Jatuporn Toy Leksut
Do We Really Need to Collect Millions of Faces for Effective Face Recognition?
Apr 11, 2016



Abstract:Face recognition capabilities have recently made extraordinary leaps. Though this progress is at least partially due to ballooning training set sizes -- huge numbers of face images downloaded and labeled for identity -- it is not clear if the formidable task of collecting so many images is truly necessary. We propose a far more accessible means of increasing training data sizes for face recognition systems. Rather than manually harvesting and labeling more faces, we simply synthesize them. We describe novel methods of enriching an existing dataset with important facial appearance variations by manipulating the faces it contains. We further apply this synthesis approach when matching query images represented using a standard convolutional neural network. The effect of training and testing with synthesized images is extensively tested on the LFW and IJB-A (verification and identification) benchmarks and Janus CS2. The performances obtained by our approach match state of the art results reported by systems trained on millions of downloaded images.
Face Recognition Using Deep Multi-Pose Representations
Mar 23, 2016


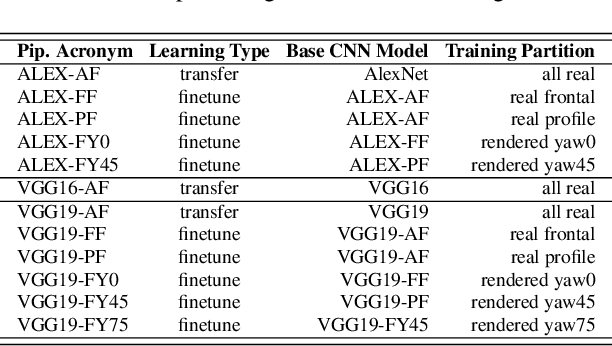
Abstract:We introduce our method and system for face recognition using multiple pose-aware deep learning models. In our representation, a face image is processed by several pose-specific deep convolutional neural network (CNN) models to generate multiple pose-specific features. 3D rendering is used to generate multiple face poses from the input image. Sensitivity of the recognition system to pose variations is reduced since we use an ensemble of pose-specific CNN features. The paper presents extensive experimental results on the effect of landmark detection, CNN layer selection and pose model selection on the performance of the recognition pipeline. Our novel representation achieves better results than the state-of-the-art on IARPA's CS2 and NIST's IJB-A in both verification and identification (i.e. search) tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge