Janosch Haber
Patterns of Lexical Ambiguity in Contextualised Language Models
Sep 29, 2021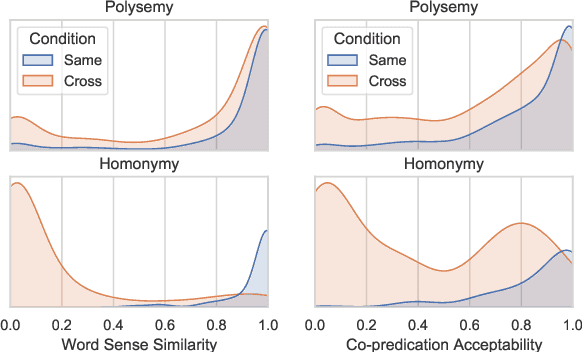
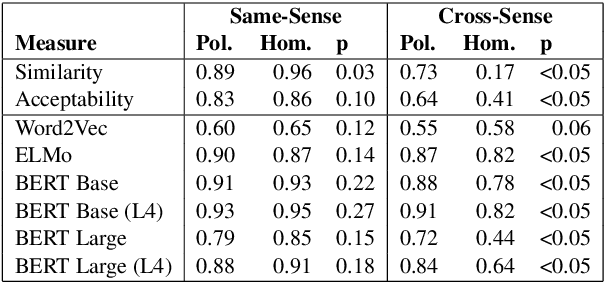
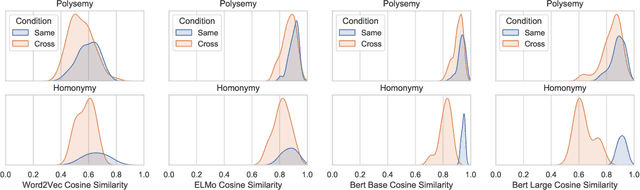
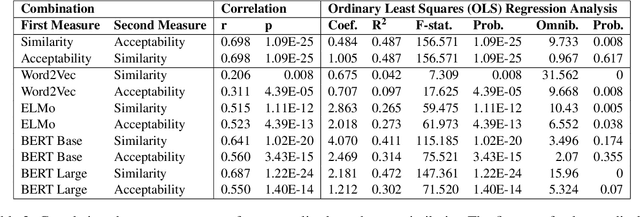
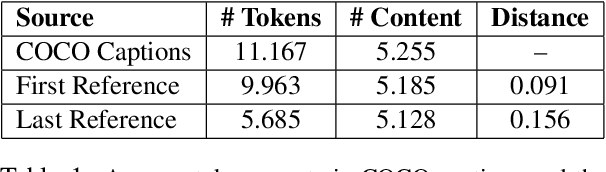
Abstract:One of the central aspects of contextualised language models is that they should be able to distinguish the meaning of lexically ambiguous words by their contexts. In this paper we investigate the extent to which the contextualised embeddings of word forms that display multiplicity of sense reflect traditional distinctions of polysemy and homonymy. To this end, we introduce an extended, human-annotated dataset of graded word sense similarity and co-predication acceptability, and evaluate how well the similarity of embeddings predicts similarity in meaning. Both types of human judgements indicate that the similarity of polysemic interpretations falls in a continuum between identity of meaning and homonymy. However, we also observe significant differences within the similarity ratings of polysemes, forming consistent patterns for different types of polysemic sense alternation. Our dataset thus appears to capture a substantial part of the complexity of lexical ambiguity, and can provide a realistic test bed for contextualised embeddings. Among the tested models, BERT Large shows the strongest correlation with the collected word sense similarity ratings, but struggles to consistently replicate the observed similarity patterns. When clustering ambiguous word forms based on their embeddings, the model displays high confidence in discerning homonyms and some types of polysemic alternations, but consistently fails for others.
The PhotoBook Dataset: Building Common Ground through Visually-Grounded Dialogue
Jun 04, 2019
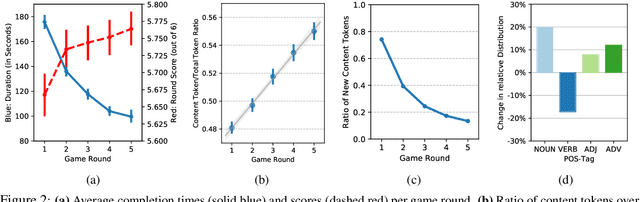
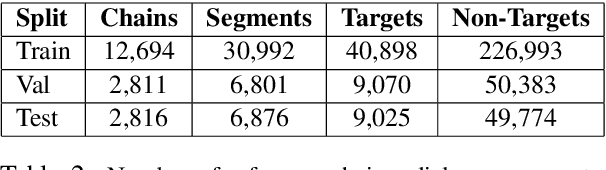
Abstract:This paper introduces the PhotoBook dataset, a large-scale collection of visually-grounded, task-oriented dialogues in English designed to investigate shared dialogue history accumulating during conversation. Taking inspiration from seminal work on dialogue analysis, we propose a data-collection task formulated as a collaborative game prompting two online participants to refer to images utilising both their visual context as well as previously established referring expressions. We provide a detailed description of the task setup and a thorough analysis of the 2,500 dialogues collected. To further illustrate the novel features of the dataset, we propose a baseline model for reference resolution which uses a simple method to take into account shared information accumulated in a reference chain. Our results show that this information is particularly important to resolve later descriptions and underline the need to develop more sophisticated models of common ground in dialogue interaction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge