Jiajiong Ma
Competitive Inner-Imaging Squeeze and Excitation for Residual Network
Jul 25, 2018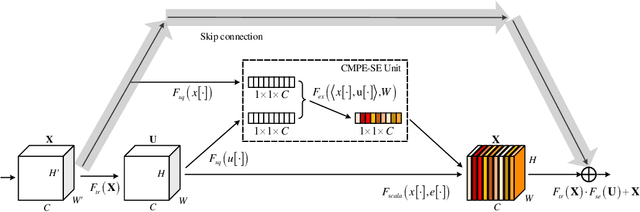
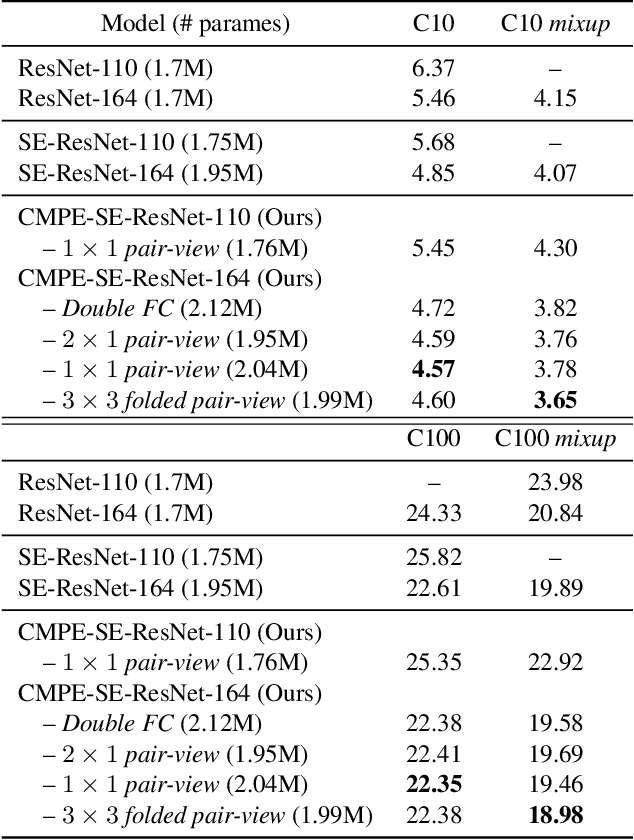
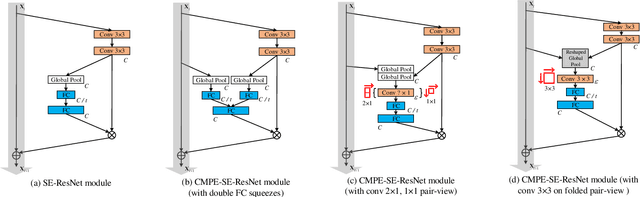
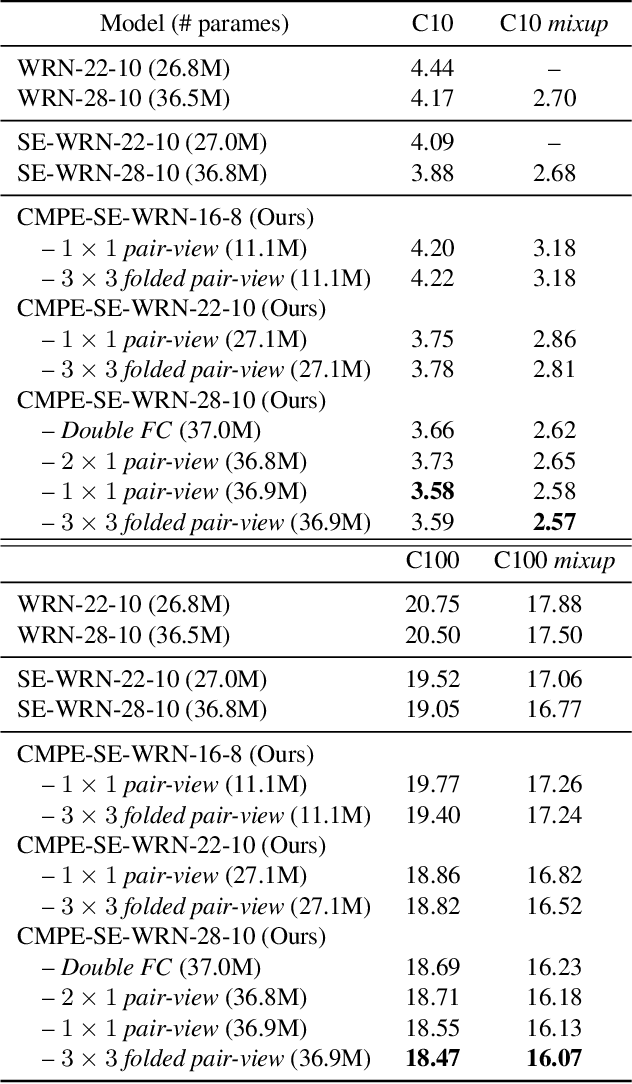
Abstract:Residual Networks make the very deep convolutional architecture works well, which use the residual unit to supplement the identity mappings. On the other hand, Squeeze-Excitation (SE) network propose an adaptively recalibrates channel-wise attention approach to model the relationship of feature maps from different convolutional channel. In this work, we propose the competitive SE mechanism for residual network, rescaling value for each channel in this structure will be determined by residual and identity mappings jointly, this design enables us to expand the meaning of channel relationship modeling in residual blocks: the modeling of competition between residual and identity mappings make identity flow can controll the complement of residual feature maps for itself. Further, we design a novel pair-view competitive SE block to shrink the consumption and re-image the global characterizations of intermediate convolutional channels. We carry out experiments on datasets: CIFAR, SVHN, ImageNet, the proposed method can be compared with the state-of-the-art results.
Tongue image constitution recognition based on Complexity Perception method
Mar 01, 2018

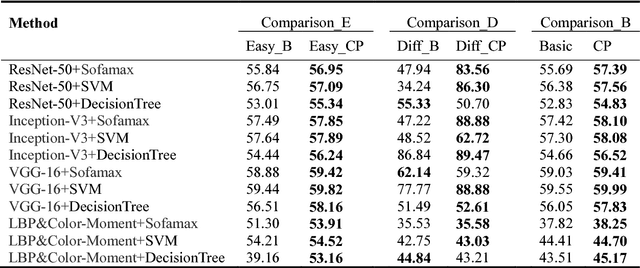

Abstract:Background and Object: In China, body constitution is highly related to physiological and pathological functions of human body and determines the tendency of the disease, which is of great importance for treatment in clinical medicine. Tongue diagnosis, as a key part of Traditional Chinese Medicine inspection, is an important way to recognize the type of constitution.In order to deploy tongue image constitution recognition system on non-invasive mobile device to achieve fast, efficient and accurate constitution recognition, an efficient method is required to deal with the challenge of this kind of complex environment. Methods: In this work, we perform the tongue area detection, tongue area calibration and constitution classification using methods which are based on deep convolutional neural network. Subject to the variation of inconstant environmental condition, the distribution of the picture is uneven, which has a bad effect on classification performance. To solve this problem, we propose a method based on the complexity of individual instances to divide dataset into two subsets and classify them separately, which is capable of improving classification accuracy. To evaluate the performance of our proposed method, we conduct experiments on three sizes of tongue datasets, in which deep convolutional neural network method and traditional digital image analysis method are respectively applied to extract features for tongue images. The proposed method is combined with the base classifier Softmax, SVM, and DecisionTree respectively. Results: As the experiments results shown, our proposed method improves the classification accuracy by 1.135% on average and achieves 59.99% constitution classification accuracy. Conclusions: Experimental results on three datasets show that our proposed method can effectively improve the classification accuracy of tongue constitution recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge