Jianquan Liu
Object-Centric Framework for Video Moment Retrieval
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Most existing video moment retrieval methods rely on temporal sequences of frame- or clip-level features that primarily encode global visual and semantic information. However, such representations often fail to capture fine-grained object semantics and appearance, which are crucial for localizing moments described by object-oriented queries involving specific entities and their interactions. In particular, temporal dynamics at the object level have been largely overlooked, limiting the effectiveness of existing approaches in scenarios requiring detailed object-level reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose a novel object-centric framework for moment retrieval. Our method first extracts query-relevant objects using a scene graph parser and then generates scene graphs from video frames to represent these objects and their relationships. Based on the scene graphs, we construct object-level feature sequences that encode rich visual and semantic information. These sequences are processed by a relational tracklet transformer, which models spatio-temporal correlations among objects over time. By explicitly capturing object-level state changes, our framework enables more accurate localization of moments aligned with object-oriented queries. We evaluated our method on three benchmarks: Charades-STA, QVHighlights, and TACoS. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across all benchmarks.
KFS-Bench: Comprehensive Evaluation of Key Frame Sampling in Long Video Understanding
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:We propose KFS-Bench, the first benchmark for key frame sampling in long video question answering (QA), featuring multi-scene annotations to enable direct and robust evaluation of sampling strategies. Key frame sampling is crucial for efficient long-form video understanding. In long video QA, selecting informative frames enables multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to improve both accuracy and efficiency. KFS-Bench addresses the limitation of prior works that only indirectly assess frame selection quality via QA accuracy. By providing ground-truth annotations of multiple disjoint scenes required per question, KFS-Bench allows us to directly analyze how different sampling approaches capture essential content across an entire long video. Using KFS-Bench, we conduct a comprehensive study of key frame sampling methods and identify that not only sampling precision but also scene coverage and sampling balance are the key factors influencing QA performance. Regarding all the factors, we design a novel sampling quality metric that correlates with QA accuracy. Furthermore, we develop a novel key frame sampling method that leverages question-video relevance to balance sampling diversity against question-frame similarity, thereby improving coverage of relevant scenes. Our adaptively balanced sampling approach achieves superior performance in both key frame sampling and QA performance. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/NEC-VID/KFS-Bench.
What is Next when Sequential Prediction Meets Implicitly Hard Interaction?
Feb 14, 2022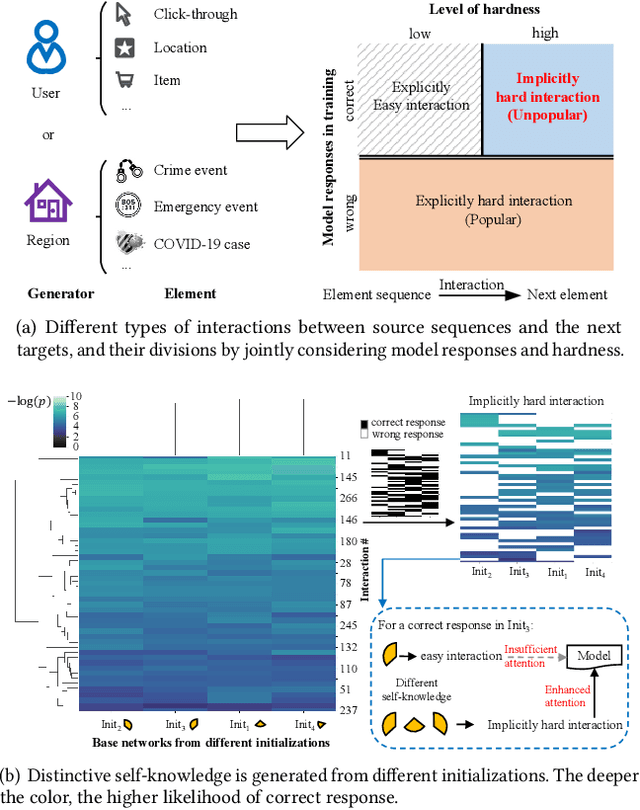
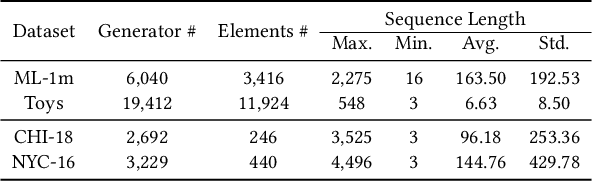
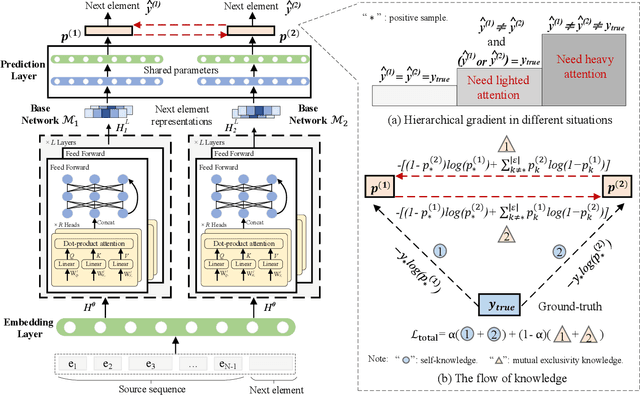
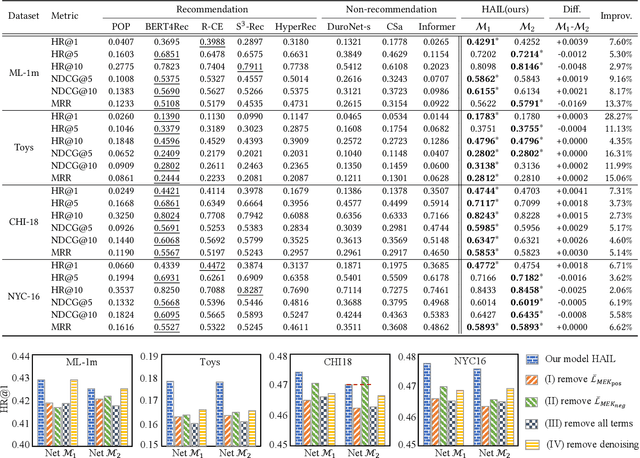
Abstract:Hard interaction learning between source sequences and their next targets is challenging, which exists in a myriad of sequential prediction tasks. During the training process, most existing methods focus on explicitly hard interactions caused by wrong responses. However, a model might conduct correct responses by capturing a subset of learnable patterns, which results in implicitly hard interactions with some unlearned patterns. As such, its generalization performance is weakened. The problem gets more serious in sequential prediction due to the interference of substantial similar candidate targets. To this end, we propose a Hardness Aware Interaction Learning framework (HAIL) that mainly consists of two base sequential learning networks and mutual exclusivity distillation (MED). The base networks are initialized differently to learn distinctive view patterns, thus gaining different training experiences. The experiences in the form of the unlikelihood of correct responses are drawn from each other by MED, which provides mutual exclusivity knowledge to figure out implicitly hard interactions. Moreover, we deduce that the unlikelihood essentially introduces additional gradients to push the pattern learning of correct responses. Our framework can be easily extended to more peer base networks. Evaluation is conducted on four datasets covering cyber and physical spaces. The experimental results demonstrate that our framework outperforms several state-of-the-art methods in terms of top-k based metrics.
Weakly-Supervised Multi-Person Action Recognition in 360$^{\circ}$ Videos
Feb 09, 2020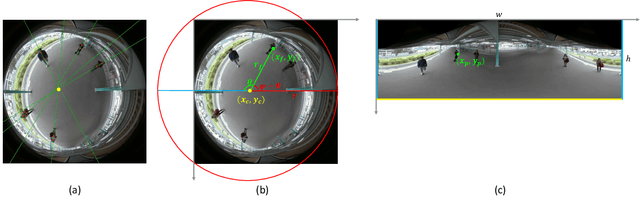
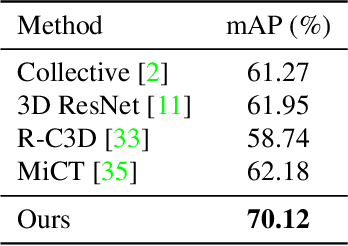
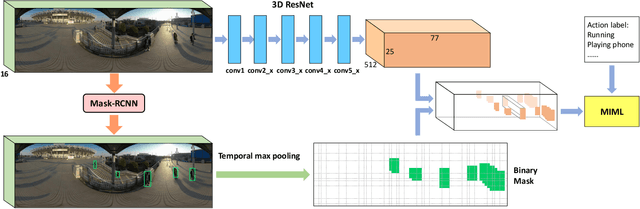

Abstract:The recent development of commodity 360$^{\circ}$ cameras have enabled a single video to capture an entire scene, which endows promising potentials in surveillance scenarios. However, research in omnidirectional video analysis has lagged behind the hardware advances. In this work, we address the important problem of action recognition in top-view 360$^{\circ}$ videos. Due to the wide filed-of-view, 360$^{\circ}$ videos usually capture multiple people performing actions at the same time. Furthermore, the appearance of people are deformed. The proposed framework first transforms omnidirectional videos into panoramic videos, then it extracts spatial-temporal features using region-based 3D CNNs for action recognition. We propose a weakly-supervised method based on multi-instance multi-label learning, which trains the model to recognize and localize multiple actions in a video using only video-level action labels as supervision. We perform experiments to quantitatively validate the efficacy of the proposed method and qualitatively demonstrate action localization results. To enable research in this direction, we introduce 360Action, the first omnidirectional video dataset for multi-person action recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge