Javier Lorenzo
Key Information Extraction in Purchase Documents using Deep Learning and Rule-based Corrections
Oct 07, 2022
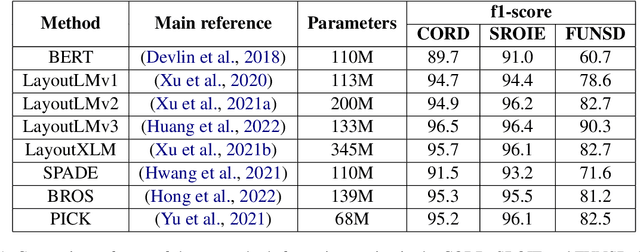

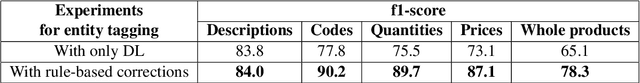
Abstract:Deep Learning (DL) is dominating the fields of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision (CV) in the recent times. However, DL commonly relies on the availability of large data annotations, so other alternative or complementary pattern-based techniques can help to improve results. In this paper, we build upon Key Information Extraction (KIE) in purchase documents using both DL and rule-based corrections. Our system initially trusts on Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and text understanding based on entity tagging to identify purchase facts of interest (e.g., product codes, descriptions, quantities, or prices). These facts are then linked to a same product group, which is recognized by means of line detection and some grouping heuristics. Once these DL approaches are processed, we contribute several mechanisms consisting of rule-based corrections for improving the baseline DL predictions. We prove the enhancements provided by these rule-based corrections over the baseline DL results in the presented experiments for purchase documents from public and NielsenIQ datasets.
RNN-based Pedestrian Crossing Prediction using Activity and Pose-related Features
Aug 26, 2020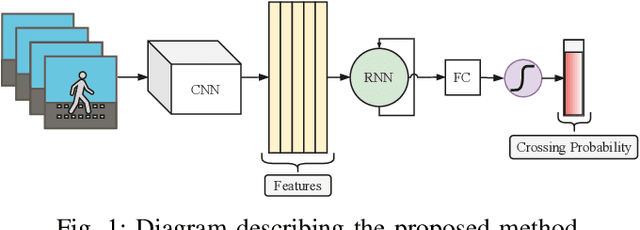

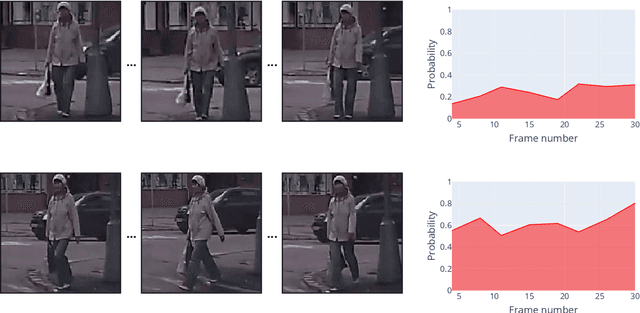
Abstract:Pedestrian crossing prediction is a crucial task for autonomous driving. Numerous studies show that an early estimation of the pedestrian's intention can decrease or even avoid a high percentage of accidents. In this paper, different variations of a deep learning system are proposed to attempt to solve this problem. The proposed models are composed of two parts: a CNN-based feature extractor and an RNN module. All the models were trained and tested on the JAAD dataset. The results obtained indicate that the choice of the features extraction method, the inclusion of additional variables such as pedestrian gaze direction and discrete orientation, and the chosen RNN type have a significant impact on the final performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge