Jean Lieber
INRIA Nancy - Grand Est / LORIA
Belief revision in the propositional closure of a qualitative algebra
Dec 12, 2014
Abstract:Belief revision is an operation that aims at modifying old be-liefs so that they become consistent with new ones. The issue of belief revision has been studied in various formalisms, in particular, in qualitative algebras (QAs) in which the result is a disjunction of belief bases that is not necessarily repre-sentable in a QA. This motivates the study of belief revision in formalisms extending QAs, namely, their propositional clo-sures: in such a closure, the result of belief revision belongs to the formalism. Moreover, this makes it possible to define a contraction operator thanks to the Harper identity. Belief revision in the propositional closure of QAs is studied, an al-gorithm for a family of revision operators is designed, and an open-source implementation is made freely available on the web.
Case Adaptation with Qualitative Algebras
Oct 10, 2013
Abstract:This paper proposes an approach for the adaptation of spatial or temporal cases in a case-based reasoning system. Qualitative algebras are used as spatial and temporal knowledge representation languages. The intuition behind this adaptation approach is to apply a substitution and then repair potential inconsistencies, thanks to belief revision on qualitative algebras. A temporal example from the cooking domain is given. (The paper on which this extended abstract is based was the recipient of the best paper award of the 2012 International Conference on Case-Based Reasoning.)
Automatic case acquisition from texts for process-oriented case-based reasoning
Apr 14, 2013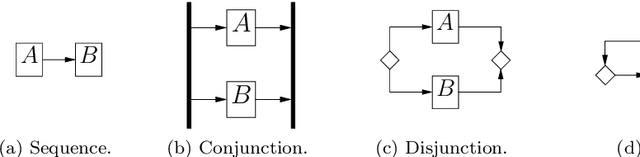


Abstract:This paper introduces a method for the automatic acquisition of a rich case representation from free text for process-oriented case-based reasoning. Case engineering is among the most complicated and costly tasks in implementing a case-based reasoning system. This is especially so for process-oriented case-based reasoning, where more expressive case representations are generally used and, in our opinion, actually required for satisfactory case adaptation. In this context, the ability to acquire cases automatically from procedural texts is a major step forward in order to reason on processes. We therefore detail a methodology that makes case acquisition from processes described as free text possible, with special attention given to assembly instruction texts. This methodology extends the techniques we used to extract actions from cooking recipes. We argue that techniques taken from natural language processing are required for this task, and that they give satisfactory results. An evaluation based on our implemented prototype extracting workflows from recipe texts is provided.
* Sous presse, publication pr\'evue en 2013
Extension du formalisme des flux opérationnels par une algèbre temporelle
Sep 25, 2012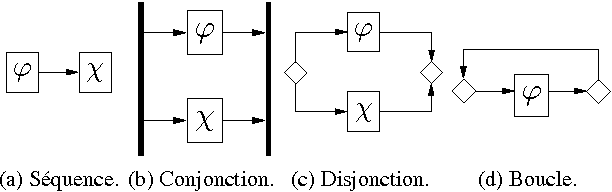
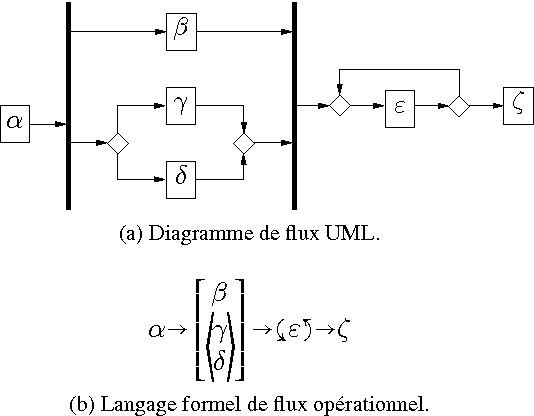


Abstract:Workflows constitute an important language to represent knowledge about processes, but also increasingly to reason on such knowledge. On the other hand, there is a limit to which time constraints between activities can be expressed. Qualitative interval algebras can model processes using finer temporal relations, but they cannot reproduce all workflow patterns. This paper defines a common ground model-theoretical semantics for both workflows and interval algebras, making it possible for reasoning systems working with either to interoperate. Thanks to this, interesting properties and inferences can be defined, both on workflows and on an extended formalism combining workflows with interval algebras. Finally, similar formalisms proposing a sound formal basis for workflows and extending them are discussed.
Semi-automatic annotation process for procedural texts: An application on cooking recipes
Sep 25, 2012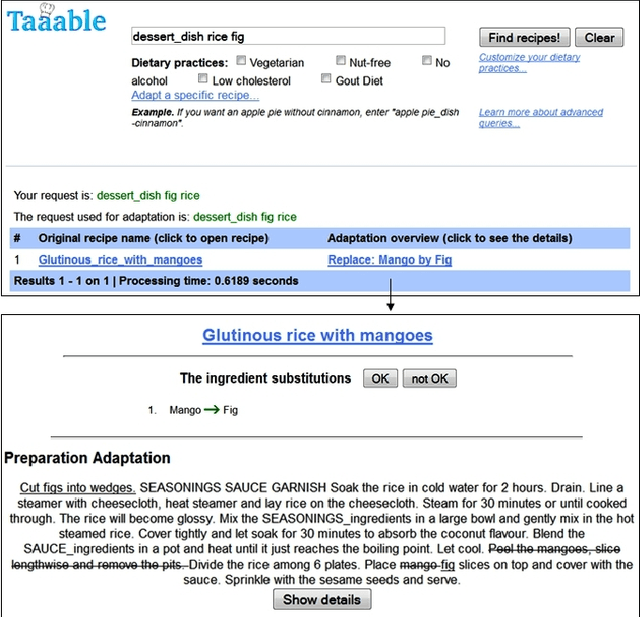
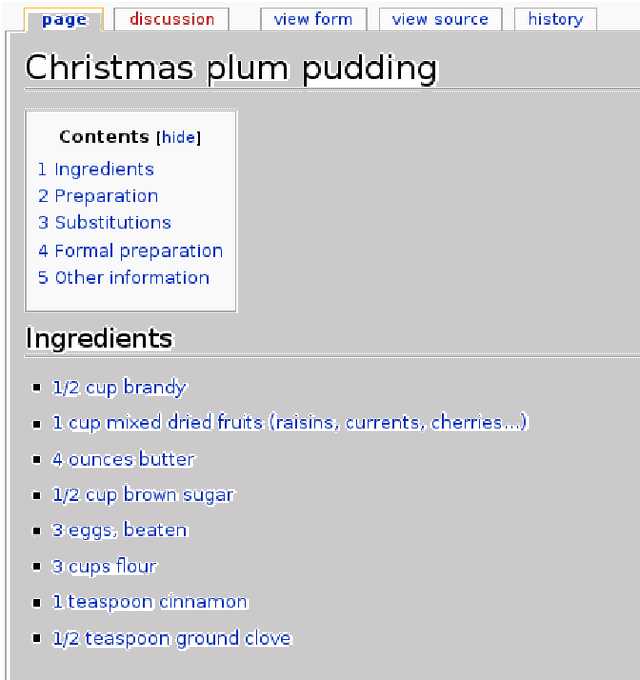
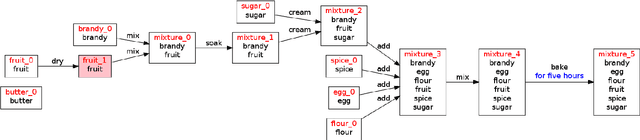
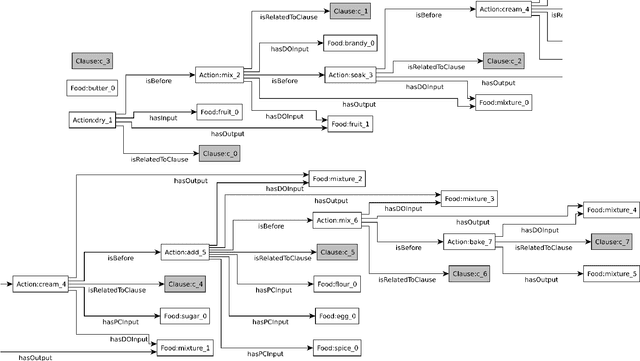
Abstract:Taaable is a case-based reasoning system that adapts cooking recipes to user constraints. Within it, the preparation part of recipes is formalised as a graph. This graph is a semantic representation of the sequence of instructions composing the cooking process and is used to compute the procedure adaptation, conjointly with the textual adaptation. It is composed of cooking actions and ingredients, among others, represented as vertices, and semantic relations between those, shown as arcs, and is built automatically thanks to natural language processing. The results of the automatic annotation process is often a disconnected graph, representing an incomplete annotation, or may contain errors. Therefore, a validating and correcting step is required. In this paper, we present an existing graphic tool named \kcatos, conceived for representing and editing decision trees, and show how it has been adapted and integrated in WikiTaaable, the semantic wiki in which the knowledge used by Taaable is stored. This interface provides the wiki users with a way to correct the case representation of the cooking process, improving at the same time the quality of the knowledge about cooking procedures stored in WikiTaaable.
Quels formalismes temporels pour représenter des connaissances extraites de textes de recettes de cuisine ?
Oct 24, 2011
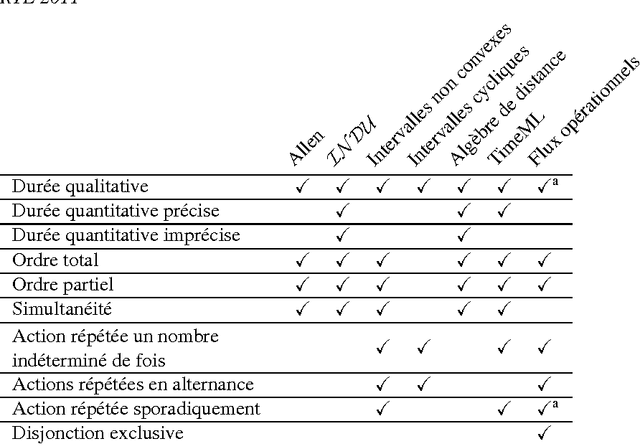

Abstract:The Taaable projet goal is to create a case-based reasoning system for retrieval and adaptation of cooking recipes. Within this framework, we are discussing the temporal aspects of recipes and the means of representing those in order to adapt their text.
Opportunistic Adaptation Knowledge Discovery
Dec 01, 2009
Abstract:Adaptation has long been considered as the Achilles' heel of case-based reasoning since it requires some domain-specific knowledge that is difficult to acquire. In this paper, two strategies are combined in order to reduce the knowledge engineering cost induced by the adaptation knowledge (CA) acquisition task: CA is learned from the case base by the means of knowledge discovery techniques, and the CA acquisition sessions are opportunistically triggered, i.e., at problem-solving time.
Edhibou: a Customizable Interface for Decision Support in a Semantic Portal
Nov 03, 2008
Abstract:The Semantic Web is becoming more and more a reality, as the required technologies have reached an appropriate level of maturity. However, at this stage, it is important to provide tools facilitating the use and deployment of these technologies by end-users. In this paper, we describe EdHibou, an automatically generated, ontology-based graphical user interface that integrates in a semantic portal. The particularity of EdHibou is that it makes use of OWL reasoning capabilities to provide intelligent features, such as decision support, upon the underlying ontology. We present an application of EdHibou to medical decision support based on a formalization of clinical guidelines in OWL and show how it can be customized thanks to an ontology of graphical components.
Case Base Mining for Adaptation Knowledge Acquisition
Mar 30, 2007Abstract:In case-based reasoning, the adaptation of a source case in order to solve the target problem is at the same time crucial and difficult to implement. The reason for this difficulty is that, in general, adaptation strongly depends on domain-dependent knowledge. This fact motivates research on adaptation knowledge acquisition (AKA). This paper presents an approach to AKA based on the principles and techniques of knowledge discovery from databases and data-mining. It is implemented in CABAMAKA, a system that explores the variations within the case base to elicit adaptation knowledge. This system has been successfully tested in an application of case-based reasoning to decision support in the domain of breast cancer treatment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge