Ivi Chatzi
Canonical Autoregressive Generation
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:State of the art large language models are trained using large amounts of tokens derived from raw text using what is called a tokenizer. Crucially, the tokenizer determines the (token) vocabulary a model will use during inference as well as, in principle, the (token) language. This is because, while the token vocabulary may allow for different tokenizations of a string, the tokenizer always maps the string to only one of these tokenizations--the canonical tokenization. However, multiple lines of empirical evidence suggest that large language models do not always generate canonical token sequences, and this comes with several negative consequences. In this work, we first show that, to generate a canonical token sequence, a model needs to generate (partial) canonical token sequences at each step of the autoregressive generation process underpinning its functioning. Building upon this theoretical result, we introduce canonical sampling, a simple and efficient sampling method that precludes a given model from generating non-canonical token sequences. Further, we also show that, in comparison with standard sampling, the distribution of token sequences generated using canonical sampling is provably closer to the true distribution of token sequences used during training.
Evaluation of Large Language Models via Coupled Token Generation
Feb 03, 2025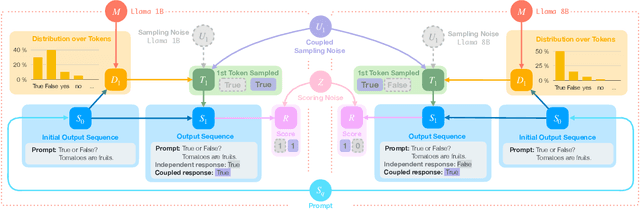
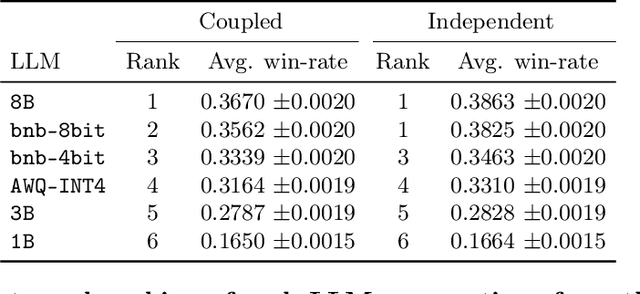
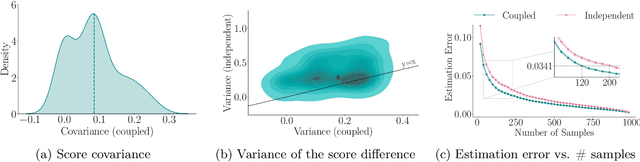
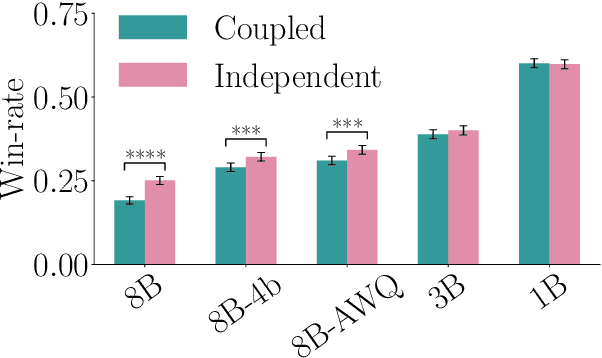
Abstract:State of the art large language models rely on randomization to respond to a prompt. As an immediate consequence, a model may respond differently to the same prompt if asked multiple times. In this work, we argue that the evaluation and ranking of large language models should control for the randomization underpinning their functioning. Our starting point is the development of a causal model for coupled autoregressive generation, which allows different large language models to sample responses with the same source of randomness. Building upon our causal model, we first show that, on evaluations based on benchmark datasets, coupled autoregressive generation leads to the same conclusions as vanilla autoregressive generation but using provably fewer samples. However, we further show that, on evaluations based on (human) pairwise comparisons, coupled and vanilla autoregressive generation can surprisingly lead to different rankings when comparing more than two models, even with an infinite amount of samples. This suggests that the apparent advantage of a model over others in existing evaluation protocols may not be genuine but rather confounded by the randomness inherent to the generation process. To illustrate and complement our theoretical results, we conduct experiments with several large language models from the Llama family. We find that, across multiple knowledge areas from the popular MMLU benchmark dataset, coupled autoregressive generation requires up to 40% fewer samples to reach the same conclusions as vanilla autoregressive generation. Further, using data from the LMSYS Chatbot Arena platform, we find that the win-rates derived from pairwise comparisons by a strong large language model to prompts differ under coupled and vanilla autoregressive generation.
Counterfactual Token Generation in Large Language Models
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:"Sure, I am happy to generate a story for you: Captain Lyra stood at the helm of her trusty ship, the Maelstrom's Fury, gazing out at the endless sea. [...] Lyra's eyes welled up with tears as she realized the bitter truth - she had sacrificed everything for fleeting riches, and lost the love of her crew, her family, and herself." Although this story, generated by a large language model, is captivating, one may wonder -- how would the story have unfolded if the model had chosen "Captain Maeve" as the protagonist instead? We cannot know. State-of-the-art large language models are stateless -- they maintain no internal memory or state. Given a prompt, they generate a sequence of tokens as an output using an autoregressive process. As a consequence, they cannot reason about counterfactual alternatives to tokens they have generated in the past. In this work, our goal is to enhance them with this functionality. To this end, we develop a causal model of token generation that builds upon the Gumbel-Max structural causal model. Our model allows any large language model to perform counterfactual token generation at almost no cost in comparison with vanilla token generation, it is embarrassingly simple to implement, and it does not require any fine-tuning nor prompt engineering. We implement our model on Llama 3 8B-instruct and conduct both qualitative and quantitative analyses of counterfactually generated text. We conclude with a demonstrative application of counterfactual token generation for bias detection, unveiling interesting insights about the model of the world constructed by large language models.
Prediction-Powered Ranking of Large Language Models
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Large language models are often ranked according to their level of alignment with human preferences -- a model is better than other models if its outputs are more frequently preferred by humans. One of the most popular ways to elicit human preferences utilizes pairwise comparisons between the outputs provided by different models to the same inputs. However, since gathering pairwise comparisons by humans is costly and time-consuming, it has become a very common practice to gather pairwise comparisons by a strong large language model -- a model strongly aligned with human preferences. Surprisingly, practitioners cannot currently measure the uncertainty that any mismatch between human and model preferences may introduce in the constructed rankings. In this work, we develop a statistical framework to bridge this gap. Given a small set of pairwise comparisons by humans and a large set of pairwise comparisons by a model, our framework provides a rank-set -- a set of possible ranking positions -- for each of the models under comparison. Moreover, it guarantees that, with a probability greater than or equal to a user-specified value, the rank-sets cover the true ranking consistent with (the distribution of) human pairwise preferences. Our framework is computationally efficient, easy to use, and does not make any assumption about the distribution of human preferences nor about the degree of alignment between the pairwise comparisons by the humans and the strong large language model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge