Jan Teichert-Kluge
Adventures in Demand Analysis Using AI
Dec 31, 2024

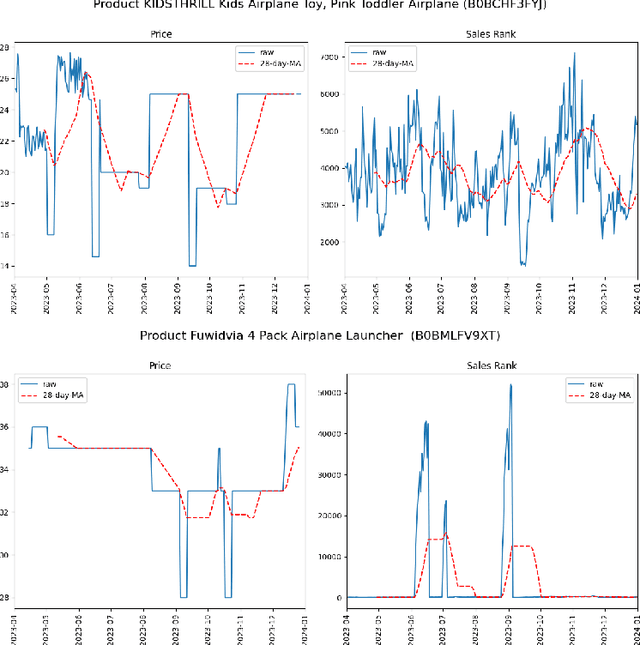

Abstract:This paper advances empirical demand analysis by integrating multimodal product representations derived from artificial intelligence (AI). Using a detailed dataset of toy cars on \textit{Amazon.com}, we combine text descriptions, images, and tabular covariates to represent each product using transformer-based embedding models. These embeddings capture nuanced attributes, such as quality, branding, and visual characteristics, that traditional methods often struggle to summarize. Moreover, we fine-tune these embeddings for causal inference tasks. We show that the resulting embeddings substantially improve the predictive accuracy of sales ranks and prices and that they lead to more credible causal estimates of price elasticity. Notably, we uncover strong heterogeneity in price elasticity driven by these product-specific features. Our findings illustrate that AI-driven representations can enrich and modernize empirical demand analysis. The insights generated may also prove valuable for applied causal inference more broadly.
DoubleMLDeep: Estimation of Causal Effects with Multimodal Data
Feb 01, 2024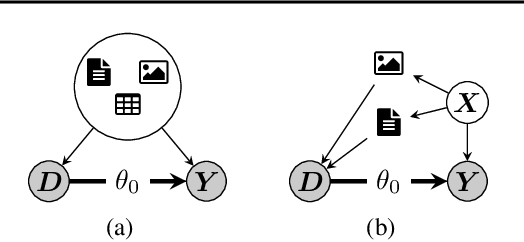
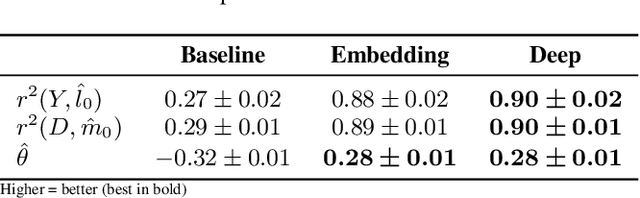
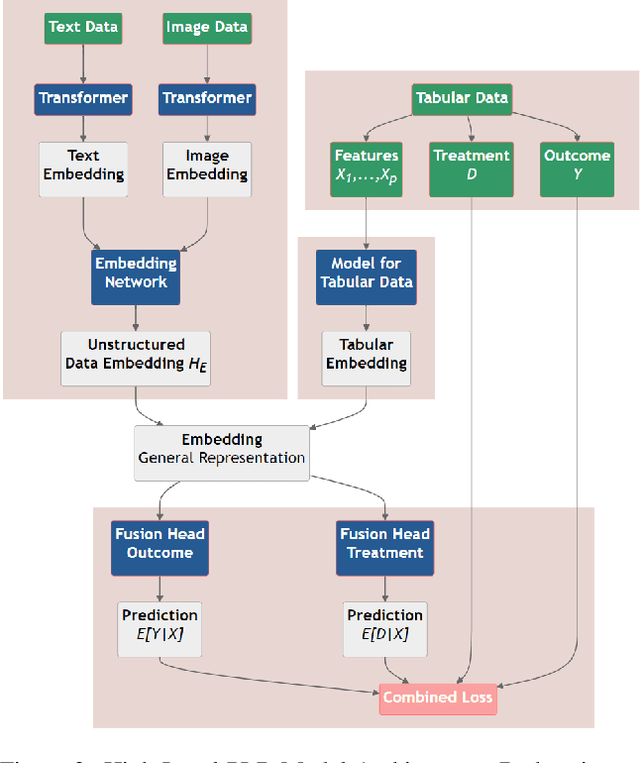
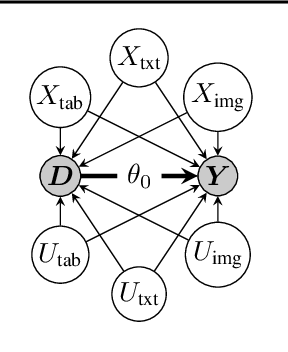
Abstract:This paper explores the use of unstructured, multimodal data, namely text and images, in causal inference and treatment effect estimation. We propose a neural network architecture that is adapted to the double machine learning (DML) framework, specifically the partially linear model. An additional contribution of our paper is a new method to generate a semi-synthetic dataset which can be used to evaluate the performance of causal effect estimation in the presence of text and images as confounders. The proposed methods and architectures are evaluated on the semi-synthetic dataset and compared to standard approaches, highlighting the potential benefit of using text and images directly in causal studies. Our findings have implications for researchers and practitioners in economics, marketing, finance, medicine and data science in general who are interested in estimating causal quantities using non-traditional data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge