Jaime D. Acevedo-Viloria
Feature-Level Fusion of Super-App and Telecommunication Alternative Data Sources for Credit Card Fraud Detection
Nov 05, 2021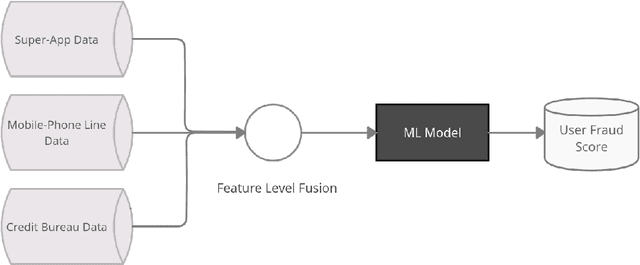
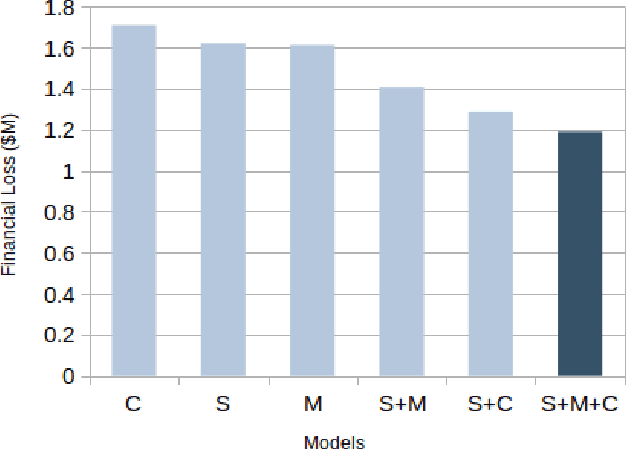
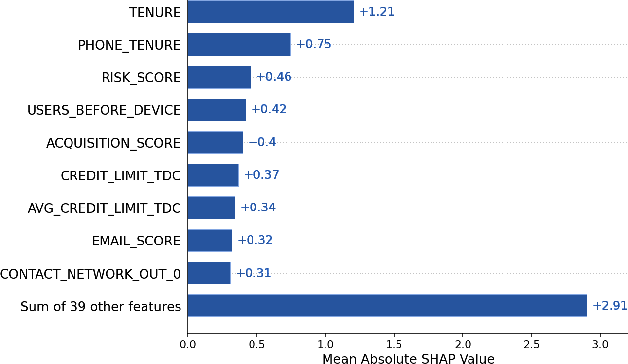
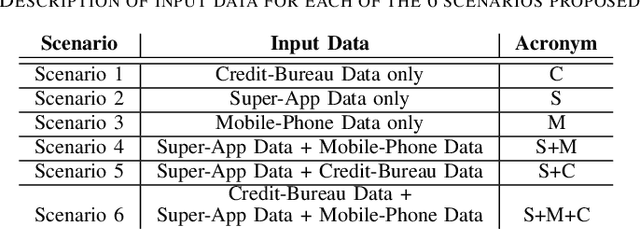
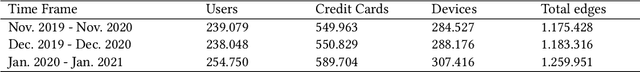
Abstract:Identity theft is a major problem for credit lenders when there's not enough data to corroborate a customer's identity. Among super-apps large digital platforms that encompass many different services this problem is even more relevant; losing a client in one branch can often mean losing them in other services. In this paper, we review the effectiveness of a feature-level fusion of super-app customer information, mobile phone line data, and traditional credit risk variables for the early detection of identity theft credit card fraud. Through the proposed framework, we achieved better performance when using a model whose input is a fusion of alternative data and traditional credit bureau data, achieving a ROC AUC score of 0.81. We evaluate our approach over approximately 90,000 users from a credit lender's digital platform database. The evaluation was performed using not only traditional ML metrics but the financial costs as well.
Relational Graph Neural Networks for Fraud Detection in a Super-App environment
Jul 30, 2021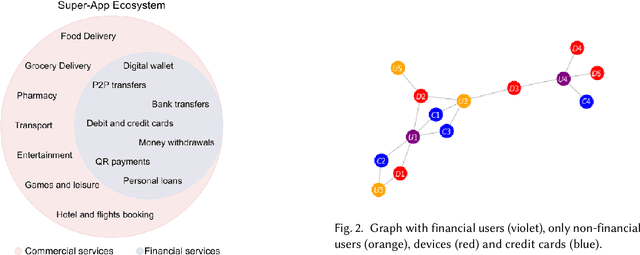

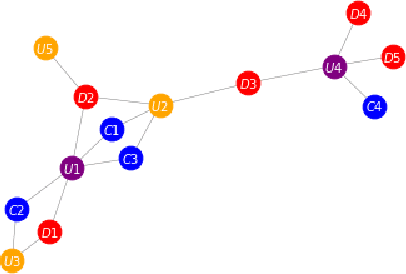
Abstract:Large digital platforms create environments where different types of user interactions are captured, these relationships offer a novel source of information for fraud detection problems. In this paper we propose a framework of relational graph convolutional networks methods for fraudulent behaviour prevention in the financial services of a Super-App. To this end, we apply the framework on different heterogeneous graphs of users, devices, and credit cards; and finally use an interpretability algorithm for graph neural networks to determine the most important relations to the classification task of the users. Our results show that there is an added value when considering models that take advantage of the alternative data of the Super-App and the interactions found in their high connectivity, further proofing how they can leverage that into better decisions and fraud detection strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge