Iuliana Marin
Effects of Different Attention Mechanisms Applied on 3D Models in Video Classification
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Human action recognition has become an important research focus in computer vision due to the wide range of applications where it is used. 3D Resnet-based CNN models, particularly MC3, R3D, and R(2+1)D, have different convolutional filters to extract spatiotemporal features. This paper investigates the impact of reducing the captured knowledge from temporal data, while increasing the resolution of the frames. To establish this experiment, we created similar designs to the three originals, but with a dropout layer added before the final classifier. Secondly, we then developed ten new versions for each one of these three designs. The variants include special attention blocks within their architecture, such as convolutional block attention module (CBAM), temporal convolution networks (TCN), in addition to multi-headed and channel attention mechanisms. The purpose behind that is to observe the extent of the influence each of these blocks has on performance for the restricted-temporal models. The results of testing all the models on UCF101 have shown accuracy of 88.98% for the variant with multiheaded attention added to the modified R(2+1)D. This paper concludes the significance of missing temporal features in the performance of the newly created increased resolution models. The variants had different behavior on class-level accuracy, despite the similarity of their enhancements to the overall performance.
* 18 pages, 6 figures, conference
Evaluating Data Augmentation Techniques for Coffee Leaf Disease Classification
Jan 11, 2024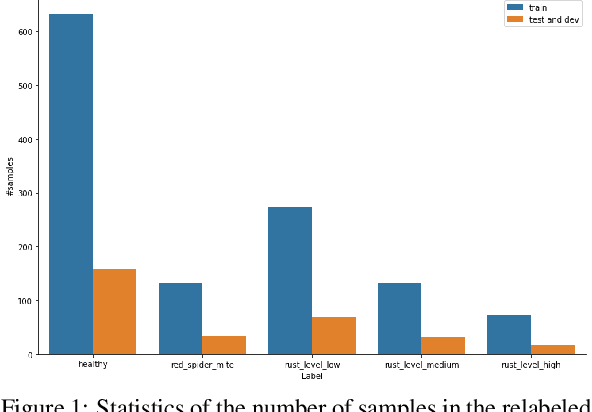
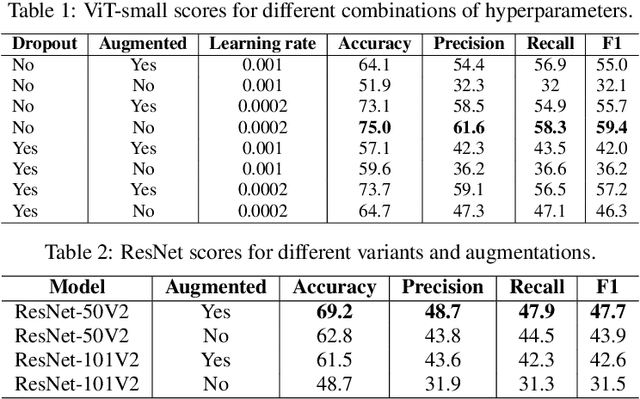
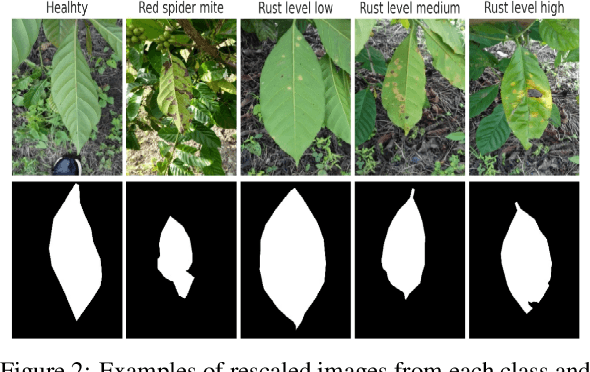
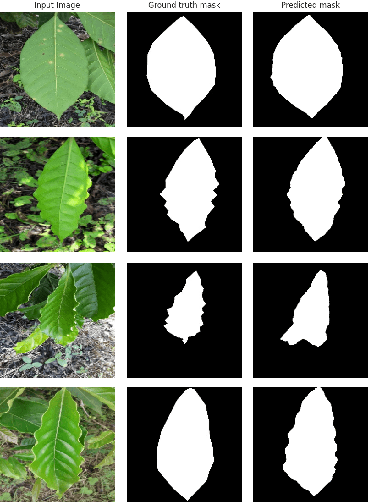
Abstract:The detection and classification of diseases in Robusta coffee leaves are essential to ensure that plants are healthy and the crop yield is kept high. However, this job requires extensive botanical knowledge and much wasted time. Therefore, this task and others similar to it have been extensively researched subjects in image classification. Regarding leaf disease classification, most approaches have used the more popular PlantVillage dataset while completely disregarding other datasets, like the Robusta Coffee Leaf (RoCoLe) dataset. As the RoCoLe dataset is imbalanced and does not have many samples, fine-tuning of pre-trained models and multiple augmentation techniques need to be used. The current paper uses the RoCoLe dataset and approaches based on deep learning for classifying coffee leaf diseases from images, incorporating the pix2pix model for segmentation and cycle-generative adversarial network (CycleGAN) for augmentation. Our study demonstrates the effectiveness of Transformer-based models, online augmentations, and CycleGAN augmentation in improving leaf disease classification. While synthetic data has limitations, it complements real data, enhancing model performance. These findings contribute to developing robust techniques for plant disease detection and classification.
From Fake to Hyperpartisan News Detection Using Domain Adaptation
Aug 04, 2023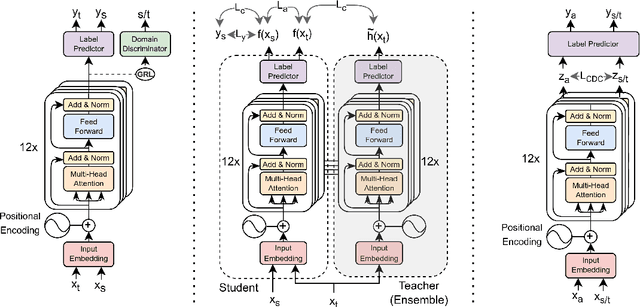
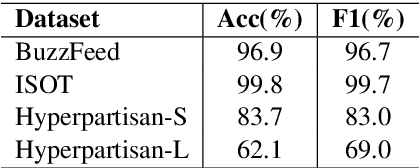

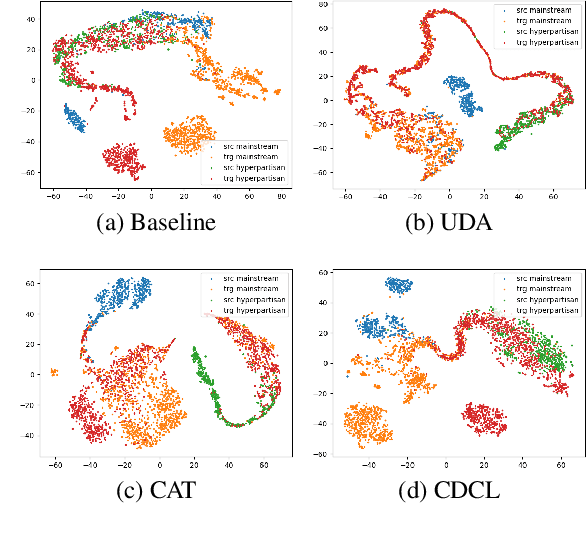
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is a popular technique that aims to reduce the domain shift between two data distributions. It was successfully applied in computer vision and natural language processing. In the current work, we explore the effects of various unsupervised domain adaptation techniques between two text classification tasks: fake and hyperpartisan news detection. We investigate the knowledge transfer from fake to hyperpartisan news detection without involving target labels during training. Thus, we evaluate UDA, cluster alignment with a teacher, and cross-domain contrastive learning. Extensive experiments show that these techniques improve performance, while including data augmentation further enhances the results. In addition, we combine clustering and topic modeling algorithms with UDA, resulting in improved performances compared to the initial UDA setup.
Smart Home Environment Modelled with a Multi-Agent System
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:A smart home can be considered a place of residence that enables the management of appliances and systems to help with day-to-day life by automated technology. In the current paper is described a prototype that simulates a context-aware environment, developed in a designed smart home. The smart home environment has been simulated using three agents and five locations in a house. The context-aware agents behave based on predefined rules designed for daily activities. Our proposal aims to reduce operational cost of running devices. In the future, monitors of health aspects belonging to home residents will sustain their healthy life daily.
* 12 pages, 8 figures, journal article
Internet of Things and Health Care in Pandemic COVID-19: System Requirements Evaluation
May 05, 2022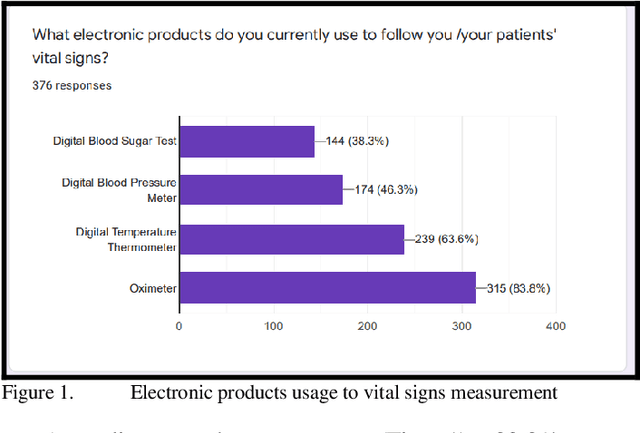
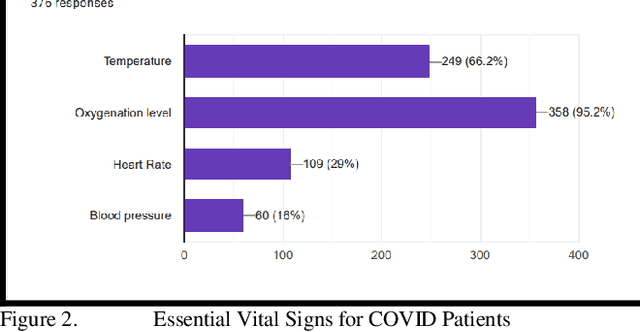
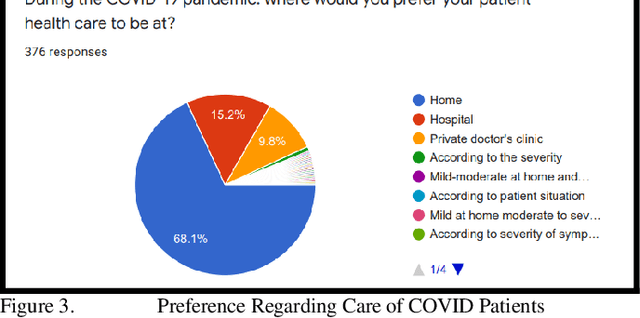
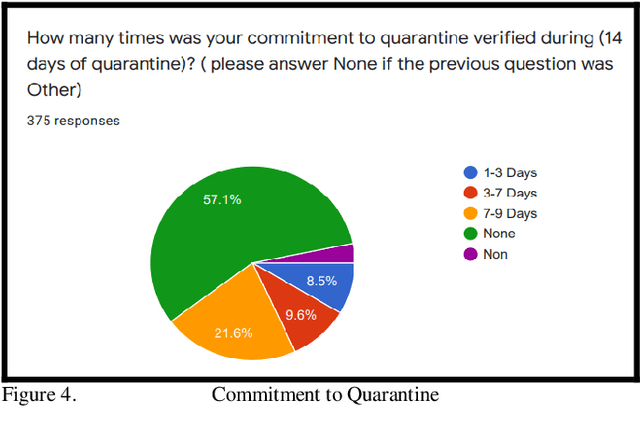
Abstract:Technology adoption in healthcare services has resulted in advancing care delivery services and improving the experiences of patients. This paper presents research that aims to find the important requirements for a remote monitoring system for patients with COVID-19. As this pandemic is growing more and more, there is a critical need for such systems. In this paper, the requirements and the value are determined for the proposed system, which integrates a smart bracelet that helps to signal patient vital signs. (376) participants completed the online quantitative survey. According to the study results, Most Healthcare Experts, (97.9%) stated that the automated wearable device is very useful, it plays an essential role in routine healthcare tasks (in early diagnosis, quarantine enforcement, and patient status monitoring), and it simplifies their routine healthcare activities. I addition, the main vital signs based on their expert opinion should include temperature (66% of participants) and oxygenation level (95% of participants). These findings are essential to any academic and industrial future efforts to develop these vital wearable systems. The future work will involve implementing the design based on the results of this study and use machine-learning algorithm to better detect the COVID-19 cases based on the monitoring of vital signs and symptoms.
Oil and Gas Pipeline Monitoring during COVID-19 Pandemic via Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Nov 15, 2021
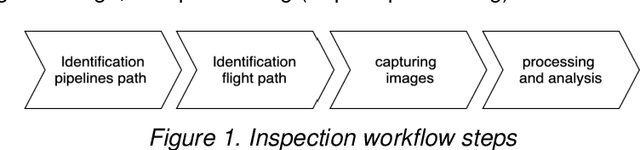
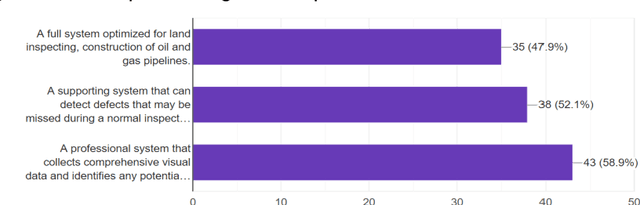
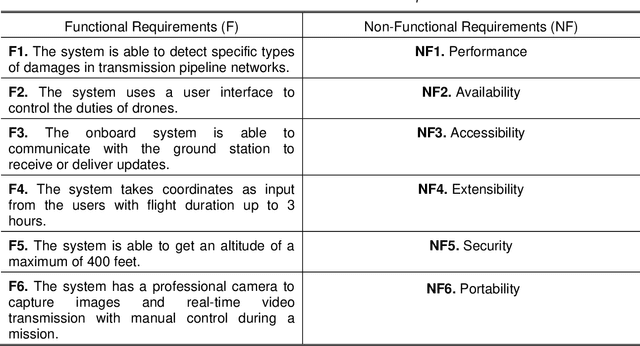
Abstract:The vast network of oil and gas transmission pipelines requires periodic monitoring for maintenance and hazard inspection to avoid equipment failure and potential accidents. The severe COVID-19 pandemic situation forced the companies to shrink the size of their teams. One risk which is faced on-site is represented by the uncontrolled release of flammable oil and gas. Among many inspection methods, the unmanned aerial vehicle system contains flexibility and stability. Unmanned aerial vehicles can transfer data in real-time, while they are doing their monitoring tasks. The current article focuses on unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with optical sensing and artificial intelligence, especially image recognition with deep learning techniques for pipeline surveillance. Unmanned aerial vehicles can be used for regular patrolling duties to identify and capture images and videos of the area of interest. Places that are hard to reach will be accessed faster, cheaper and with less risk. The current paper is based on the idea of capturing video and images of drone-based inspections, which can discover several potential hazardous problems before they become dangerous. Damage can emerge as a weakening of the cladding on the external pipe insulation. There can also be the case when the thickness of piping through external corrosion can occur. The paper describes a survey completed by experts from the oil and gas industry done for finding the functional and non-functional requirements of the proposed system.
Novel Design and Implementation of a Vehicle Controlling and Tracking System
Jan 29, 2021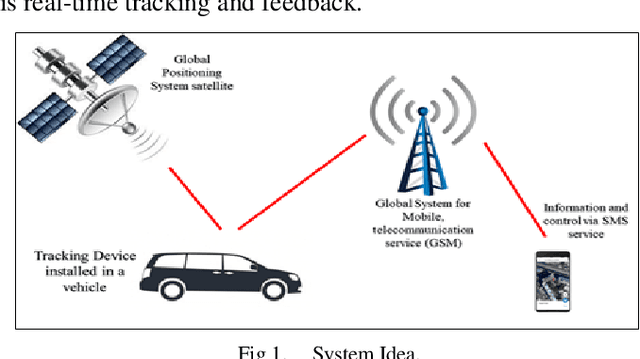

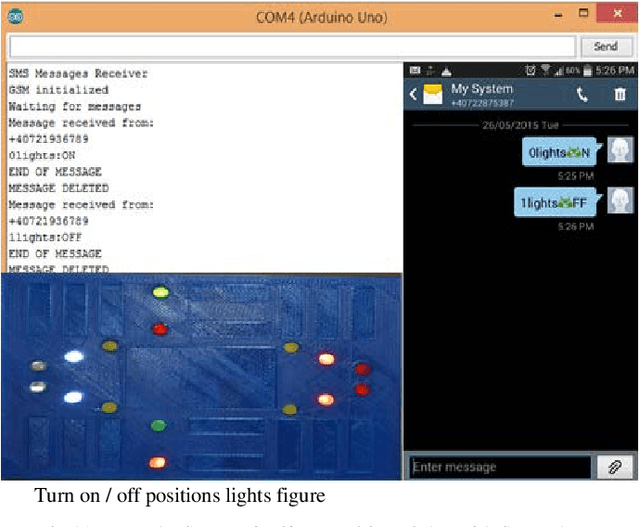
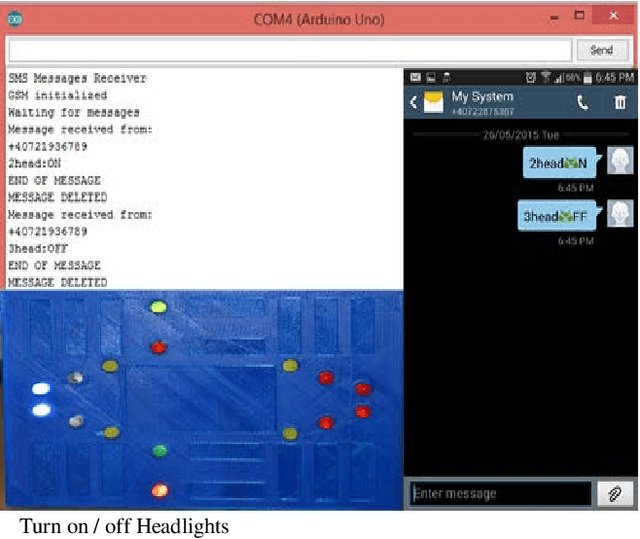
Abstract:The purpose of this project is to build a system that will quickly track the location of a stolen vehicle, thereby reducing the cost and effort of police. Moreover, the vehicle's computer system can be controlled remotely by the owners of the vehicle or police. More precisely, the goal of this work is to design a, develop remote control of the vehicle, and find the locations with Latitude (LAT) and Longitude (LONG).
Enterprise domain ontology learning from web-based corpus
Jan 29, 2021

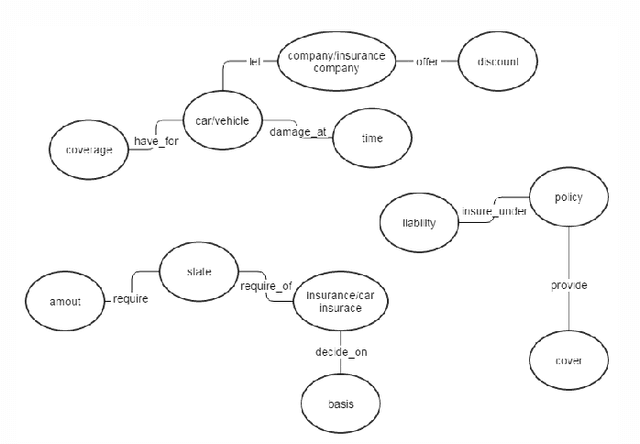

Abstract:Enterprise knowledge is a key asset in the competing and fast-changing corporate landscape. The ability to learn, store and distribute implicit and explicit knowledge can be the difference between success and failure. While enterprise knowledge management is a well-defined research domain, current implementations lack orientation towards small and medium enterprise. We propose a semantic search engine for relevant documents in an enterprise, based on automatic generated domain ontologies. In this paper we focus on the component for ontology learning and population.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge