Indu Manickam
Solving High-Dimensional Inverse Problems with Auxiliary Uncertainty via Operator Learning with Limited Data
Mar 20, 2023Abstract:In complex large-scale systems such as climate, important effects are caused by a combination of confounding processes that are not fully observable. The identification of sources from observations of system state is vital for attribution and prediction, which inform critical policy decisions. The difficulty of these types of inverse problems lies in the inability to isolate sources and the cost of simulating computational models. Surrogate models may enable the many-query algorithms required for source identification, but data challenges arise from high dimensionality of the state and source, limited ensembles of costly model simulations to train a surrogate model, and few and potentially noisy state observations for inversion due to measurement limitations. The influence of auxiliary processes adds an additional layer of uncertainty that further confounds source identification. We introduce a framework based on (1) calibrating deep neural network surrogates to the flow maps provided by an ensemble of simulations obtained by varying sources, and (2) using these surrogates in a Bayesian framework to identify sources from observations via optimization. Focusing on an atmospheric dispersion exemplar, we find that the expressive and computationally efficient nature of the deep neural network operator surrogates in appropriately reduced dimension allows for source identification with uncertainty quantification using limited data. Introducing a variable wind field as an auxiliary process, we find that a Bayesian approximation error approach is essential for reliable source inversion when uncertainty due to wind stresses the algorithm.
Error-in-variables modelling for operator learning
Apr 22, 2022
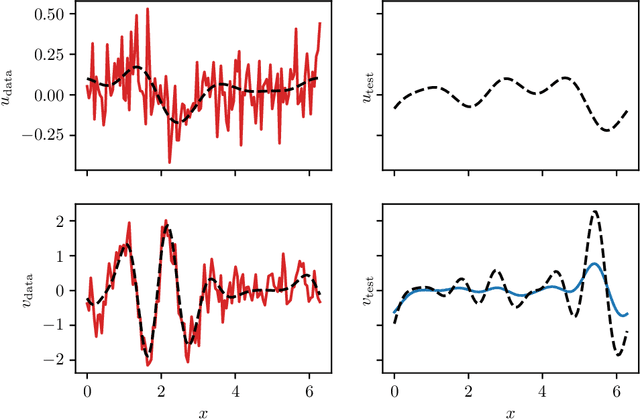

Abstract:Deep operator learning has emerged as a promising tool for reduced-order modelling and PDE model discovery. Leveraging the expressive power of deep neural networks, especially in high dimensions, such methods learn the mapping between functional state variables. While proposed methods have assumed noise only in the dependent variables, experimental and numerical data for operator learning typically exhibit noise in the independent variables as well, since both variables represent signals that are subject to measurement error. In regression on scalar data, failure to account for noisy independent variables can lead to biased parameter estimates. With noisy independent variables, linear models fitted via ordinary least squares (OLS) will show attenuation bias, wherein the slope will be underestimated. In this work, we derive an analogue of attenuation bias for linear operator regression with white noise in both the independent and dependent variables. In the nonlinear setting, we computationally demonstrate underprediction of the action of the Burgers operator in the presence of noise in the independent variable. We propose error-in-variables (EiV) models for two operator regression methods, MOR-Physics and DeepONet, and demonstrate that these new models reduce bias in the presence of noisy independent variables for a variety of operator learning problems. Considering the Burgers operator in 1D and 2D, we demonstrate that EiV operator learning robustly recovers operators in high-noise regimes that defeat OLS operator learning. We also introduce an EiV model for time-evolving PDE discovery and show that OLS and EiV perform similarly in learning the Kuramoto-Sivashinsky evolution operator from corrupted data, suggesting that the effect of bias in OLS operator learning depends on the regularity of the target operator.
IdeoTrace: A Framework for Ideology Tracing with a Case Study on the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election
May 30, 2019



Abstract:The 2016 United States presidential election has been characterized as a period of extreme divisiveness that was exacerbated on social media by the influence of fake news, trolls, and social bots. However, the extent to which the public became more polarized in response to these influences over the course of the election is not well understood. In this paper we propose IdeoTrace, a framework for (i) jointly estimating the ideology of social media users and news websites and (ii) tracing changes in user ideology over time. We apply this framework to the last two months of the election period for a group of 47508 Twitter users and demonstrate that both liberal and conservative users became more polarized over time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge