Jian Su
Battle of the Large Language Models: Dolly vs LLaMA vs Vicuna vs Guanaco vs Bard vs ChatGPT -- A Text-to-SQL Parsing Comparison
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:The success of ChatGPT has ignited an AI race, with researchers striving to develop new large language models (LLMs) that can match or surpass the language understanding and generation abilities of commercial ones. In recent times, a number of models have emerged, claiming performance near that of GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 through various instruction-tuning methods. As practitioners of Text-to-SQL parsing, we are grateful for their valuable contributions to open-source research. However, it is important to approach these claims with a sense of scrutiny and ascertain the actual effectiveness of these models. Therefore, we pit six popular large language models against each other, systematically evaluating their Text-to-SQL parsing capability on nine benchmark datasets with five different prompting strategies, covering both zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Regrettably, the open-sourced models fell significantly short of the performance achieved by closed-source models like GPT-3.5, highlighting the need for further work to bridge the performance gap between these models.
Semantic Pivoting Model for Effective Event Detection
Nov 01, 2022



Abstract:Event Detection, which aims to identify and classify mentions of event instances from unstructured articles, is an important task in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Existing techniques for event detection only use homogeneous one-hot vectors to represent the event type classes, ignoring the fact that the semantic meaning of the types is important to the task. Such an approach is inefficient and prone to overfitting. In this paper, we propose a Semantic Pivoting Model for Effective Event Detection (SPEED), which explicitly incorporates prior information during training and captures semantically meaningful correlations between input and events. Experimental results show that our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance and outperforms the baselines in multiple settings without using any external resources.
Densely Connected Attention Propagation for Reading Comprehension
Nov 10, 2018
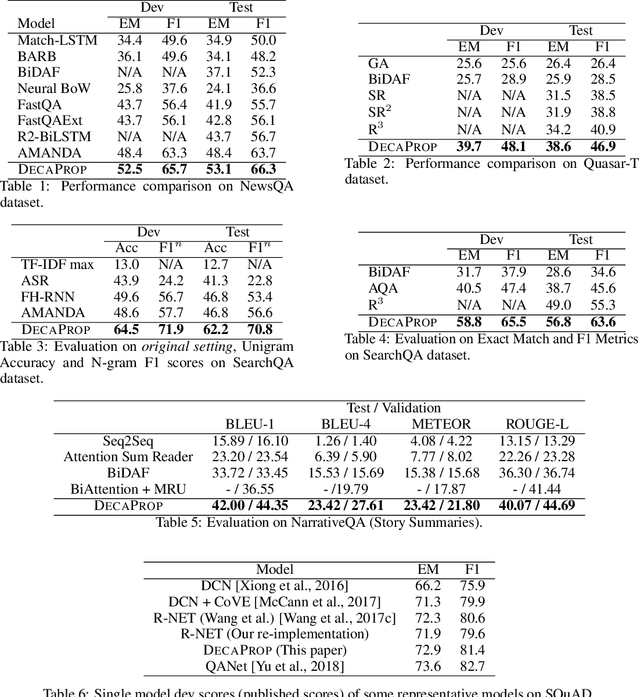

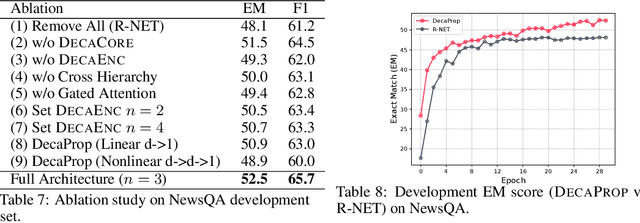
Abstract:We propose DecaProp (Densely Connected Attention Propagation), a new densely connected neural architecture for reading comprehension (RC). There are two distinct characteristics of our model. Firstly, our model densely connects all pairwise layers of the network, modeling relationships between passage and query across all hierarchical levels. Secondly, the dense connectors in our network are learned via attention instead of standard residual skip-connectors. To this end, we propose novel Bidirectional Attention Connectors (BAC) for efficiently forging connections throughout the network. We conduct extensive experiments on four challenging RC benchmarks. Our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art results on all four, outperforming existing baselines by up to $2.6\%-14.2\%$ in absolute F1 score.
Reasoning with Sarcasm by Reading In-between
May 08, 2018
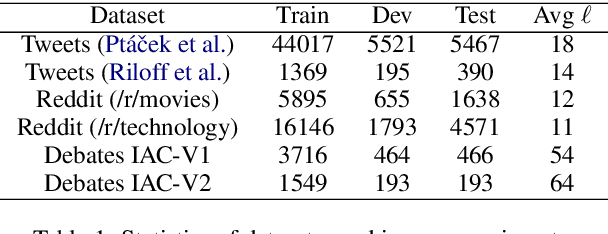
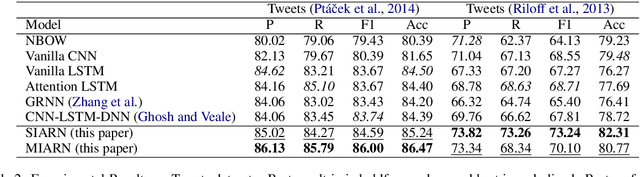
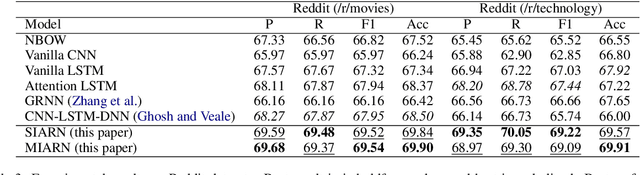
Abstract:Sarcasm is a sophisticated speech act which commonly manifests on social communities such as Twitter and Reddit. The prevalence of sarcasm on the social web is highly disruptive to opinion mining systems due to not only its tendency of polarity flipping but also usage of figurative language. Sarcasm commonly manifests with a contrastive theme either between positive-negative sentiments or between literal-figurative scenarios. In this paper, we revisit the notion of modeling contrast in order to reason with sarcasm. More specifically, we propose an attention-based neural model that looks in-between instead of across, enabling it to explicitly model contrast and incongruity. We conduct extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets from Twitter, Reddit and the Internet Argument Corpus. Our proposed model not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on all datasets but also enjoys improved interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge