Jiayin Lan
CE-GOCD: Central Entity-Guided Graph Optimization for Community Detection to Augment LLM Scientific Question Answering
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for question answering over scientific research papers. Existing retrieval augmentation methods often rely on isolated text chunks or concepts, but overlook deeper semantic connections between papers. This impairs the LLM's comprehension of scientific literature, hindering the comprehensiveness and specificity of its responses. To address this, we propose Central Entity-Guided Graph Optimization for Community Detection (CE-GOCD), a method that augments LLMs' scientific question answering by explicitly modeling and leveraging semantic substructures within academic knowledge graphs. Our approach operates by: (1) leveraging paper titles as central entities for targeted subgraph retrieval, (2) enhancing implicit semantic discovery via subgraph pruning and completion, and (3) applying community detection to distill coherent paper groups with shared themes. We evaluated the proposed method on three NLP literature-based question-answering datasets, and the results demonstrate its superiority over other retrieval-augmented baseline approaches, confirming the effectiveness of our framework.
NLP-AKG: Few-Shot Construction of NLP Academic Knowledge Graph Based on LLM
Feb 20, 2025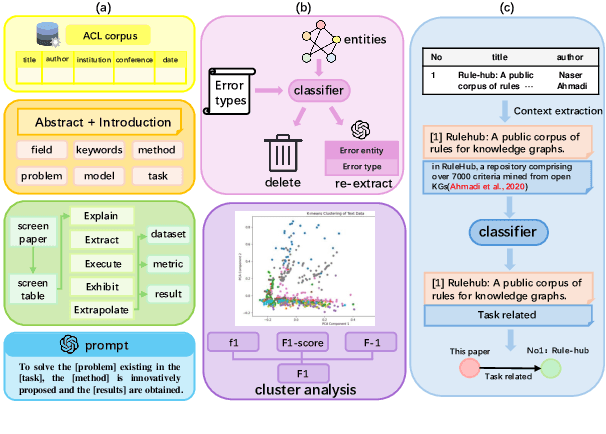
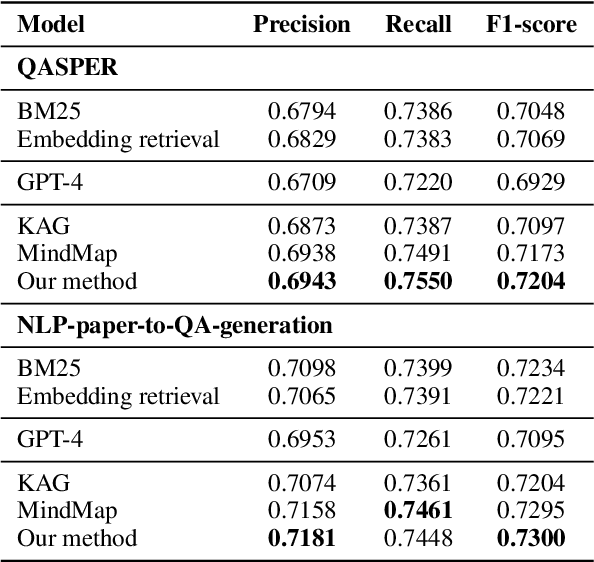
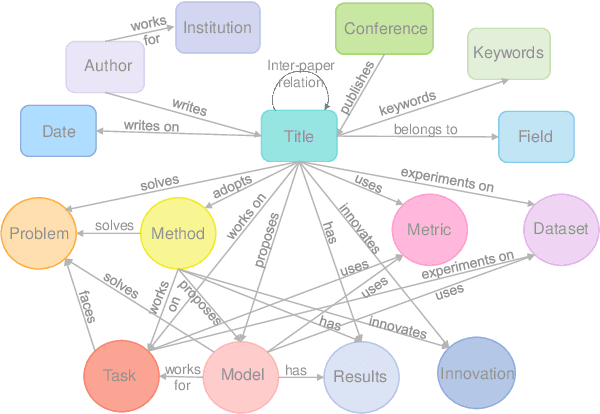
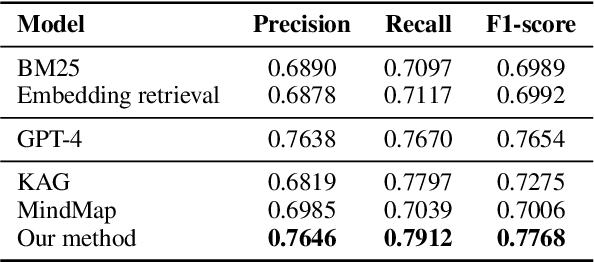
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely applied in question answering over scientific research papers. To enhance the professionalism and accuracy of responses, many studies employ external knowledge augmentation. However, existing structures of external knowledge in scientific literature often focus solely on either paper entities or domain concepts, neglecting the intrinsic connections between papers through shared domain concepts. This results in less comprehensive and specific answers when addressing questions that combine papers and concepts. To address this, we propose a novel knowledge graph framework that captures deep conceptual relations between academic papers, constructing a relational network via intra-paper semantic elements and inter-paper citation relations. Using a few-shot knowledge graph construction method based on LLM, we develop NLP-AKG, an academic knowledge graph for the NLP domain, by extracting 620,353 entities and 2,271,584 relations from 60,826 papers in ACL Anthology. Based on this, we propose a 'sub-graph community summary' method and validate its effectiveness on three NLP scientific literature question answering datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge