Jagabondhu Hazra
Geospatial Chain of Thought Reasoning for Enhanced Visual Question Answering on Satellite Imagery
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Geospatial chain of thought (CoT) reasoning is essential for advancing Visual Question Answering (VQA) on satellite imagery, particularly in climate related applications such as disaster monitoring, infrastructure risk assessment, urban resilience planning, and policy support. Existing VQA models enable scalable interpretation of remote sensing data but often lack the structured reasoning required for complex geospatial queries. We propose a VQA framework that integrates CoT reasoning with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to improve interpretability, robustness, and accuracy. By generating intermediate rationales, the model better handles tasks involving detection, classification, spatial relations, and comparative analysis, which are critical for reliable decision support in high stakes climate domains. Experiments show that CoT supervision improves accuracy by 34.9\% over direct baselines, while DPO yields additional gains in accuracy and reasoning quality. The resulting system advances VQA for multispectral Earth observation by enabling richer geospatial reasoning and more effective climate use cases.
Supply chain emission estimation using large language models
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Large enterprises face a crucial imperative to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially goal 13, which focuses on combating climate change and its impacts. To mitigate the effects of climate change, reducing enterprise Scope 3 (supply chain emissions) is vital, as it accounts for more than 90\% of total emission inventories. However, tracking Scope 3 emissions proves challenging, as data must be collected from thousands of upstream and downstream suppliers.To address the above mentioned challenges, we propose a first-of-a-kind framework that uses domain-adapted NLP foundation models to estimate Scope 3 emissions, by utilizing financial transactions as a proxy for purchased goods and services. We compared the performance of the proposed framework with the state-of-art text classification models such as TF-IDF, word2Vec, and Zero shot learning. Our results show that the domain-adapted foundation model outperforms state-of-the-art text mining techniques and performs as well as a subject matter expert (SME). The proposed framework could accelerate the Scope 3 estimation at Enterprise scale and will help to take appropriate climate actions to achieve SDG 13.
Small, Sparse, but Substantial: Techniques for Segmenting Small Agricultural Fields Using Sparse Ground Data
May 05, 2020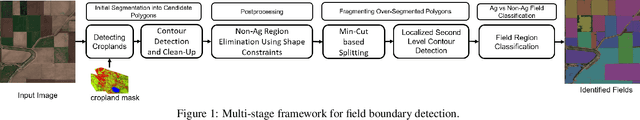
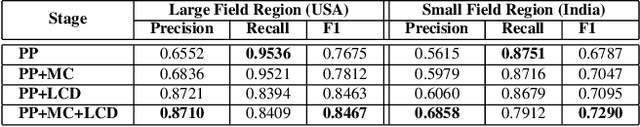
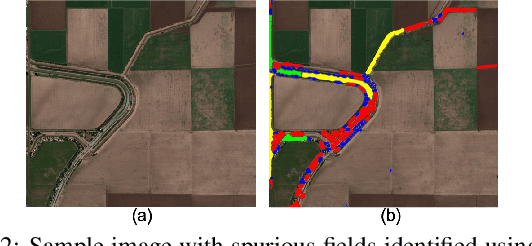
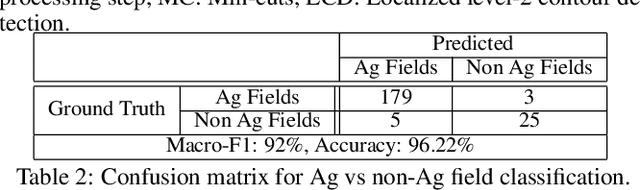
Abstract:The recent thrust on digital agriculture (DA) has renewed significant research interest in the automated delineation of agricultural fields. Most prior work addressing this problem have focused on detecting medium to large fields, while there is strong evidence that around 40\% of the fields world-wide and 70% of the fields in Asia and Africa are small. The lack of adequate labeled images for small fields, huge variations in their color, texture, and shape, and faint boundary lines separating them make it difficult to develop an end-to-end learning model for detecting such fields. Hence, in this paper, we present a multi-stage approach that uses a combination of machine learning and image processing techniques. In the first stage, we leverage state-of-the-art edge detection algorithms such as holistically-nested edge detection (HED) to extract first-level contours and polygons. In the second stage, we propose image-processing techniques to identify polygons that are non-fields, over-segmentations, or noise and eliminate them. The next stage tackles under-segmentations using a combination of a novel ``cut-point'' based technique and localized second-level edge detection to obtain individual parcels. Since a few small, non-cropped but vegetated or constructed pockets can be interspersed in areas that are predominantly croplands, in the final stage, we train a classifier for identifying each parcel from the previous stage as an agricultural field or not. In an evaluation using high-resolution imagery, we show that our approach has a high F-Score of 0.84 in areas with large fields and reasonable accuracy with an F-Score of 0.73 in areas with small fields, which is encouraging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge