Igor Bogoslavskyi
System Design of the Ultra Mobility Vehicle: A Driving, Balancing, and Jumping Bicycle Robot
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:Trials cyclists and mountain bike riders can hop, jump, balance, and drive on one or both wheels. This versatility allows them to achieve speed and energy-efficiency on smooth terrain and agility over rough terrain. Inspired by these athletes, we present the design and control of a robotic platform, Ultra Mobility Vehicle (UMV), which combines a bicycle and a reaction mass to move dynamically with minimal actuated degrees of freedom. We employ a simulation-driven design optimization process to synthesize a spatial linkage topology with a focus on vertical jump height and momentum-based balancing on a single wheel contact. Using a constrained Reinforcement Learning (RL) framework, we demonstrate zero-shot transfer of diverse athletic behaviors, including track-stands, jumps, wheelies, rear wheel hopping, and front flips. This 23.5 kg robot is capable of high speeds (8 m/s) and jumping on and over large obstacles (1 m tall, or 130% of the robot's nominal height).
Fast and Robust Normal Estimation for Sparse LiDAR Scans
Apr 22, 2024Abstract:Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology has proven to be an important part of many robotics systems. Surface normals estimated from LiDAR data are commonly used for a variety of tasks in such systems. As most of the today's mechanical LiDAR sensors produce sparse data, estimating normals from a single scan in a robust manner poses difficulties. In this paper, we address the problem of estimating normals for sparse LiDAR data avoiding the typical issues of smoothing out the normals in high curvature areas. Mechanical LiDARs rotate a set of rigidly mounted lasers. One firing of such a set of lasers produces an array of points where each point's neighbor is known due to the known firing pattern of the scanner. We use this knowledge to connect these points to their neighbors and label them using the angles of the lines connecting them. When estimating normals at these points, we only consider points with the same label as neighbors. This allows us to avoid estimating normals in high curvature areas. We evaluate our approach on various data, both self-recorded and publicly available, acquired using various sparse LiDAR sensors. We show that using our method for normal estimation leads to normals that are more robust in areas with high curvature which leads to maps of higher quality. We also show that our method only incurs a constant factor runtime overhead with respect to a lightweight baseline normal estimation procedure and is therefore suited for operation in computationally demanding environments.
A General Framework for Flexible Multi-Cue Photometric Point Cloud Registration
Sep 13, 2017
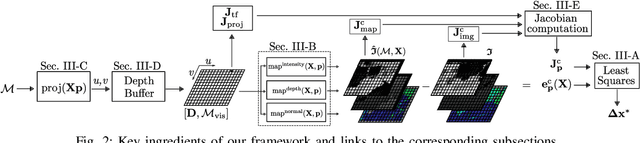

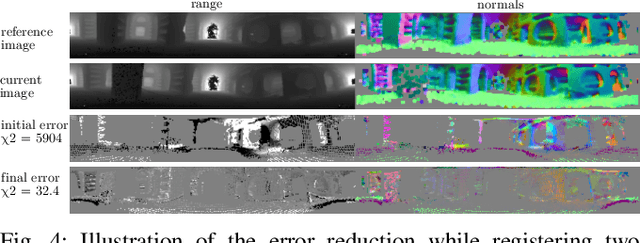
Abstract:The ability to build maps is a key functionality for the majority of mobile robots. A central ingredient to most mapping systems is the registration or alignment of the recorded sensor data. In this paper, we present a general methodology for photometric registration that can deal with multiple different cues. We provide examples for registering RGBD as well as 3D LIDAR data. In contrast to popular point cloud registration approaches such as ICP our method does not rely on explicit data association and exploits multiple modalities such as raw range and image data streams. Color, depth, and normal information are handled in an uniform manner and the registration is obtained by minimizing the pixel-wise difference between two multi-channel images. We developed a flexible and general framework and implemented our approach inside that framework. We also released our implementation as open source C++ code. The experiments show that our approach allows for an accurate registration of the sensor data without requiring an explicit data association or model-specific adaptations to datasets or sensors. Our approach exploits the different cues in a natural and consistent way and the registration can be done at framerate for a typical range or imaging sensor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge