Jianguo Lu
System-integrated intrinsic static-dynamic pressure sensing enabled by charge excitation and 3D gradient engineering for autonomous robotic interaction
May 30, 2025Abstract:High-resolution pressure sensing that distinguishes static and dynamic inputs is vital for intelligent robotics but remains challenging for self-powered sensors. We present a self-powered intrinsic static-dynamic pressure sensor (iSD Sensor) that integrates charge excitation with a 3D gradient-engineered structure, achieving enhanced voltage outputs-over 25X for static and 15X for dynamic modes. The sensor exhibits multi-region sensitivities (up to 34.7 V/kPa static, 48.4 V/kPa dynamic), a low detection limit of 6.13 Pa, and rapid response/recovery times (83/43 ms). This design enables nuanced tactile perception and supports dual-mode robotic control: proportional actuation via static signals and fast triggering via dynamic inputs. Integrated into a wireless closed-loop system, the iSD Sensor enables precise functions such as finger bending, object grasping, and sign language output.
Whitening Not Recommended for Classification Tasks in LLMs
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Sentence embedding is a cornerstone in NLP. Whitening has been claimed to be an effective operation to improve embedding quality obtained from Large Language Models (LLMs). However, we find that the efficacy of whitening is model-dependent and task-dependent. In particular, whitening degenerates embeddings for classification tasks. The conclusion is supported by extensive experiments. We also explored a variety of whitening operations, including PCA, ZCA, PCA-Cor, ZCA-Cor and Cholesky whitenings. A by-product of our research is embedding evaluation platform for LLMs called SentEval+.
Dual-branch residual network for lung nodule segmentation
May 21, 2019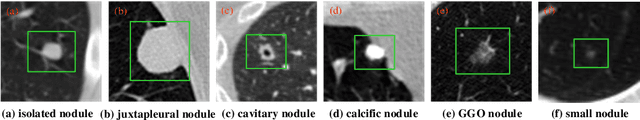
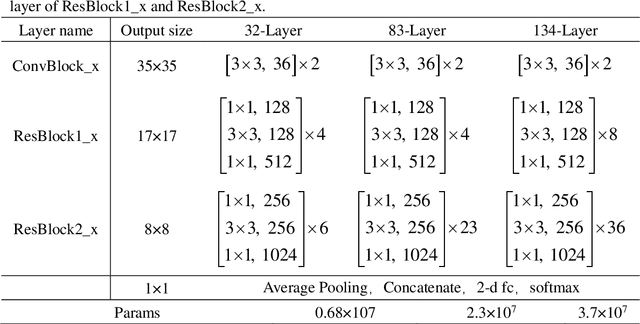
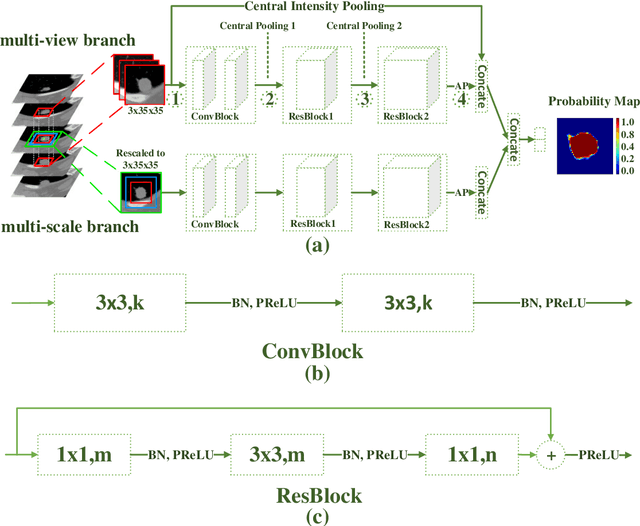
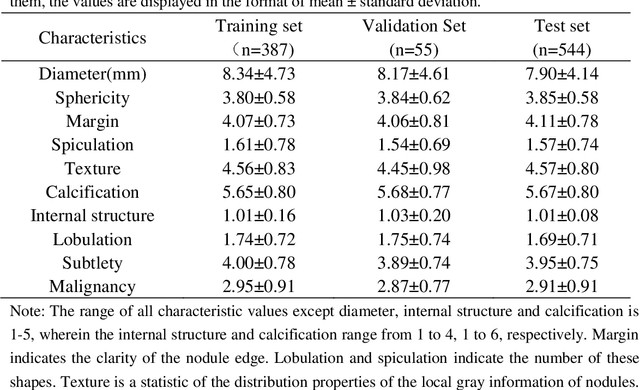
Abstract:An accurate segmentation of lung nodules in computed tomography (CT) images is critical to lung cancer analysis and diagnosis. However, due to the variety of lung nodules and the similarity of visual characteristics between nodules and their surroundings, a robust segmentation of nodules becomes a challenging problem. In this study, we propose the Dual-branch Residual Network (DB-ResNet) which is a data-driven model. Our approach integrates two new schemes to improve the generalization capability of the model: 1) the proposed model can simultaneously capture multi-view and multi-scale features of different nodules in CT images; 2) we combine the features of the intensity and the convolution neural networks (CNN). We propose a pooling method, called the central intensity-pooling layer (CIP), to extract the intensity features of the center voxel of the block, and then use the CNN to obtain the convolutional features of the center voxel of the block. In addition, we designed a weighted sampling strategy based on the boundary of nodules for the selection of those voxels using the weighting score, to increase the accuracy of the model. The proposed method has been extensively evaluated on the LIDC dataset containing 986 nodules. Experimental results show that the DB-ResNet achieves superior segmentation performance with an average dice score of 82.74% on the dataset. Moreover, we compared our results with those of four radiologists on the same dataset. The comparison showed that our average dice score was 0.49% higher than that of human experts. This proves that our proposed method is as good as the experienced radiologist.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge