James Robert Lloyd
One-Shot Learning in Discriminative Neural Networks
Jul 18, 2017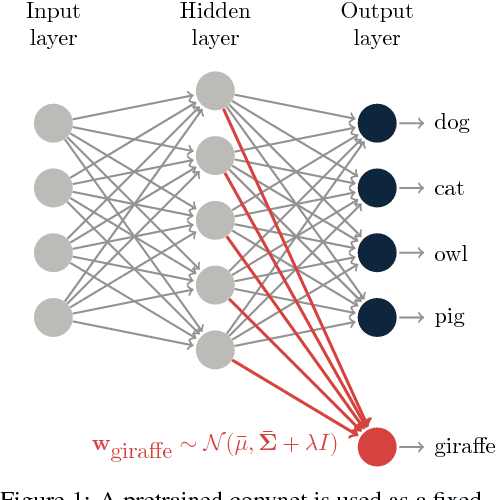
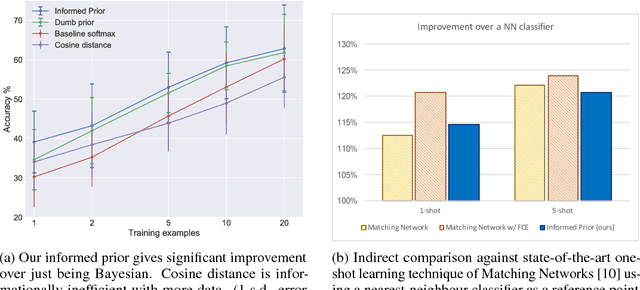
Abstract:We consider the task of one-shot learning of visual categories. In this paper we explore a Bayesian procedure for updating a pretrained convnet to classify a novel image category for which data is limited. We decompose this convnet into a fixed feature extractor and softmax classifier. We assume that the target weights for the new task come from the same distribution as the pretrained softmax weights, which we model as a multivariate Gaussian. By using this as a prior for the new weights, we demonstrate competitive performance with state-of-the-art methods whilst also being consistent with 'normal' methods for training deep networks on large data.
Automatic Construction and Natural-Language Description of Nonparametric Regression Models
Apr 24, 2014



Abstract:This paper presents the beginnings of an automatic statistician, focusing on regression problems. Our system explores an open-ended space of statistical models to discover a good explanation of a data set, and then produces a detailed report with figures and natural-language text. Our approach treats unknown regression functions nonparametrically using Gaussian processes, which has two important consequences. First, Gaussian processes can model functions in terms of high-level properties (e.g. smoothness, trends, periodicity, changepoints). Taken together with the compositional structure of our language of models this allows us to automatically describe functions in simple terms. Second, the use of flexible nonparametric models and a rich language for composing them in an open-ended manner also results in state-of-the-art extrapolation performance evaluated over 13 real time series data sets from various domains.
Gaussian Process Conditional Copulas with Applications to Financial Time Series
Jul 01, 2013



Abstract:The estimation of dependencies between multiple variables is a central problem in the analysis of financial time series. A common approach is to express these dependencies in terms of a copula function. Typically the copula function is assumed to be constant but this may be inaccurate when there are covariates that could have a large influence on the dependence structure of the data. To account for this, a Bayesian framework for the estimation of conditional copulas is proposed. In this framework the parameters of a copula are non-linearly related to some arbitrary conditioning variables. We evaluate the ability of our method to predict time-varying dependencies on several equities and currencies and observe consistent performance gains compared to static copula models and other time-varying copula methods.
Structure Discovery in Nonparametric Regression through Compositional Kernel Search
May 13, 2013



Abstract:Despite its importance, choosing the structural form of the kernel in nonparametric regression remains a black art. We define a space of kernel structures which are built compositionally by adding and multiplying a small number of base kernels. We present a method for searching over this space of structures which mirrors the scientific discovery process. The learned structures can often decompose functions into interpretable components and enable long-range extrapolation on time-series datasets. Our structure search method outperforms many widely used kernels and kernel combination methods on a variety of prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge