Jiahe Cui
Vectorization of Raster Manga by Deep Reinforcement Learning
Oct 10, 2021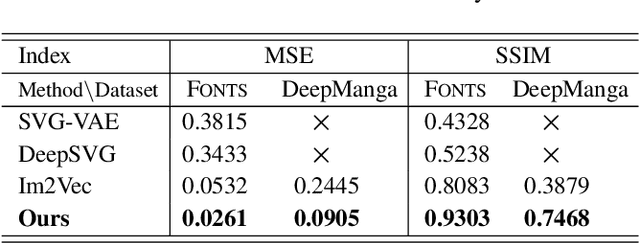
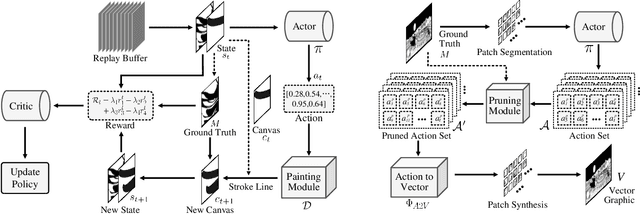
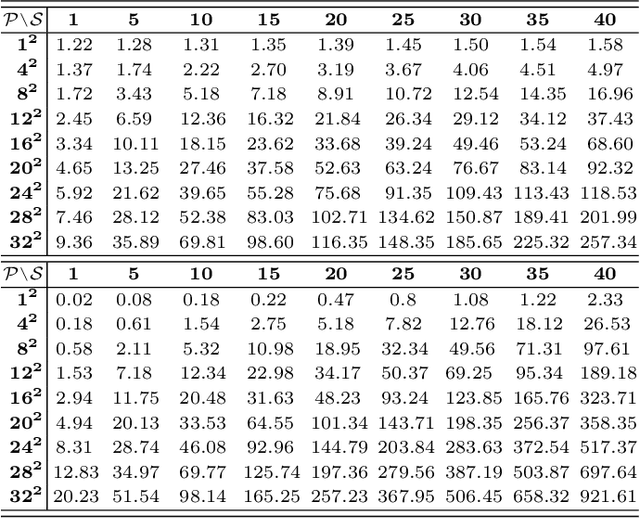
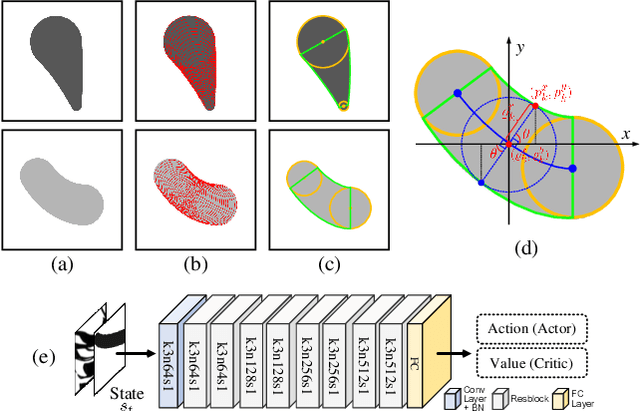
Abstract:Manga is a popular Japanese-style comic form that consists of black-and-white stroke lines. Compared with images of real-world scenarios, the simpler textures and fewer color gradients of mangas are the extra natures that can be vectorized. In this paper, we propose Mang2Vec, the first approach for vectorizing raster mangas using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). Unlike existing learning-based works of image vectorization, we present a new view that considers an entire manga as a collection of basic primitives "stroke line", and the sequence of strokes lines can be deep decomposed for further vectorization. We train a designed DRL agent to produce the most suitable sequence of stroke lines, which is constrained to follow the visual feature of the target manga. Next, the control parameters of strokes are collected to translated to vector format. To improve our performances on visual quality and storage size, we further propose an SA reward to generate accurate stokes, and a pruning mechanism to avoid producing error and redundant strokes. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that our Mang2Vec can produce impressive results and reaches the state-of-the-art level.
ACSC: Automatic Calibration for Non-repetitive Scanning Solid-State LiDAR and Camera Systems
Nov 17, 2020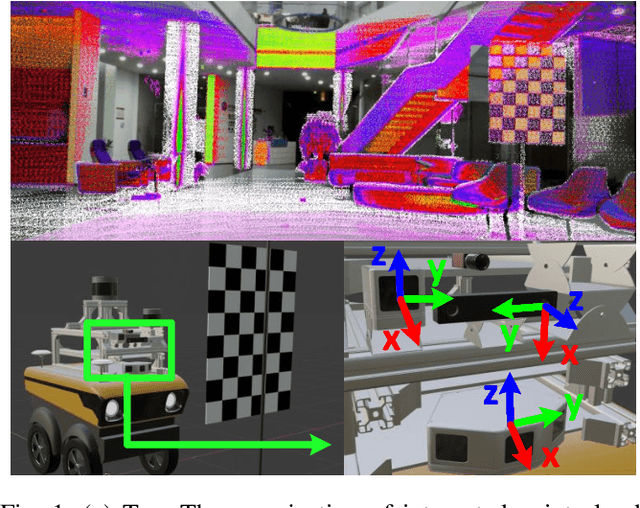
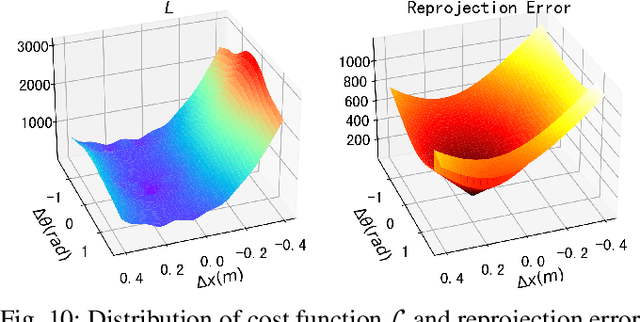

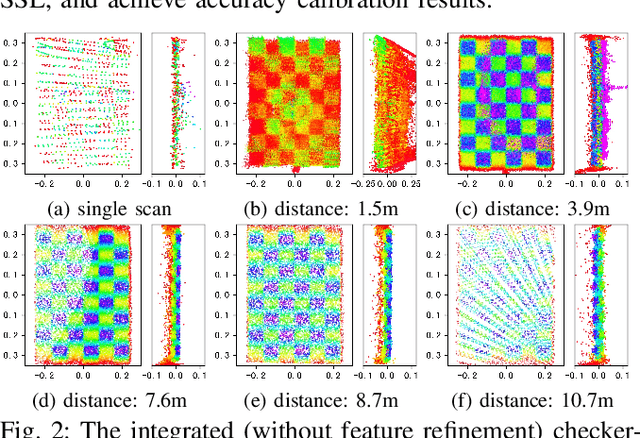
Abstract:Recently, the rapid development of Solid-State LiDAR (SSL) enables low-cost and efficient obtainment of 3D point clouds from the environment, which has inspired a large quantity of studies and applications. However, the non-uniformity of its scanning pattern, and the inconsistency of the ranging error distribution bring challenges to its calibration task. In this paper, we proposed a fully automatic calibration method for the non-repetitive scanning SSL and camera systems. First, a temporal-spatial-based geometric feature refinement method is presented, to extract effective features from SSL point clouds; then, the 3D corners of the calibration target (a printed checkerboard) are estimated with the reflectance distribution of points. Based on the above, a target-based extrinsic calibration method is finally proposed. We evaluate the proposed method on different types of LiDAR and camera sensor combinations in real conditions, and achieve accuracy and robustness calibration results. The code is available at https://github.com/HViktorTsoi/ACSC.git .
Unpaired Photo-to-manga Translation Based on The Methodology of Manga Drawing
Apr 22, 2020
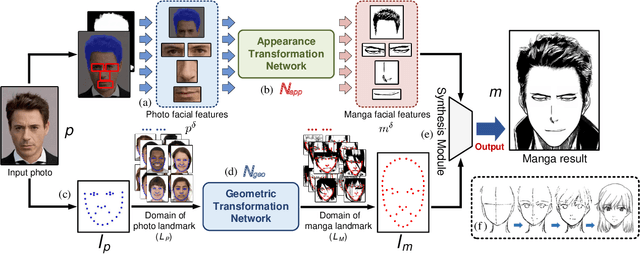
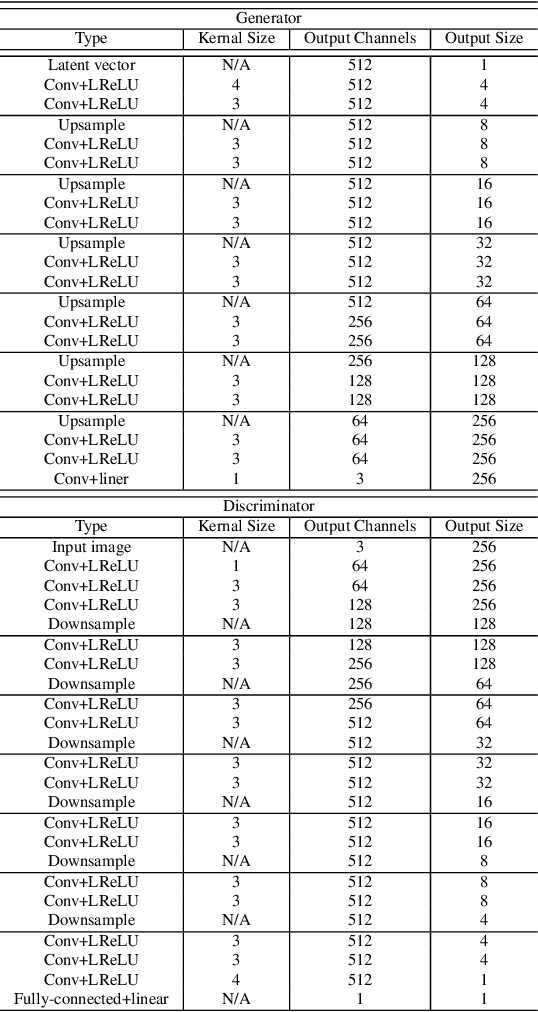
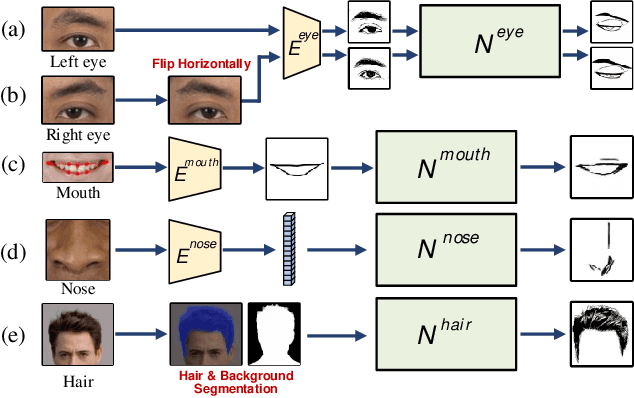
Abstract:Manga is a world popular comic form originated in Japan, which typically employs black-and-white stroke lines and geometric exaggeration to describe humans' appearances, poses, and actions. In this paper, we propose MangaGAN, the first method based on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for unpaired photo-to-manga translation. Inspired by how experienced manga artists draw manga, MangaGAN generates the geometric features of manga face by a designed GAN model and delicately translates each facial region into the manga domain by a tailored multi-GANs architecture. For training MangaGAN, we construct a new dataset collected from a popular manga work, containing manga facial features, landmarks, bodies, and so on. Moreover, to produce high-quality manga faces, we further propose a structural smoothing loss to smooth stroke-lines and avoid noisy pixels, and a similarity preserving module to improve the similarity between domains of photo and manga. Extensive experiments show that MangaGAN can produce high-quality manga faces which preserve both the facial similarity and a popular manga style, and outperforms other related state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge