Jacek Kustra
Learning to Recognize Correctly Completed Procedure Steps in Egocentric Assembly Videos through Spatio-Temporal Modeling
Oct 14, 2025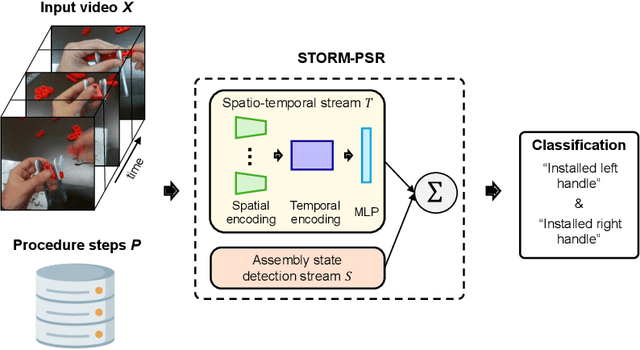
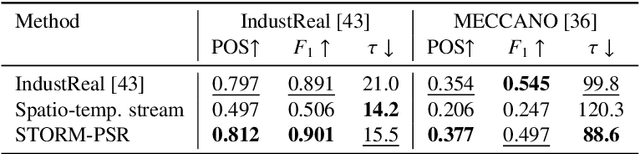
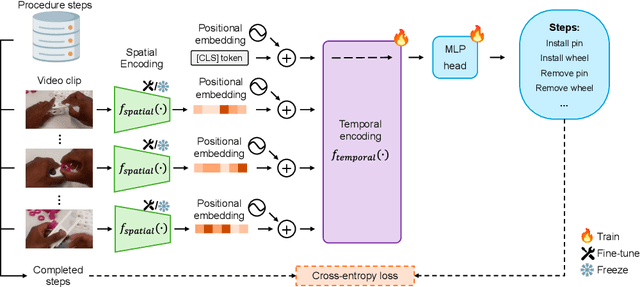
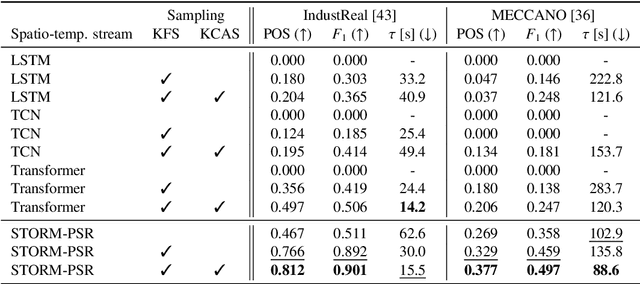
Abstract:Procedure step recognition (PSR) aims to identify all correctly completed steps and their sequential order in videos of procedural tasks. The existing state-of-the-art models rely solely on detecting assembly object states in individual video frames. By neglecting temporal features, model robustness and accuracy are limited, especially when objects are partially occluded. To overcome these limitations, we propose Spatio-Temporal Occlusion-Resilient Modeling for Procedure Step Recognition (STORM-PSR), a dual-stream framework for PSR that leverages both spatial and temporal features. The assembly state detection stream operates effectively with unobstructed views of the object, while the spatio-temporal stream captures both spatial and temporal features to recognize step completions even under partial occlusion. This stream includes a spatial encoder, pre-trained using a novel weakly supervised approach to capture meaningful spatial representations, and a transformer-based temporal encoder that learns how these spatial features relate over time. STORM-PSR is evaluated on the MECCANO and IndustReal datasets, reducing the average delay between actual and predicted assembly step completions by 11.2% and 26.1%, respectively, compared to prior methods. We demonstrate that this reduction in delay is driven by the spatio-temporal stream, which does not rely on unobstructed views of the object to infer completed steps. The code for STORM-PSR, along with the newly annotated MECCANO labels, is made publicly available at https://timschoonbeek.github.io/stormpsr .
Find the Assembly Mistakes: Error Segmentation for Industrial Applications
Aug 23, 2024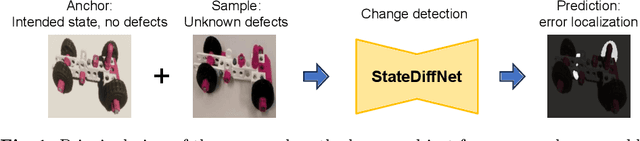
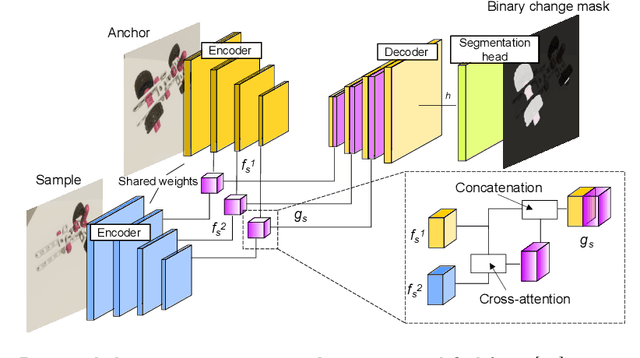
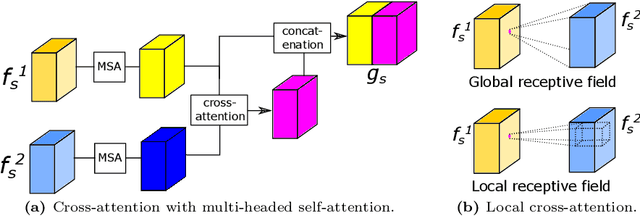
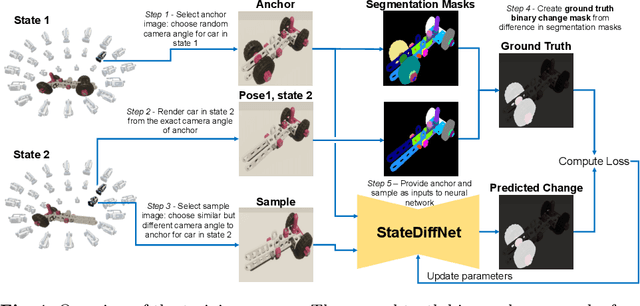
Abstract:Recognizing errors in assembly and maintenance procedures is valuable for industrial applications, since it can increase worker efficiency and prevent unplanned down-time. Although assembly state recognition is gaining attention, none of the current works investigate assembly error localization. Therefore, we propose StateDiffNet, which localizes assembly errors based on detecting the differences between a (correct) intended assembly state and a test image from a similar viewpoint. StateDiffNet is trained on synthetically generated image pairs, providing full control over the type of meaningful change that should be detected. The proposed approach is the first to correctly localize assembly errors taken from real ego-centric video data for both states and error types that are never presented during training. Furthermore, the deployment of change detection to this industrial application provides valuable insights and considerations into the mechanisms of state-of-the-art change detection algorithms. The code and data generation pipeline are publicly available at: https://timschoonbeek.github.io/error_seg.
Supervised Representation Learning towards Generalizable Assembly State Recognition
Aug 21, 2024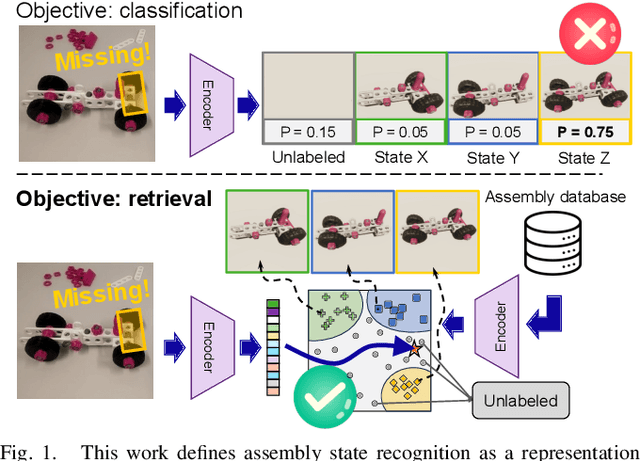
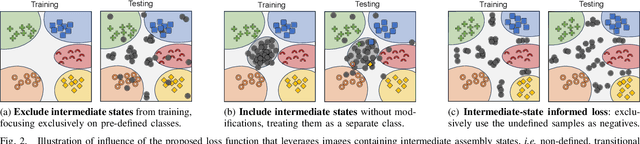
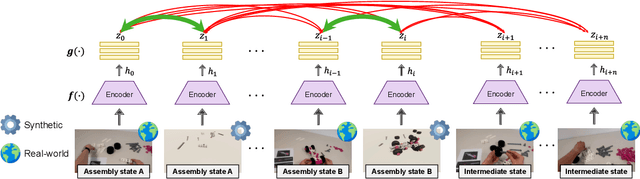
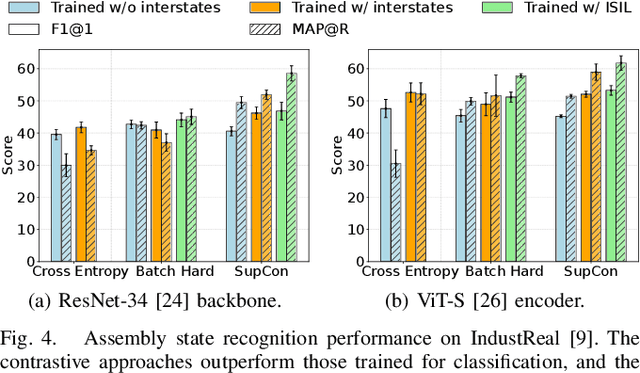
Abstract:Assembly state recognition facilitates the execution of assembly procedures, offering feedback to enhance efficiency and minimize errors. However, recognizing assembly states poses challenges in scalability, since parts are frequently updated, and the robustness to execution errors remains underexplored. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an approach based on representation learning and the novel intermediate-state informed loss function modification (ISIL). ISIL leverages unlabeled transitions between states and demonstrates significant improvements in clustering and classification performance for all tested architectures and losses. Despite being trained exclusively on images without execution errors, thorough analysis on error states demonstrates that our approach accurately distinguishes between correct states and states with various types of execution errors. The integration of the proposed algorithm can offer meaningful assistance to workers and mitigate unexpected losses due to procedural mishaps in industrial settings. The code is available at: https://timschoonbeek.github.io/state_rec
Towards an automated method based on Iterated Local Search optimization for tuning the parameters of Support Vector Machines
Jul 11, 2017Abstract:We provide preliminary details and formulation of an optimization strategy under current development that is able to automatically tune the parameters of a Support Vector Machine over new datasets. The optimization strategy is a heuristic based on Iterated Local Search, a modification of classic hill climbing which iterates calls to a local search routine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge