Jeffrey Gleason
"It's not a representation of me": Examining Accent Bias and Digital Exclusion in Synthetic AI Voice Services
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) speech generation and voice cloning technologies have produced naturalistic speech and accurate voice replication, yet their influence on sociotechnical systems across diverse accents and linguistic traits is not fully understood. This study evaluates two synthetic AI voice services (Speechify and ElevenLabs) through a mixed methods approach using surveys and interviews to assess technical performance and uncover how users' lived experiences influence their perceptions of accent variations in these speech technologies. Our findings reveal technical performance disparities across five regional, English-language accents and demonstrate how current speech generation technologies may inadvertently reinforce linguistic privilege and accent-based discrimination, potentially creating new forms of digital exclusion. Overall, our study highlights the need for inclusive design and regulation by providing actionable insights for developers, policymakers, and organizations to ensure equitable and socially responsible AI speech technologies.
Semantic Classification of Tabular Datasets via Character-Level Convolutional Neural Networks
Jan 24, 2019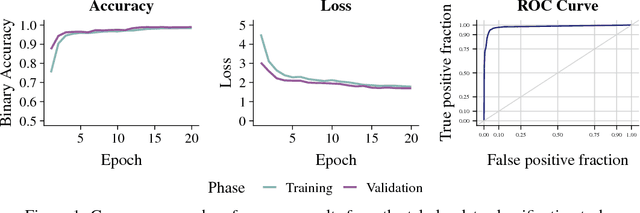
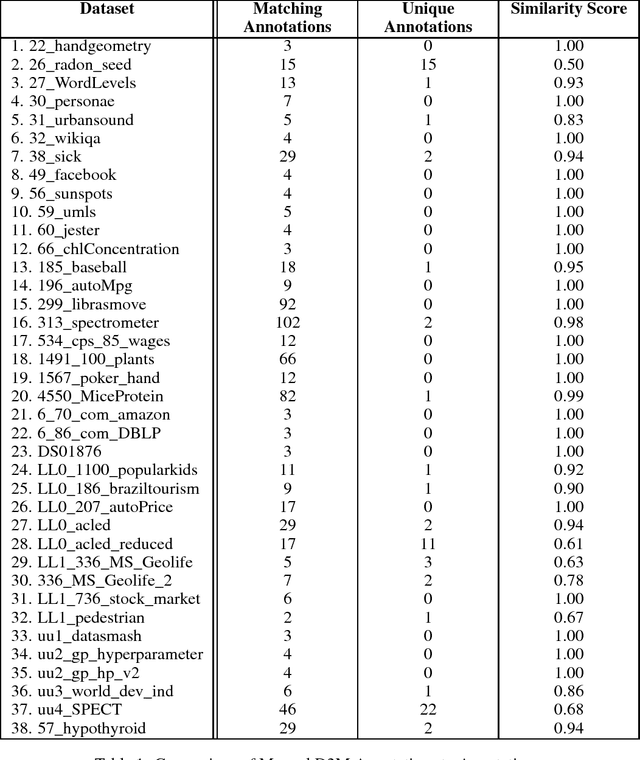
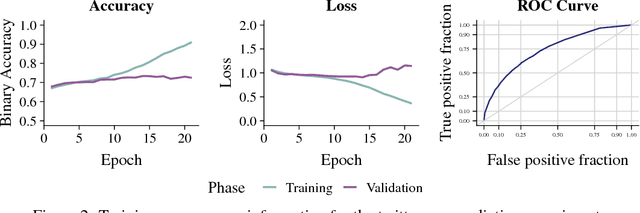
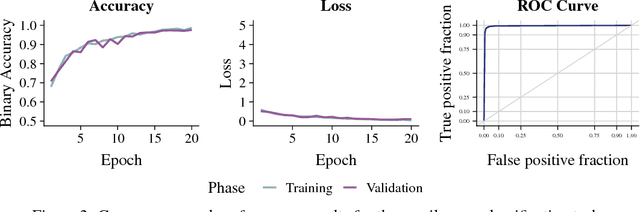
Abstract:A character-level convolutional neural network (CNN) motivated by applications in "automated machine learning" (AutoML) is proposed to semantically classify columns in tabular data. Simulated data containing a set of base classes is first used to learn an initial set of weights. Hand-labeled data from the CKAN repository is then used in a transfer-learning paradigm to adapt the initial weights to a more sophisticated representation of the problem (e.g., including more classes). In doing so, realistic data imperfections are learned and the set of classes handled can be expanded from the base set with reduced labeled data and computing power requirements. Results show the effectiveness and flexibility of this approach in three diverse domains: semantic classification of tabular data, age prediction from social media posts, and email spam classification. In addition to providing further evidence of the effectiveness of transfer learning in natural language processing (NLP), our experiments suggest that analyzing the semantic structure of language at the character level without additional metadata---i.e., network structure, headers, etc.---can produce competitive accuracy for type classification, spam classification, and social media age prediction. We present our open-source toolkit SIMON, an acronym for Semantic Inference for the Modeling of ONtologies, which implements this approach in a user-friendly and scalable/parallelizable fashion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge