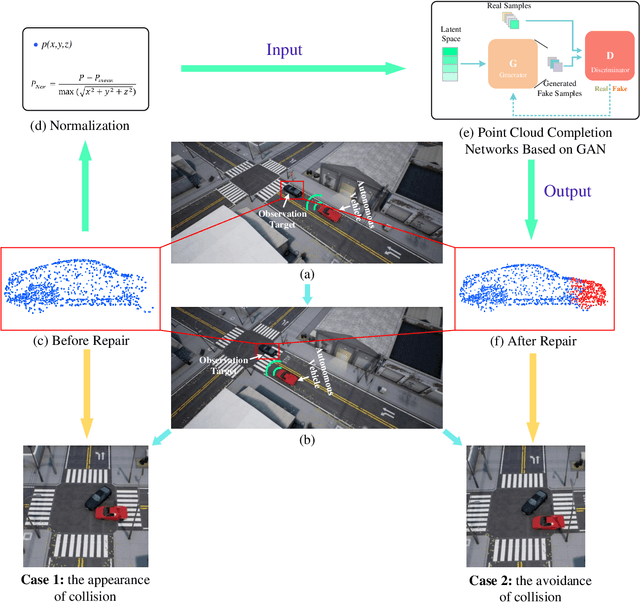
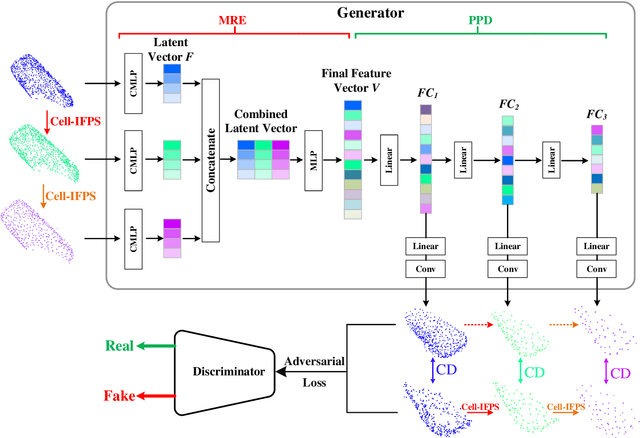
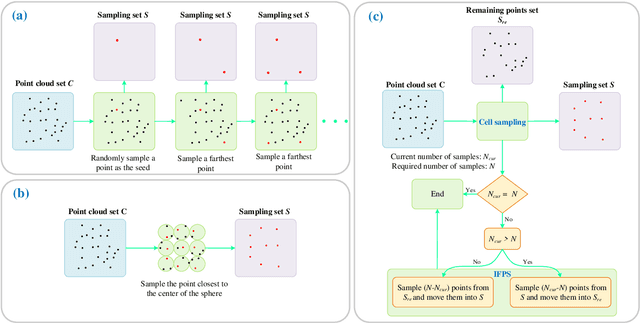
Abstract:Autonomous driving is the key technology of intelligent logistics in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In autonomous driving, the appearance of incomplete point clouds losing geometric and semantic information is inevitable owing to limitations of occlusion, sensor resolution, and viewing angle when the Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) is applied. The emergence of incomplete point clouds, especially incomplete vehicle point clouds, would lead to the reduction of the accuracy of autonomous driving vehicles in object detection, traffic alert, and collision avoidance. Existing point cloud completion networks, such as Point Fractal Network (PF-Net), focus on the accuracy of point cloud completion, without considering the efficiency of inference process, which makes it difficult for them to be deployed for vehicle point cloud repair in autonomous driving. To address the above problem, in this paper, we propose an efficient deep learning approach to repair incomplete vehicle point cloud accurately and efficiently in autonomous driving. In the proposed method, an efficient downsampling algorithm combining incremental sampling and one-time sampling is presented to improves the inference speed of the PF-Net based on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, a real dataset is used, and an autonomous driving scene is created, where three incomplete vehicle point clouds with 5 different sizes are set for three autonomous driving situations. The improved PF-Net can achieve the speedups of over 19x with almost the same accuracy when compared to the original PF-Net. Experimental results demonstrate that the improved PF-Net can be applied to efficiently complete vehicle point clouds in autonomous driving.
KCoreMotif: An Efficient Graph Clustering Algorithm for Large Networks by Exploiting k-core Decomposition and Motifs
Aug 21, 2020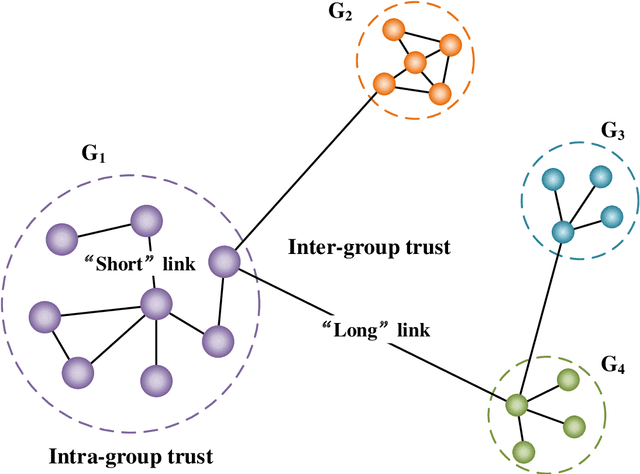
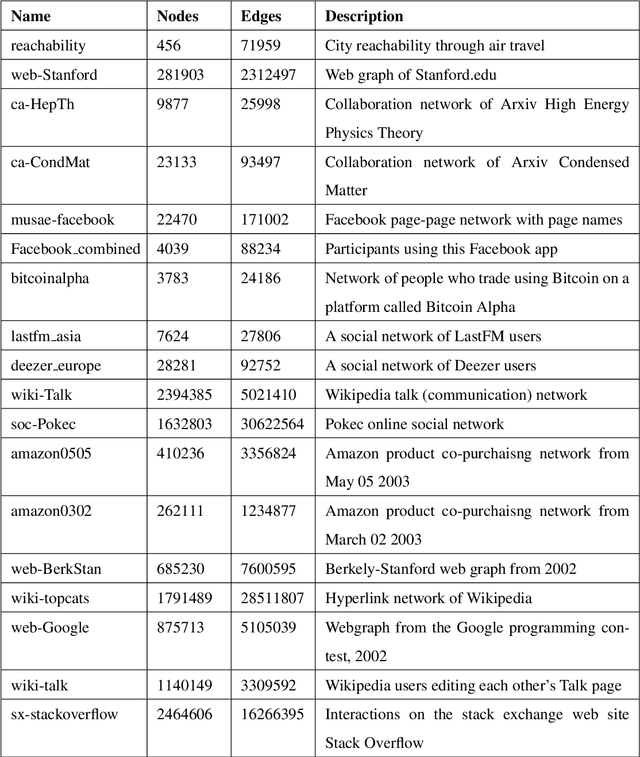
Abstract:Clustering analysis has been widely used in trust evaluation on various complex networks such as wireless sensors networks and online social networks. Spectral clustering is one of the most commonly used algorithms for graph-structured data (networks). However, the conventional spectral clustering is inherently difficult to work with large-scale networks due to the fact that it needs computationally expensive matrix manipulations. To deal with large networks, in this paper, we propose an efficient graph clustering algorithm, KCoreMotif, specifically for large networks by exploiting k-core decomposition and motifs. The essential idea behind the proposed clustering algorithm is to perform the efficient motif-based spectral clustering algorithm on k-core subgraphs, rather than on the entire graph. More specifically, (1) we first conduct the k-core decomposition of the large input network; (2) we then perform the motif-based spectral clustering for the top k-core subgraphs; (3) we group the remaining vertices in the rest (k-1)-core subgraphs into previously found clusters; and finally obtain the desired clusters of the large input network. To evaluate the performance of the proposed graph clustering algorithm KCoreMotif, we use both the conventional and the motif-based spectral clustering algorithms as the baselines and compare our algorithm with them for 18 groups of real-world datasets. Comparative results demonstrate that the proposed graph clustering algorithm is accurate yet efficient for large networks, which also means that it can be further used to evaluate the intra-cluster and inter-cluster trusts on large networks.
Julia Language in Machine Learning: Algorithms, Applications, and Open Issues
Mar 23, 2020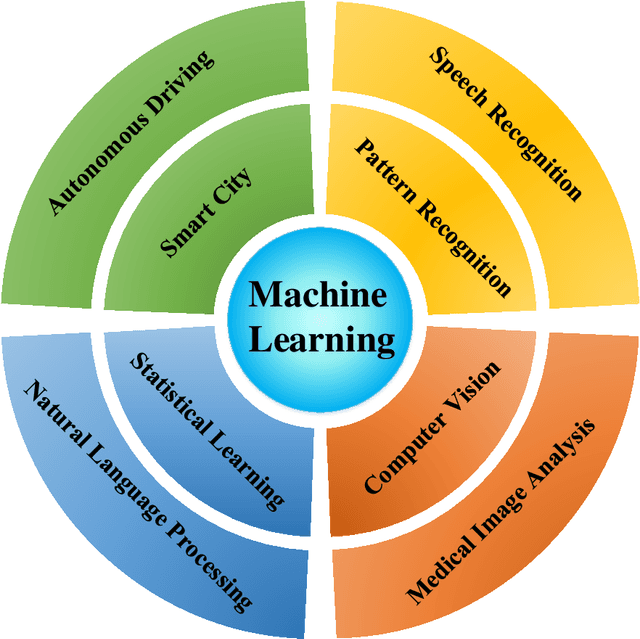
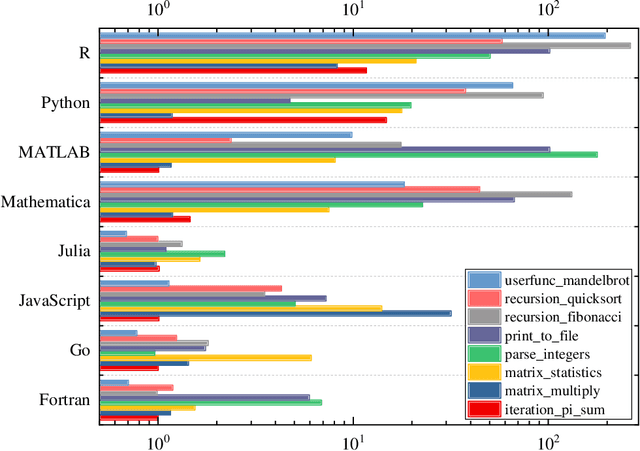
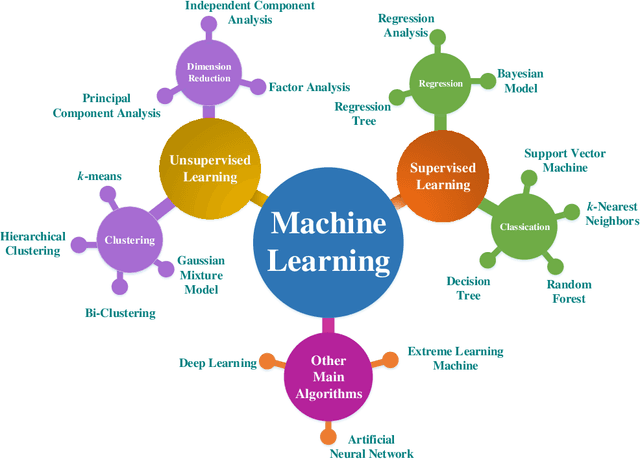
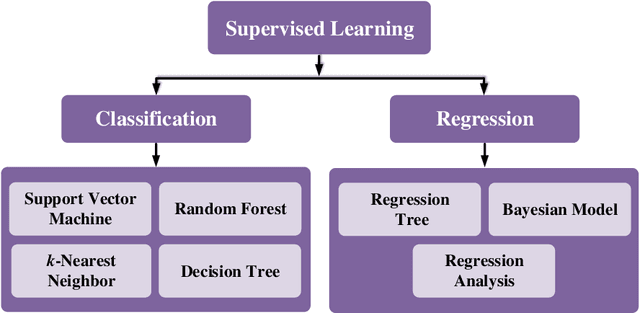
Abstract:Machine learning is driving development across many fields in science and engineering. A simple and efficient programming language could accelerate applications of machine learning in various fields. Currently, the programming languages most commonly used to develop machine learning algorithms include Python, MATLAB, and C/C ++. However, none of these languages well balance both efficiency and simplicity. The Julia language is a fast, easy-to-use, and open-source programming language that was originally designed for high-performance computing, which can well balance the efficiency and simplicity. This paper summarizes the related research work and developments in the application of the Julia language in machine learning. It first surveys the popular machine learning algorithms that are developed in the Julia language. Then, it investigates applications of the machine learning algorithms implemented with the Julia language. Finally, it discusses the open issues and the potential future directions that arise in the use of the Julia language in machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge