Jayant Kumar
Smart Multi-Modal Search: Contextual Sparse and Dense Embedding Integration in Adobe Express
Aug 26, 2024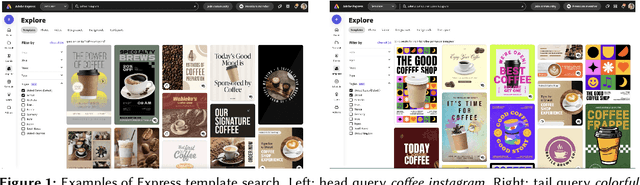
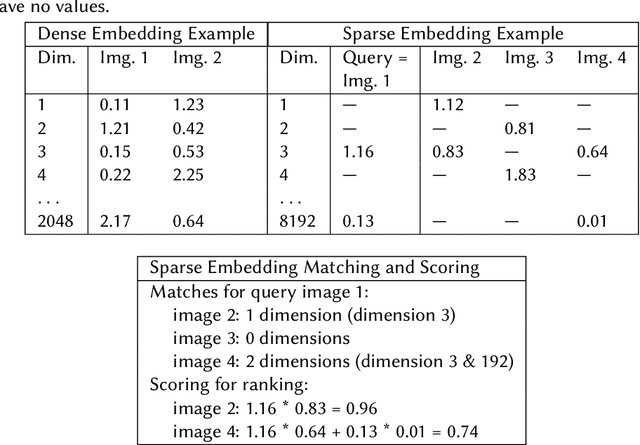

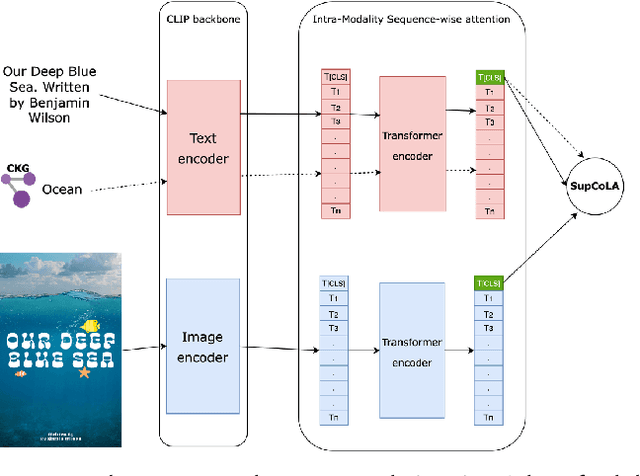
Abstract:As user content and queries become increasingly multi-modal, the need for effective multi-modal search systems has grown. Traditional search systems often rely on textual and metadata annotations for indexed images, while multi-modal embeddings like CLIP enable direct search using text and image embeddings. However, embedding-based approaches face challenges in integrating contextual features such as user locale and recency. Building a scalable multi-modal search system requires fine-tuning several components. This paper presents a multi-modal search architecture and a series of AB tests that optimize embeddings and multi-modal technologies in Adobe Express template search. We address considerations such as embedding model selection, the roles of embeddings in matching and ranking, and the balance between dense and sparse embeddings. Our iterative approach demonstrates how utilizing sparse, dense, and contextual features enhances short and long query search, significantly reduces null rates (over 70\%), and increases click-through rates (CTR). Our findings provide insights into developing robust multi-modal search systems, thereby enhancing relevance for complex queries.
Semantic In-Domain Product Identification for Search Queries
Apr 13, 2024



Abstract:Accurate explicit and implicit product identification in search queries is critical for enhancing user experiences, especially at a company like Adobe which has over 50 products and covers queries across hundreds of tools. In this work, we present a novel approach to training a product classifier from user behavioral data. Our semantic model led to >25% relative improvement in CTR (click through rate) across the deployed surfaces; a >50% decrease in null rate; a 2x increase in the app cards surfaced, which helps drive product visibility.
Augmenting Knowledge Graph Hierarchies Using Neural Transformers
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Knowledge graphs are useful tools to organize, recommend and sort data. Hierarchies in knowledge graphs provide significant benefit in improving understanding and compartmentalization of the data within a knowledge graph. This work leverages large language models to generate and augment hierarchies in an existing knowledge graph. For small (<100,000 node) domain-specific KGs, we find that a combination of few-shot prompting with one-shot generation works well, while larger KG may require cyclical generation. We present techniques for augmenting hierarchies, which led to coverage increase by 98% for intents and 99% for colors in our knowledge graph.
Contextual Font Recommendations based on User Intent
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:Adobe Fonts has a rich library of over 20,000 unique fonts that Adobe users utilize for creating graphics, posters, composites etc. Due to the nature of the large library, knowing what font to select can be a daunting task that requires a lot of experience. For most users in Adobe products, especially casual users of Adobe Express, this often means choosing the default font instead of utilizing the rich and diverse fonts available. In this work, we create an intent-driven system to provide contextual font recommendations to users to aid in their creative journey. Our system takes in multilingual text input and recommends suitable fonts based on the user's intent. Based on user entitlements, the mix of free and paid fonts is adjusted. The feature is currently used by millions of Adobe Express users with a CTR of >25%.
LayoutBERT: Masked Language Layout Model for Object Insertion
Apr 30, 2022



Abstract:Image compositing is one of the most fundamental steps in creative workflows. It involves taking objects/parts of several images to create a new image, called a composite. Currently, this process is done manually by creating accurate masks of objects to be inserted and carefully blending them with the target scene or images, usually with the help of tools such as Photoshop or GIMP. While there have been several works on automatic selection of objects for creating masks, the problem of object placement within an image with the correct position, scale, and harmony remains a difficult problem with limited exploration. Automatic object insertion in images or designs is a difficult problem as it requires understanding of the scene geometry and the color harmony between objects. We propose LayoutBERT for the object insertion task. It uses a novel self-supervised masked language model objective and bidirectional multi-head self-attention. It outperforms previous layout-based likelihood models and shows favorable properties in terms of model capacity. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for object insertion in the image compositing setting and other settings like documents and design templates. We further demonstrate the usefulness of the learned representations for layout-based retrieval tasks. We provide both qualitative and quantitative evaluations on datasets from diverse domains like COCO, PublayNet, and two new datasets which we call Image Layouts and Template Layouts. Image Layouts which consists of 5.8 million images with layout annotations is the largest image layout dataset to our knowledge. We also share ablation study results on the effect of dataset size, model size and class sample size for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge