J. Michael Harrison
Drift Control of High-Dimensional RBM: A Computational Method Based on Neural Networks
Sep 20, 2023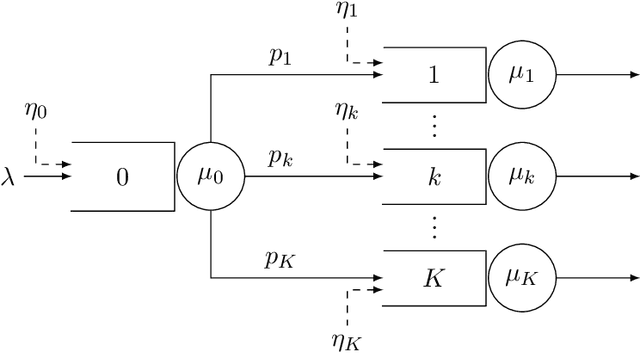
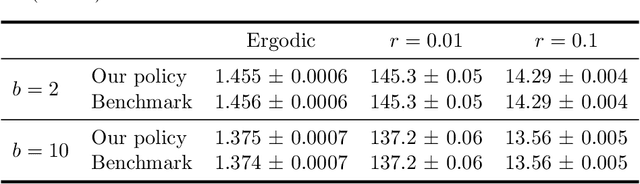
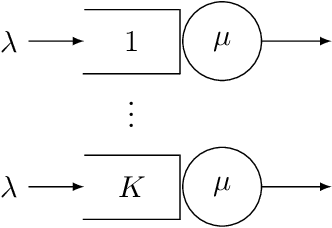
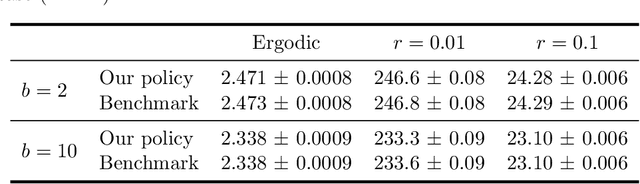
Abstract:Motivated by applications in queueing theory, we consider a stochastic control problem whose state space is the $d$-dimensional positive orthant. The controlled process $Z$ evolves as a reflected Brownian motion whose covariance matrix is exogenously specified, as are its directions of reflection from the orthant's boundary surfaces. A system manager chooses a drift vector $\theta(t)$ at each time $t$ based on the history of $Z$, and the cost rate at time $t$ depends on both $Z(t)$ and $\theta(t)$. In our initial problem formulation, the objective is to minimize expected discounted cost over an infinite planning horizon, after which we treat the corresponding ergodic control problem. Extending earlier work by Han et al. (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 8505-8510), we develop and illustrate a simulation-based computational method that relies heavily on deep neural network technology. For test problems studied thus far, our method is accurate to within a fraction of one percent, and is computationally feasible in dimensions up to at least $d=30$.
Advertising Media and Target Audience Optimization via High-dimensional Bandits
Sep 17, 2022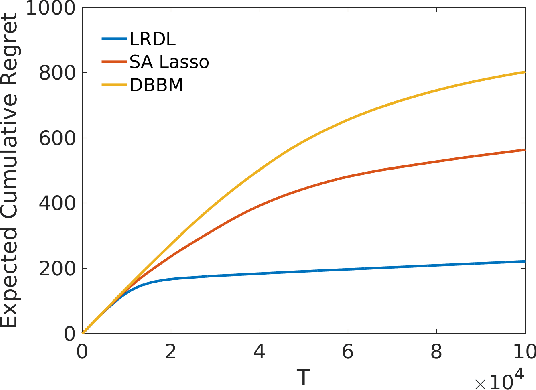
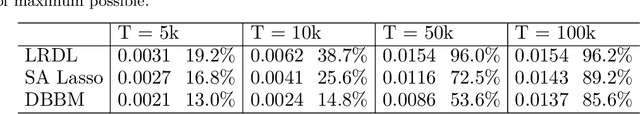
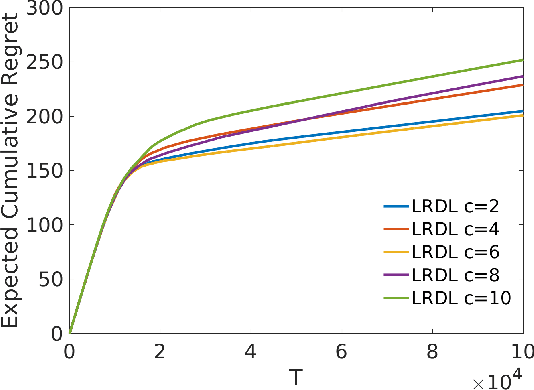
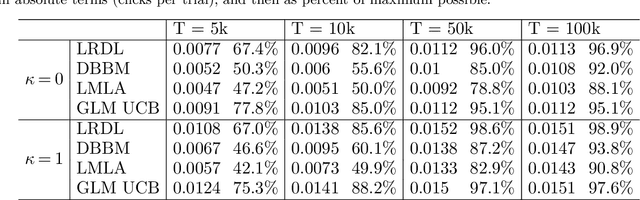
Abstract:We present a data-driven algorithm that advertisers can use to automate their digital ad-campaigns at online publishers. The algorithm enables the advertiser to search across available target audiences and ad-media to find the best possible combination for its campaign via online experimentation. The problem of finding the best audience-ad combination is complicated by a number of distinctive challenges, including (a) a need for active exploration to resolve prior uncertainty and to speed the search for profitable combinations, (b) many combinations to choose from, giving rise to high-dimensional search formulations, and (c) very low success probabilities, typically just a fraction of one percent. Our algorithm (designated LRDL, an acronym for Logistic Regression with Debiased Lasso) addresses these challenges by combining four elements: a multiarmed bandit framework for active exploration; a Lasso penalty function to handle high dimensionality; an inbuilt debiasing kernel that handles the regularization bias induced by the Lasso; and a semi-parametric regression model for outcomes that promotes cross-learning across arms. The algorithm is implemented as a Thompson Sampler, and to the best of our knowledge, it is the first that can practically address all of the challenges above. Simulations with real and synthetic data show the method is effective and document its superior performance against several benchmarks from the recent high-dimensional bandit literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge