Jacob O. Wobbrock
ScreenAudit: Detecting Screen Reader Accessibility Errors in Mobile Apps Using Large Language Models
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Many mobile apps are inaccessible, thereby excluding people from their potential benefits. Existing rule-based accessibility checkers aim to mitigate these failures by identifying errors early during development but are constrained in the types of errors they can detect. We present ScreenAudit, an LLM-powered system designed to traverse mobile app screens, extract metadata and transcripts, and identify screen reader accessibility errors overlooked by existing checkers. We recruited six accessibility experts including one screen reader user to evaluate ScreenAudit's reports across 14 unique app screens. Our findings indicate that ScreenAudit achieves an average coverage of 69.2%, compared to only 31.3% with a widely-used accessibility checker. Expert feedback indicated that ScreenAudit delivered higher-quality feedback and addressed more aspects of screen reader accessibility compared to existing checkers, and that ScreenAudit would benefit app developers in real-world settings.
Creativity in the Age of AI: Evaluating the Impact of Generative AI on Design Outputs and Designers' Creative Thinking
Oct 31, 2024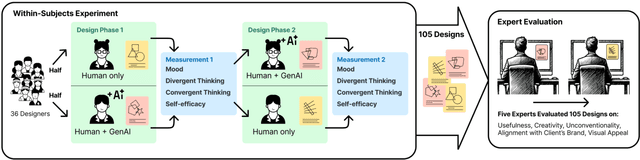
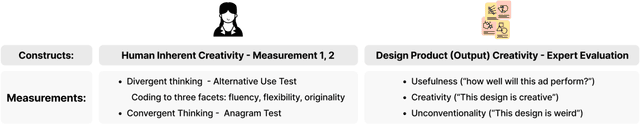
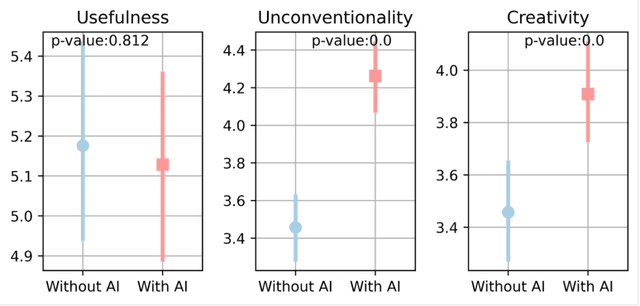
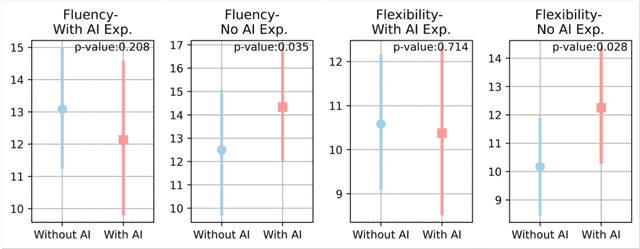
Abstract:As generative AI (GenAI) increasingly permeates design workflows, its impact on design outcomes and designers' creative capabilities warrants investigation. We conducted a within-subjects experiment where we asked participants to design advertisements both with and without GenAI support. Our results show that expert evaluators rated GenAI-supported designs as more creative and unconventional ("weird") despite no significant differences in visual appeal, brand alignment, or usefulness, which highlights the decoupling of novelty from usefulness-traditional dual components of creativity-in the context of GenAI usage. Moreover, while GenAI does not significantly enhance designers' overall creative thinking abilities, users were affected differently based on native language and prior AI exposure. Native English speakers experienced reduced relaxation when using AI, whereas designers new to GenAI exhibited gains in divergent thinking, such as idea fluency and flexibility. These findings underscore the variable impact of GenAI on different user groups, suggesting the potential for customized AI tools.
Engaging with Children's Artwork in Mixed Visual-Ability Families
Jul 26, 2024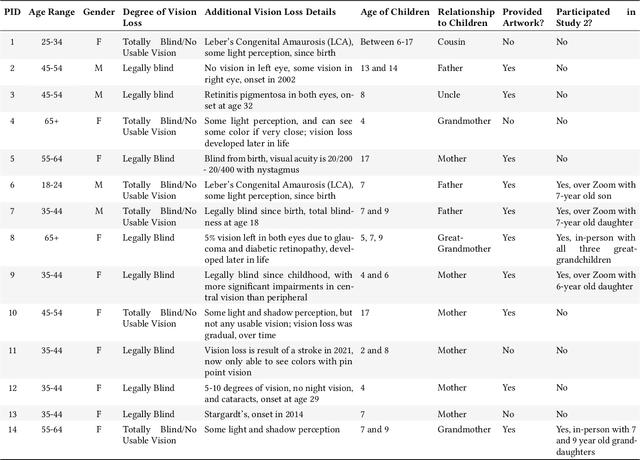



Abstract:We present two studies exploring how blind or low-vision (BLV) family members engage with their sighted children's artwork, strategies to support understanding and interpretation, and the potential role of technology, such as AI, therein. Our first study involved 14 BLV individuals, and the second included five groups of BLV individuals with their children. Through semi-structured interviews with AI descriptions of children's artwork and multi-sensory design probes, we found that BLV family members value artwork engagement as a bonding opportunity, preferring the child's storytelling and interpretation over other nonvisual representations. Additionally, despite some inaccuracies, BLV family members felt that AI-generated descriptions could facilitate dialogue with their children and aid self-guided art discovery. We close with specific design considerations for supporting artwork engagement in mixed visual-ability families, including enabling artwork access through various methods, supporting children's corrections of AI output, and distinctions in context vs. content and interpretation vs. description of children's artwork.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge