Harikesh S. Nair
Advertising Media and Target Audience Optimization via High-dimensional Bandits
Sep 17, 2022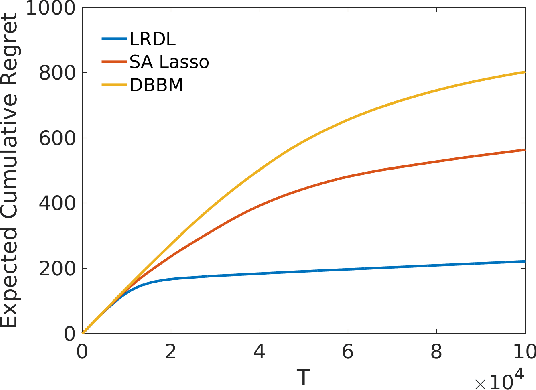
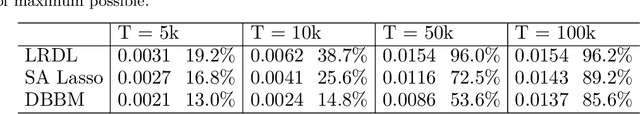
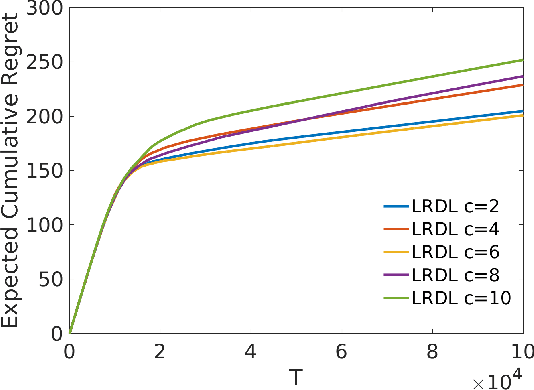
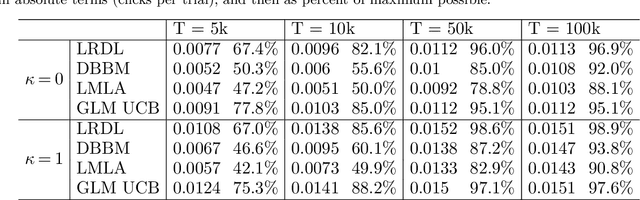
Abstract:We present a data-driven algorithm that advertisers can use to automate their digital ad-campaigns at online publishers. The algorithm enables the advertiser to search across available target audiences and ad-media to find the best possible combination for its campaign via online experimentation. The problem of finding the best audience-ad combination is complicated by a number of distinctive challenges, including (a) a need for active exploration to resolve prior uncertainty and to speed the search for profitable combinations, (b) many combinations to choose from, giving rise to high-dimensional search formulations, and (c) very low success probabilities, typically just a fraction of one percent. Our algorithm (designated LRDL, an acronym for Logistic Regression with Debiased Lasso) addresses these challenges by combining four elements: a multiarmed bandit framework for active exploration; a Lasso penalty function to handle high dimensionality; an inbuilt debiasing kernel that handles the regularization bias induced by the Lasso; and a semi-parametric regression model for outcomes that promotes cross-learning across arms. The algorithm is implemented as a Thompson Sampler, and to the best of our knowledge, it is the first that can practically address all of the challenges above. Simulations with real and synthetic data show the method is effective and document its superior performance against several benchmarks from the recent high-dimensional bandit literature.
Comparison Lift: Bandit-based Experimentation System for Online Advertising
Sep 16, 2020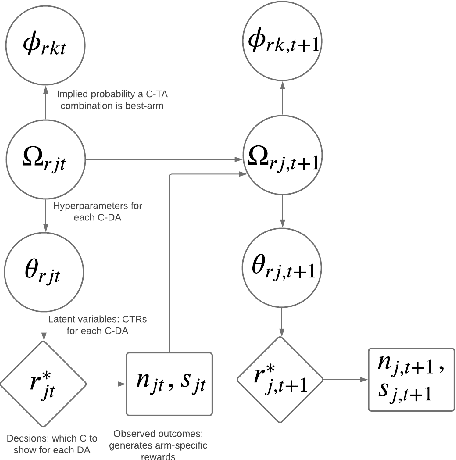
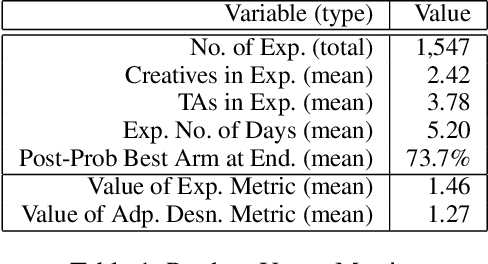
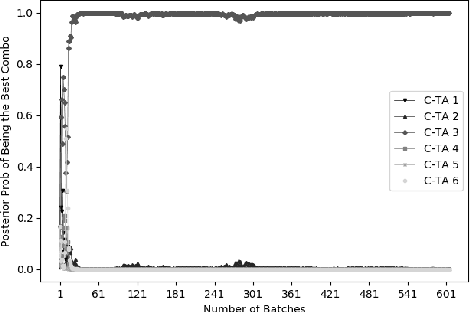
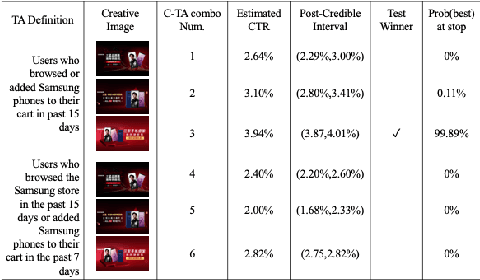
Abstract:Comparison Lift is an experimentation-as-a-service (EaaS) application for testing online advertising audiences and creatives at JD.com. Unlike many other EaaS tools that focus primarily on fixed sample A/B testing, Comparison Lift deploys a custom bandit-based experimentation algorithm. The advantages of the bandit-based approach are two-fold. First, it aligns the randomization induced in the test with the advertiser's goals from testing. Second, by adapting experimental design to information acquired during the test, it reduces substantially the cost of experimentation to the advertiser. Since launch in May 2019, Comparison Lift has been utilized in over 1,500 experiments. We estimate that utilization of the product has helped increase click-through rates of participating advertising campaigns by 46% on average. We estimate that the adaptive design in the product has generated 27% more clicks on average during testing compared to a fixed sample A/B design. Both suggest significant value generation and cost savings to advertisers from the product.
Online Inference for Advertising Auctions
Aug 22, 2019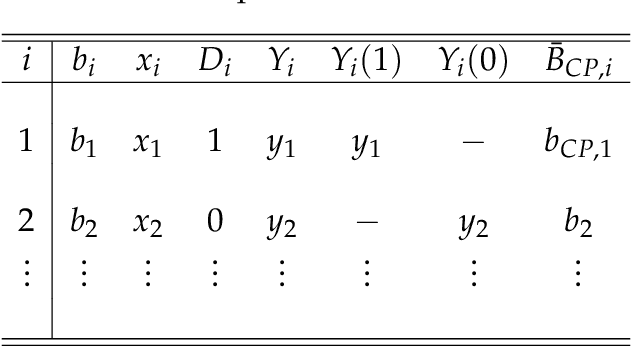
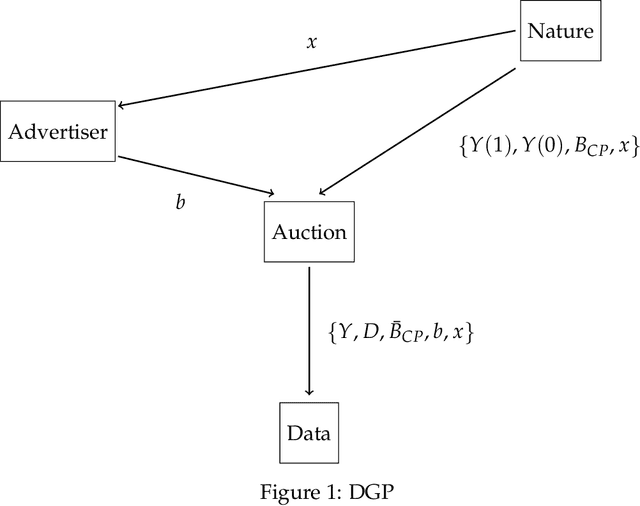
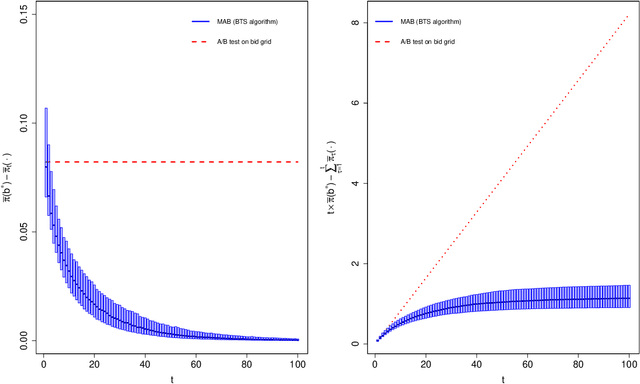
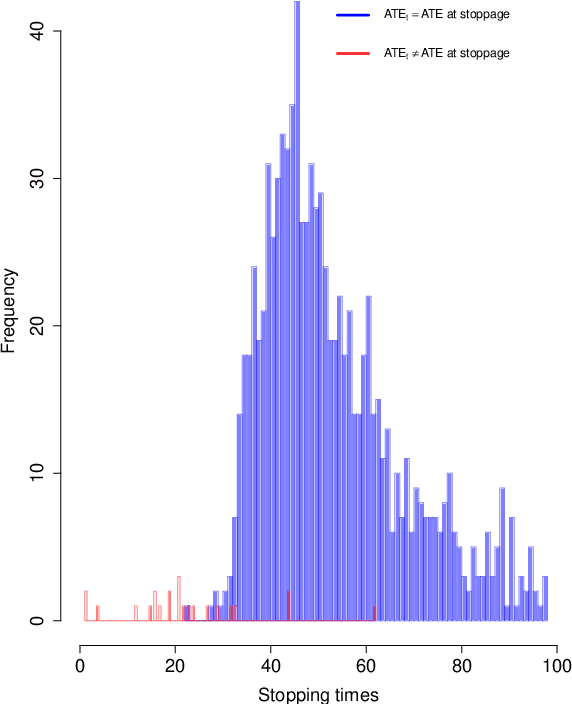
Abstract:Advertisers that engage in real-time bidding (RTB) to display their ads commonly have two goals: learning their optimal bidding policy and estimating the expected effect of exposing users to their ads. Typical strategies to accomplish one of these goals tend to ignore the other, creating an apparent tension between the two. This paper exploits the economic structure of the bid optimization problem faced by advertisers to show that these two objectives can actually be perfectly aligned. By framing the advertiser's problem as a multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem, we propose a modified Thompson Sampling (TS) algorithm that concurrently learns the optimal bidding policy and estimates the expected effect of displaying the ad while minimizing economic losses from potential sub-optimal bidding. Simulations show that not only the proposed method successfully accomplishes the advertiser's goals, but also does so at a much lower cost than more conventional experimentation policies aimed at performing causal inference.
Online Evaluation of Audiences for Targeted Advertising via Bandit Experiments
Jul 18, 2019



Abstract:Firms implementing digital advertising campaigns face a complex problem in determining the right match between their advertising creatives and target audiences. Typical solutions to the problem have leveraged non-experimental methods, or used "split-testing" strategies that have not explicitly addressed the complexities induced by targeted audiences that can potentially overlap with one another. This paper presents an adaptive algorithm that addresses the problem via online experimentation. The algorithm is set up as a contextual bandit and addresses the overlap issue by partitioning the target audiences into disjoint, non-overlapping sub-populations. It learns an optimal creative display policy in the disjoint space, while assessing in parallel which creative has the best match in the space of possibly overlapping target audiences. Experiments show that the proposed method is more efficient compared to naive "split-testing" or non-adaptive "A/B/n" testing based methods. We also describe a testing product we built that uses the algorithm. The product is currently deployed on the advertising platform of JD.com, an eCommerce company and a publisher of digital ads in China.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge