Jean-Baptiste Remy
FastGAE: Fast, Scalable and Effective Graph Autoencoders with Stochastic Subgraph Decoding
Feb 20, 2020
Abstract:Graph autoencoders (AE) and variational autoencoders (VAE) are powerful node embedding methods, but suffer from scalability issues. In this paper, we introduce FastGAE, a general framework to scale graph AE and VAE to large graphs with millions of nodes and edges. Our strategy, based on node sampling and subgraph decoding, significantly speeds up the training of graph AE and VAE while preserving or even improving performances. We demonstrate the effectiveness of FastGAE on numerous real-world graphs, outperforming the few existing approaches to scale graph AE and VAE by a wide margin.
Bidirectional Context-Aware Hierarchical Attention Network for Document Understanding
Aug 16, 2019

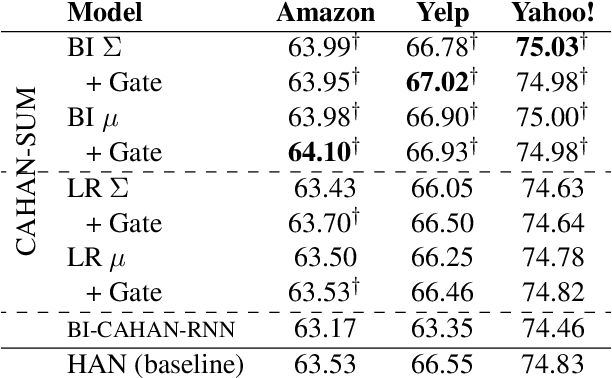
Abstract:The Hierarchical Attention Network (HAN) has made great strides, but it suffers a major limitation: at level 1, each sentence is encoded in complete isolation. In this work, we propose and compare several modifications of HAN in which the sentence encoder is able to make context-aware attentional decisions (CAHAN). Furthermore, we propose a bidirectional document encoder that processes the document forwards and backwards, using the preceding and following sentences as context. Experiments on three large-scale sentiment and topic classification datasets show that the bidirectional version of CAHAN outperforms HAN everywhere, with only a modest increase in computation time. While results are promising, we expect the superiority of CAHAN to be even more evident on tasks requiring a deeper understanding of the input documents, such as abstractive summarization. Code is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge