Jieyue He
Equal contributor
AGHINT: Attribute-Guided Representation Learning on Heterogeneous Information Networks with Transformer
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:Recently, heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) have achieved impressive success in representation learning by capturing long-range dependencies and heterogeneity at the node level. However, few existing studies have delved into the utilization of node attributes in heterogeneous information networks (HINs). In this paper, we investigate the impact of inter-node attribute disparities on HGNNs performance within the benchmark task, i.e., node classification, and empirically find that typical models exhibit significant performance decline when classifying nodes whose attributes markedly differ from their neighbors. To alleviate this issue, we propose a novel Attribute-Guided heterogeneous Information Networks representation learning model with Transformer (AGHINT), which allows a more effective aggregation of neighbor node information under the guidance of attributes. Specifically, AGHINT transcends the constraints of the original graph structure by directly integrating higher-order similar neighbor features into the learning process and modifies the message-passing mechanism between nodes based on their attribute disparities. Extensive experimental results on three real-world heterogeneous graph benchmarks with target node attributes demonstrate that AGHINT outperforms the state-of-the-art.
Type-based Neural Link Prediction Adapter for Complex Query Answering
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Answering complex logical queries on incomplete knowledge graphs (KGs) is a fundamental and challenging task in multi-hop reasoning. Recent work defines this task as an end-to-end optimization problem, which significantly reduces the training cost and enhances the generalization of the model by a pretrained link predictors for query answering. However, most existing proposals ignore the critical semantic knowledge inherently available in KGs, such as type information, which could help answer complex logical queries. To this end, we propose TypE-based Neural Link Prediction Adapter (TENLPA), a novel model that constructs type-based entity-relation graphs to discover the latent relationships between entities and relations by leveraging type information in KGs. Meanwhile, in order to effectively combine type information with complex logical queries, an adaptive learning mechanism is introduced, which is trained by back-propagating during the complex query answering process to achieve adaptive adjustment of neural link predictors. Experiments on 3 standard datasets show that TENLPA model achieves state-of-the-art performance on complex query answering with good generalization and robustness.
RoKEPG: RoBERTa and Knowledge Enhancement for Prescription Generation of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Nov 29, 2023



Abstract:Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescription is the most critical form of TCM treatment, and uncovering the complex nonlinear relationship between symptoms and TCM is of great significance for clinical practice and assisting physicians in diagnosis and treatment. Although there have been some studies on TCM prescription generation, these studies consider a single factor and directly model the symptom-prescription generation problem mainly based on symptom descriptions, lacking guidance from TCM knowledge. To this end, we propose a RoBERTa and Knowledge Enhancement model for Prescription Generation of Traditional Chinese Medicine (RoKEPG). RoKEPG is firstly pre-trained by our constructed TCM corpus, followed by fine-tuning the pre-trained model, and the model is guided to generate TCM prescriptions by introducing four classes of knowledge of TCM through the attention mask matrix. Experimental results on the publicly available TCM prescription dataset show that RoKEPG improves the F1 metric by about 2% over the baseline model with the best results.
MultiModal-Learning for Predicting Molecular Properties: A Framework Based on Image and Graph Structures
Nov 28, 2023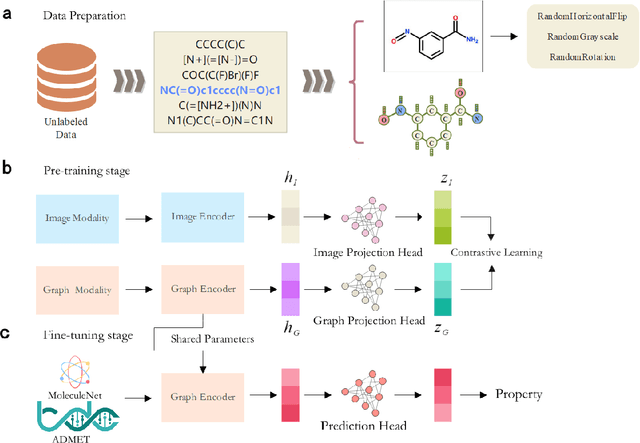
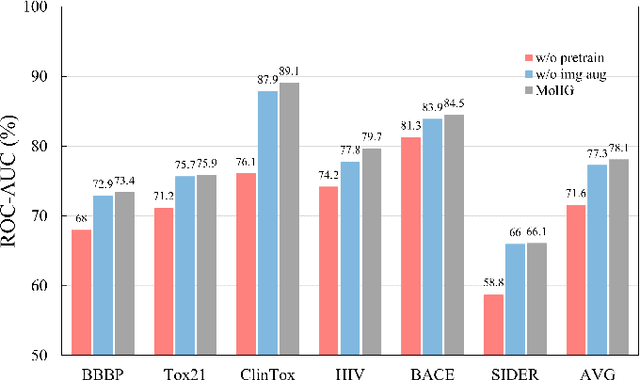
Abstract:The quest for accurate prediction of drug molecule properties poses a fundamental challenge in the realm of Artificial Intelligence Drug Discovery (AIDD). An effective representation of drug molecules emerges as a pivotal component in this pursuit. Contemporary leading-edge research predominantly resorts to self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques to extract meaningful structural representations from large-scale, unlabeled molecular data, subsequently fine-tuning these representations for an array of downstream tasks. However, an inherent shortcoming of these studies lies in their singular reliance on one modality of molecular information, such as molecule image or SMILES representations, thus neglecting the potential complementarity of various molecular modalities. In response to this limitation, we propose MolIG, a novel MultiModaL molecular pre-training framework for predicting molecular properties based on Image and Graph structures. MolIG model innovatively leverages the coherence and correlation between molecule graph and molecule image to execute self-supervised tasks, effectively amalgamating the strengths of both molecular representation forms. This holistic approach allows for the capture of pivotal molecular structural characteristics and high-level semantic information. Upon completion of pre-training, Graph Neural Network (GNN) Encoder is used for the prediction of downstream tasks. In comparison to advanced baseline models, MolIG exhibits enhanced performance in downstream tasks pertaining to molecular property prediction within benchmark groups such as MoleculeNet Benchmark Group and ADMET Benchmark Group.
ACDNet: Attention-guided Collaborative Decision Network for Effective Medication Recommendation
Jul 06, 2023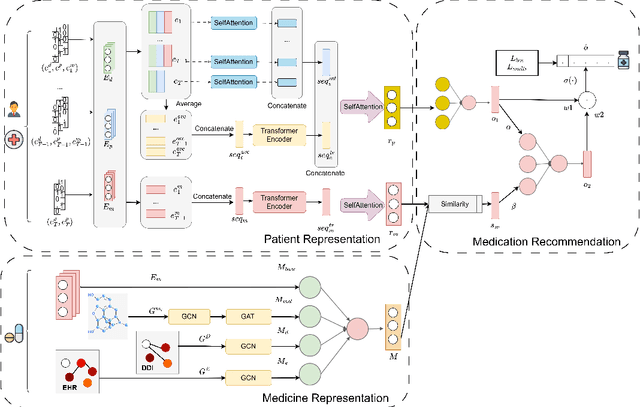
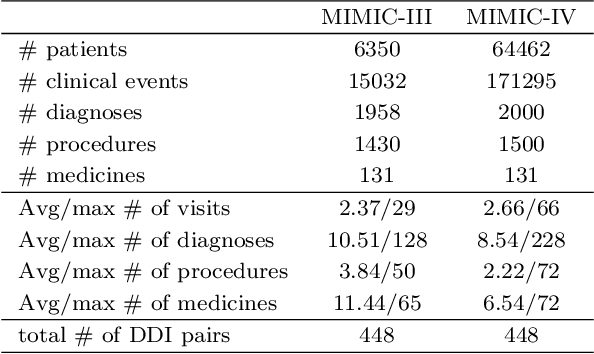
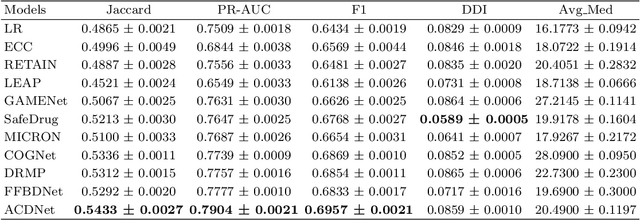
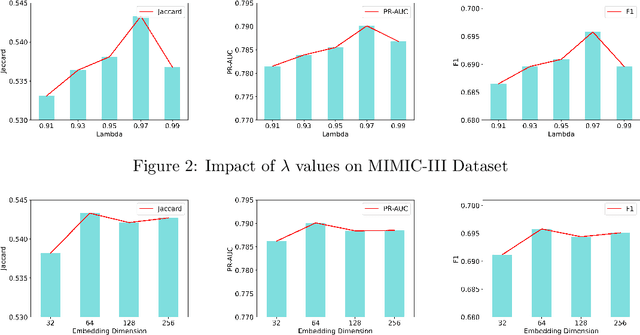
Abstract:Medication recommendation using Electronic Health Records (EHR) is challenging due to complex medical data. Current approaches extract longitudinal information from patient EHR to personalize recommendations. However, existing models often lack sufficient patient representation and overlook the importance of considering the similarity between a patient's medication records and specific medicines. Therefore, an Attention-guided Collaborative Decision Network (ACDNet) for medication recommendation is proposed in this paper. Specifically, ACDNet utilizes attention mechanism and Transformer to effectively capture patient health conditions and medication records by modeling their historical visits at both global and local levels. ACDNet also employs a collaborative decision framework, utilizing the similarity between medication records and medicine representation to facilitate the recommendation process. The experimental results on two extensive medical datasets, MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV, clearly demonstrate that ACDNet outperforms state-of-the-art models in terms of Jaccard, PR-AUC, and F1 score, reaffirming its superiority. Moreover, the ablation experiments provide solid evidence of the effectiveness of each module in ACDNet, validating their contribution to the overall performance. Furthermore, a detailed case study reinforces the effectiveness of ACDNet in medication recommendation based on EHR data, showcasing its practical value in real-world healthcare scenarios.
Hybrid Attentional Memory Network for Computational drug repositioning
Jun 12, 2020



Abstract:Drug repositioning is designed to discover new uses of known drugs, which is an important and efficient method of drug discovery. Researchers only use one certain type of Collaborative Filtering (CF) models for drug repositioning currently, like the neighborhood based approaches which are good at mining the local information contained in few strong drug-disease associations, or the latent factor based models which are effectively capture the global information shared by a majority of drug-disease associations. Few researchers have combined these two types of CF models to derive a hybrid model with the advantages of both of them. Besides, the cold start problem has always been a major challenge in the field of computational drug repositioning, which restricts the inference ability of relevant models. Inspired by the memory network, we propose the Hybrid Attentional Memory Network (HAMN) model, a deep architecture combines two classes of CF model in a nonlinear manner. Firstly, the memory unit and the attention mechanism are combined to generate the neighborhood contribution representation to capture the local structure of few strong drug-disease associations. Then a variant version of the autoencoder is used to extract the latent factor of drugs and diseases to capture the overall information shared by a majority of drug-disease associations. In that process, ancillary information of drugs and diseases can help to alleviate the cold start problem. Finally, in the prediction stage, the neighborhood contribution representation is combined with the drug latent factor and disease latent factor to produce the predicted value. Comprehensive experimental results on two real data sets show that our proposed HAMN model is superior to other comparison models according to the AUC, AUPR and HR indicators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge