Ivan Meza
Triplet loss based embeddings for forensic speaker identification in Spanish
Feb 24, 2021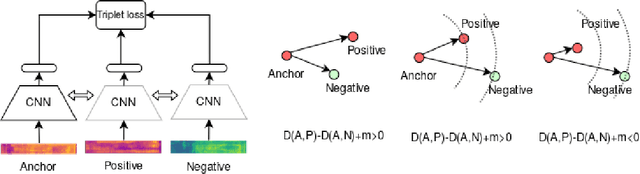
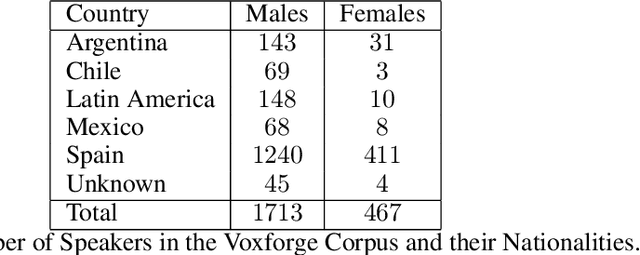
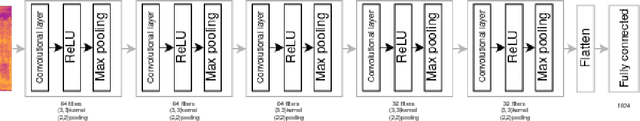
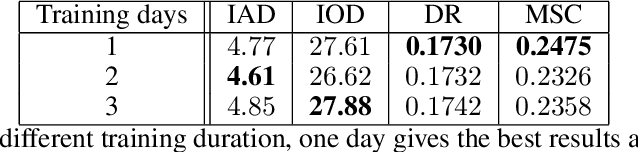
Abstract:With the advent of digital technology, it is more common that committed crimes or legal disputes involve some form of speech recording where the identity of a speaker is questioned [1]. In face of this situation, the field of forensic speaker identification has been looking to shed light on the problem by quantifying how much a speech recording belongs to a particular person in relation to a population. In this work, we explore the use of speech embeddings obtained by training a CNN using the triplet loss. In particular, we focus on the Spanish language which has not been extensively studies. We propose extracting the embeddings from speech spectrograms samples, then explore several configurations of such spectrograms, and finally, quantify the embeddings quality. We also show some limitations of our data setting which is predominantly composed by male speakers. At the end, we propose two approaches to calculate the Likelihood Radio given out speech embeddings and we show that triplet loss is a good alternative to create speech embeddings for forensic speaker identification.
Lost in Translation: Analysis of Information Loss During Machine Translation Between Polysynthetic and Fusional Languages
Jul 01, 2018

Abstract:Machine translation from polysynthetic to fusional languages is a challenging task, which gets further complicated by the limited amount of parallel text available. Thus, translation performance is far from the state of the art for high-resource and more intensively studied language pairs. To shed light on the phenomena which hamper automatic translation to and from polysynthetic languages, we study translations from three low-resource, polysynthetic languages (Nahuatl, Wixarika and Yorem Nokki) into Spanish and vice versa. Doing so, we find that in a morpheme-to-morpheme alignment an important amount of information contained in polysynthetic morphemes has no Spanish counterpart, and its translation is often omitted. We further conduct a qualitative analysis and, thus, identify morpheme types that are commonly hard to align or ignored in the translation process.
Challenges of language technologies for the indigenous languages of the Americas
Jun 12, 2018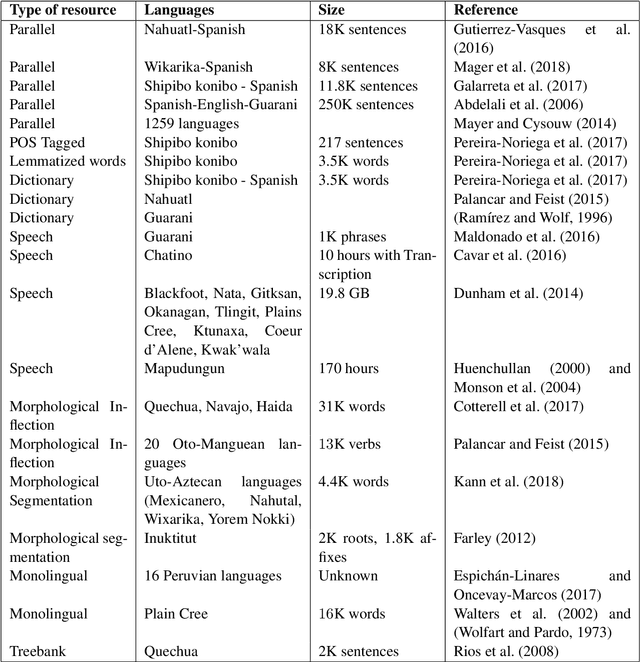
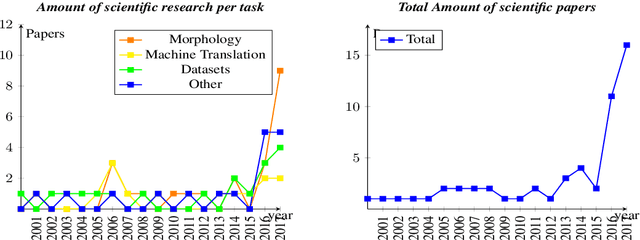
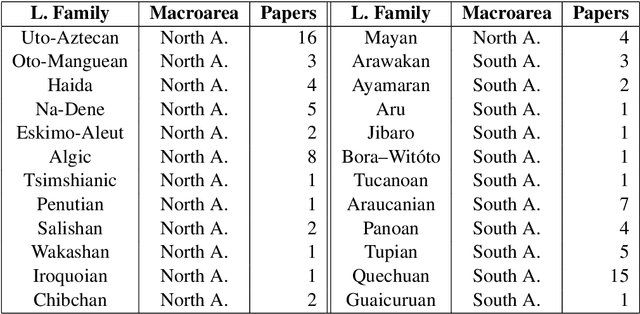
Abstract:Indigenous languages of the American continent are highly diverse. However, they have received little attention from the technological perspective. In this paper, we review the research, the digital resources and the available NLP systems that focus on these languages. We present the main challenges and research questions that arise when distant languages and low-resource scenarios are faced. We would like to encourage NLP research in linguistically rich and diverse areas like the Americas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge