Jahyun Goo
FitHuBERT: Going Thinner and Deeper for Knowledge Distillation of Speech Self-Supervised Learning
Jul 01, 2022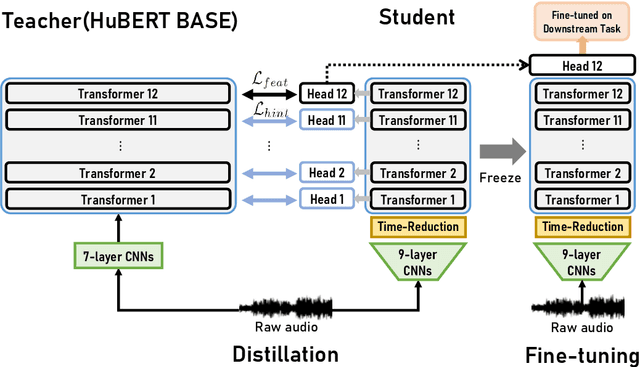
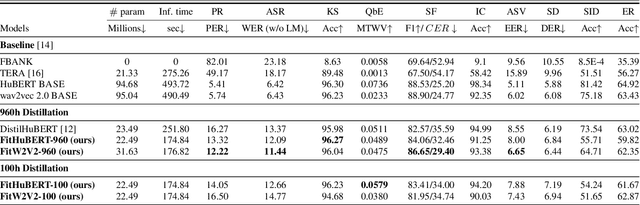
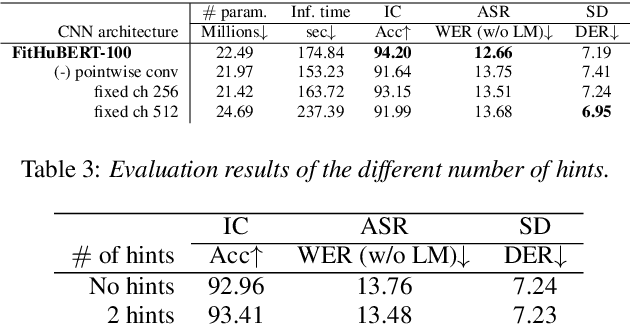
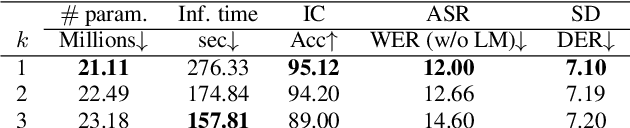
Abstract:Large-scale speech self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged to the main field of speech processing, however, the problem of computational cost arising from its vast size makes a high entry barrier to academia. In addition, existing distillation techniques of speech SSL models compress the model by reducing layers, which induces performance degradation in linguistic pattern recognition tasks such as phoneme recognition (PR). In this paper, we propose FitHuBERT, which makes thinner in dimension throughout almost all model components and deeper in layer compared to prior speech SSL distillation works. Moreover, we employ a time-reduction layer to speed up inference time and propose a method of hint-based distillation for less performance degradation. Our method reduces the model to 23.8% in size and 35.9% in inference time compared to HuBERT. Also, we achieve 12.1% word error rate and 13.3% phoneme error rate on the SUPERB benchmark which is superior than prior work.
Multi-Task Network for Noise-Robust Keyword Spotting and Speaker Verification using CTC-based Soft VAD and Global Query Attention
May 16, 2020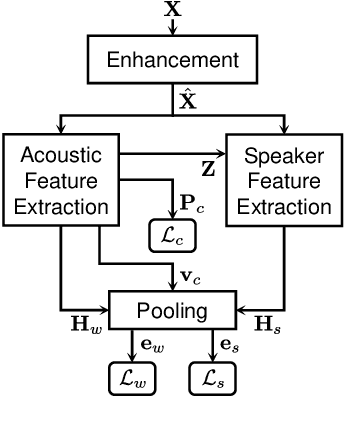
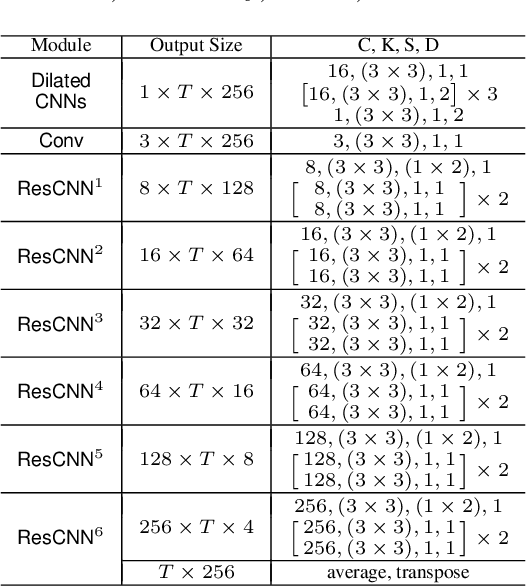
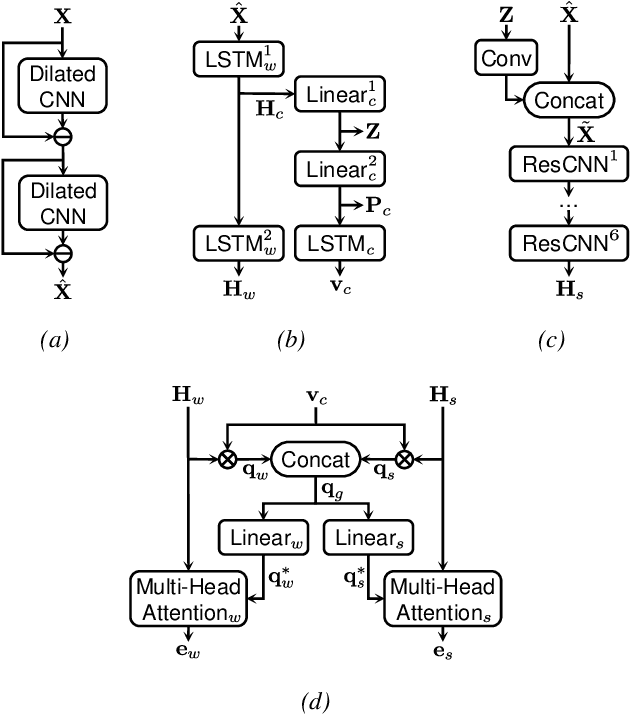
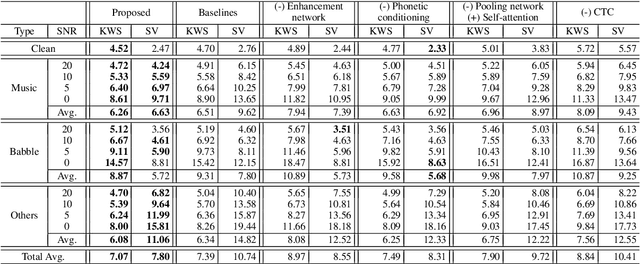
Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) and speaker verification (SV) have been studied independently although it is known that acoustic and speaker domains are complementary. In this paper, we propose a multi-task network that performs KWS and SV simultaneously to fully utilize the interrelated domain information. The multi-task network tightly combines sub-networks aiming at performance improvement in challenging conditions such as noisy environments, open-vocabulary KWS, and short-duration SV, by introducing novel techniques of connectionist temporal classification (CTC)-based soft voice activity detection (VAD) and global query attention. Frame-level acoustic and speaker information is integrated with phonetically originated weights so that forms a word-level global representation. Then it is used for the aggregation of feature vectors to generate discriminative embeddings. Our proposed approach shows 4.06% and 26.71% relative improvements in equal error rate (EER) compared to the baselines for both tasks. We also present a visualization example and results of ablation experiments.
Additional Shared Decoder on Siamese Multi-view Encoders for Learning Acoustic Word Embeddings
Oct 01, 2019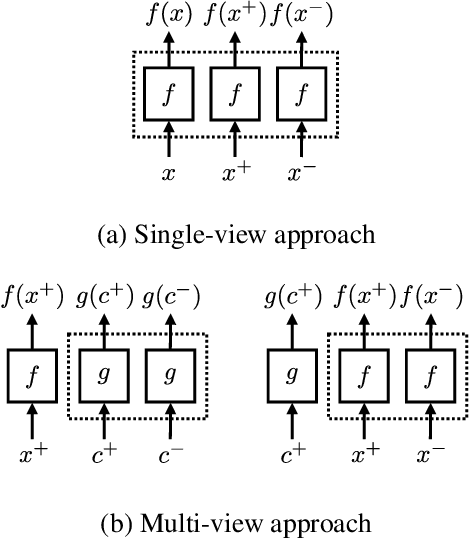
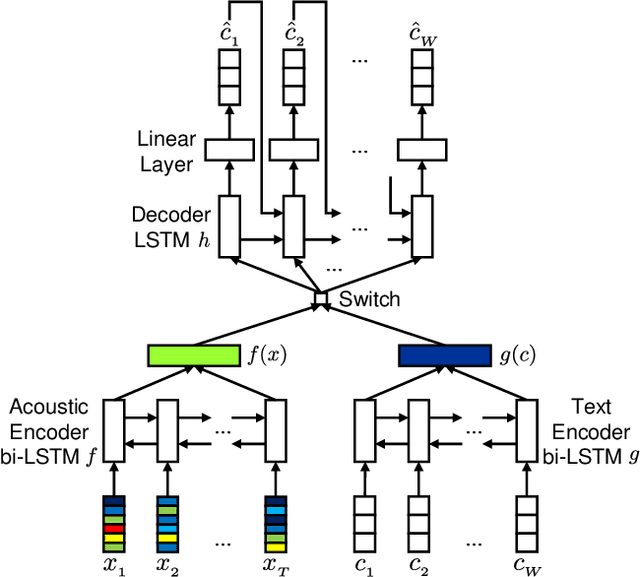
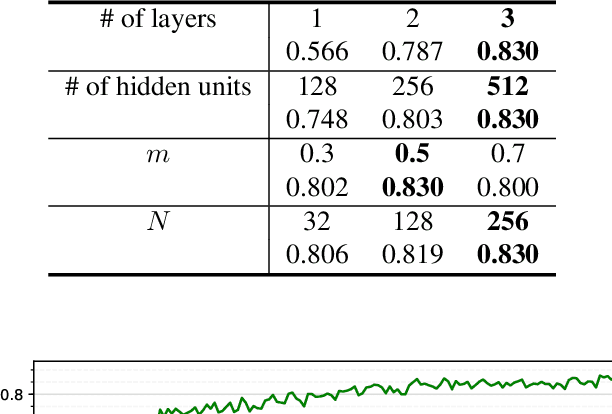
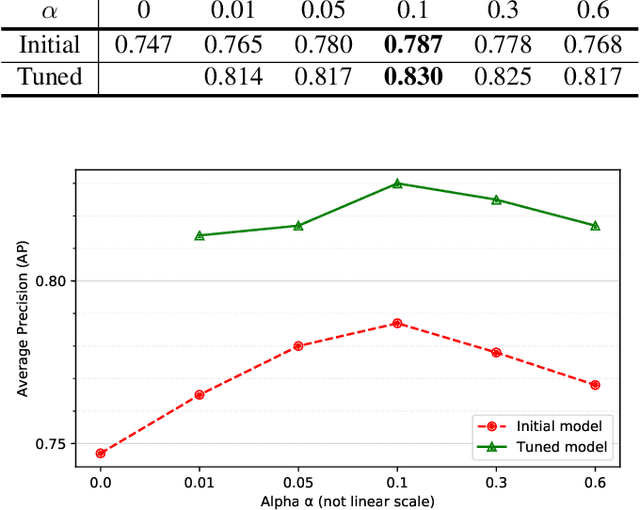
Abstract:Acoustic word embeddings --- fixed-dimensional vector representations of arbitrary-length words --- have attracted increasing interest in query-by-example spoken term detection. Recently, on the fact that the orthography of text labels partly reflects the phonetic similarity between the words' pronunciation, a multi-view approach has been introduced that jointly learns acoustic and text embeddings. It showed that it is possible to learn discriminative embeddings by designing the objective which takes text labels as well as word segments. In this paper, we propose a network architecture that expands the multi-view approach by combining the Siamese multi-view encoders with a shared decoder network to maximize the effect of the relationship between acoustic and text embeddings in embedding space. Discriminatively trained with multi-view triplet loss and decoding loss, our proposed approach achieves better performance on acoustic word discrimination task with the WSJ dataset, resulting in 11.1% relative improvement in average precision. We also present experimental results on cross-view word discrimination and word level speech recognition tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge