Jakub Łucki
Tony
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
An Adversarial Perspective on Machine Unlearning for AI Safety
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Large language models are finetuned to refuse questions about hazardous knowledge, but these protections can often be bypassed. Unlearning methods aim at completely removing hazardous capabilities from models and make them inaccessible to adversaries. This work challenges the fundamental differences between unlearning and traditional safety post-training from an adversarial perspective. We demonstrate that existing jailbreak methods, previously reported as ineffective against unlearning, can be successful when applied carefully. Furthermore, we develop a variety of adaptive methods that recover most supposedly unlearned capabilities. For instance, we show that finetuning on 10 unrelated examples or removing specific directions in the activation space can recover most hazardous capabilities for models edited with RMU, a state-of-the-art unlearning method. Our findings challenge the robustness of current unlearning approaches and question their advantages over safety training.
Can We Understand Plasticity Through Neural Collapse?
Apr 03, 2024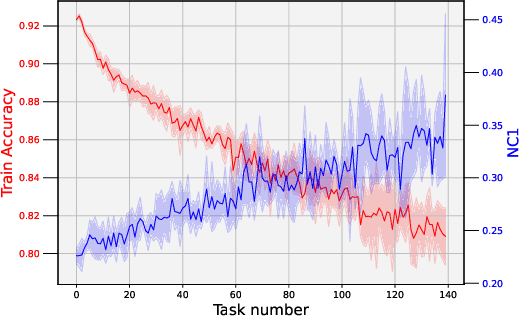
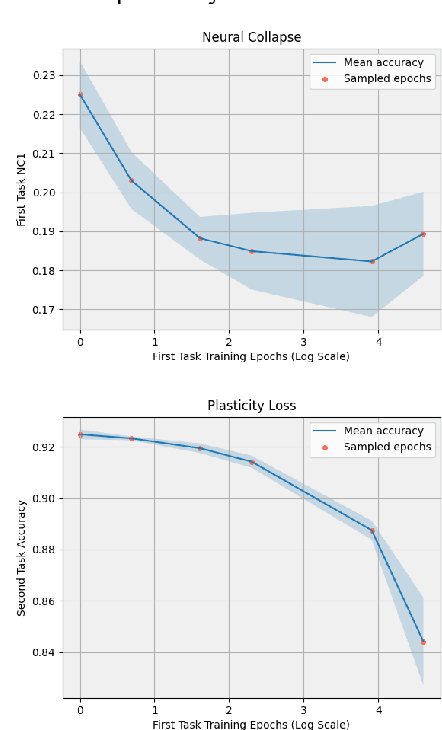
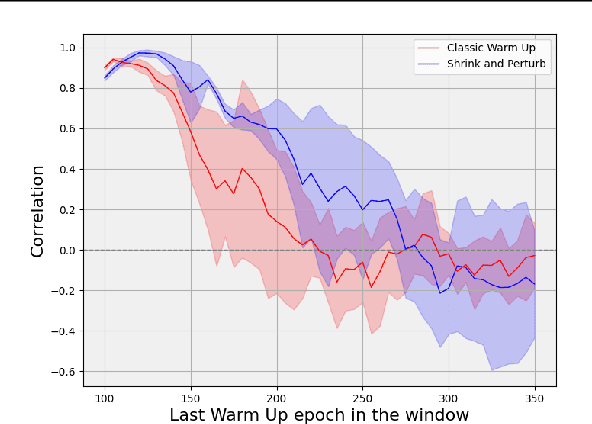
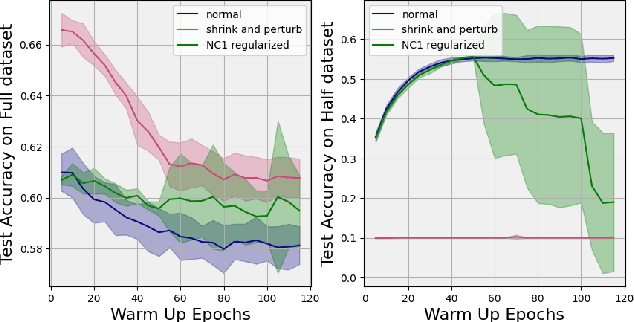
Abstract:This paper explores the connection between two recently identified phenomena in deep learning: plasticity loss and neural collapse. We analyze their correlation in different scenarios, revealing a significant association during the initial training phase on the first task. Additionally, we introduce a regularization approach to mitigate neural collapse, demonstrating its effectiveness in alleviating plasticity loss in this specific setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge