Ibuki Kuroyanagi
Improving Anomalous Sound Detection through Pseudo-anomalous Set Selection and Pseudo-label Utilization under Unlabeled Conditions
May 25, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses performance degradation in anomalous sound detection (ASD) when neither sufficiently similar machine data nor operational state labels are available. We present an integrated pipeline that combines three complementary components derived from prior work and extends them to the unlabeled ASD setting. First, we adapt an anomaly score based selector to curate external audio data resembling the normal sounds of the target machine. Second, we utilize triplet learning to assign pseudo-labels to unlabeled data, enabling finer classification of operational sounds and detection of subtle anomalies. Third, we employ iterative training to refine both the pseudo-anomalous set selection and pseudo-label assignment, progressively improving detection accuracy. Experiments on the DCASE2022-2024 Task 2 datasets demonstrate that, in unlabeled settings, our approach achieves an average AUC increase of over 6.6 points compared to conventional methods. In labeled settings, incorporating external data from the pseudo-anomalous set further boosts performance. These results highlight the practicality and robustness of our methods in scenarios with scarce machine data and labels, facilitating ASD deployment across diverse industrial settings with minimal annotation effort.
Self-supervised learning method using multiple sampling strategies for general-purpose audio representation
May 25, 2025


Abstract:We propose a self-supervised learning method using multiple sampling strategies to obtain general-purpose audio representation. Multiple sampling strategies are used in the proposed method to construct contrastive losses from different perspectives and learn representations based on them. In this study, in addition to the widely used clip-level sampling strategy, we introduce two new strategies, a frame-level strategy and a task-specific strategy. The proposed multiple strategies improve the performance of frame-level classification and other tasks like pitch detection, which are not the focus of the conventional single clip-level sampling strategy. We pre-trained the method on a subset of Audioset and applied it to a downstream task with frozen weights. The proposed method improved clip classification, sound event detection, and pitch detection performance by 25%, 20%, and 3.6%.
Serial-OE: Anomalous sound detection based on serial method with outlier exposure capable of using small amounts of anomalous data for training
May 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce Serial-OE, a new approach to anomalous sound detection (ASD) that leverages small amounts of anomalous data to improve the performance. Conventional ASD methods rely primarily on the modeling of normal data, due to the cost of collecting anomalous data from various possible types of equipment breakdowns. Our method improves upon existing ASD systems by implementing an outlier exposure framework that utilizes normal and pseudo-anomalous data for training, with the capability to also use small amounts of real anomalous data. A comprehensive evaluation using the DCASE2020 Task2 dataset shows that our method outperforms state-of-the-art ASD models. We also investigate the impact on performance of using a small amount of anomalous data during training, of using data without machine ID information, and of using contaminated training data. Our experimental results reveal the potential of using a very limited amount of anomalous data during training to address the limitations of existing methods using only normal data for training due to the scarcity of anomalous data. This study contributes to the field by presenting a method that can be dynamically adapted to include anomalous data during the operational phase of an ASD system, paving the way for more accurate ASD.
Improvements of Discriminative Feature Space Training for Anomalous Sound Detection in Unlabeled Conditions
Sep 14, 2024Abstract:In anomalous sound detection, the discriminative method has demonstrated superior performance. This approach constructs a discriminative feature space through the classification of the meta-information labels for normal sounds. This feature space reflects the differences in machine sounds and effectively captures anomalous sounds. However, its performance significantly degrades when the meta-information labels are missing. In this paper, we improve the performance of a discriminative method under unlabeled conditions by two approaches. First, we enhance the feature extractor to perform better under unlabeled conditions. Our enhanced feature extractor utilizes multi-resolution spectrograms with a new training strategy. Second, we propose various pseudo-labeling methods to effectively train the feature extractor. The experimental evaluations show that the proposed feature extractor and pseudo-labeling methods significantly improve performance under unlabeled conditions.
Improvement of Serial Approach to Anomalous Sound Detection by Incorporating Two Binary Cross-Entropies for Outlier Exposure
Jun 13, 2022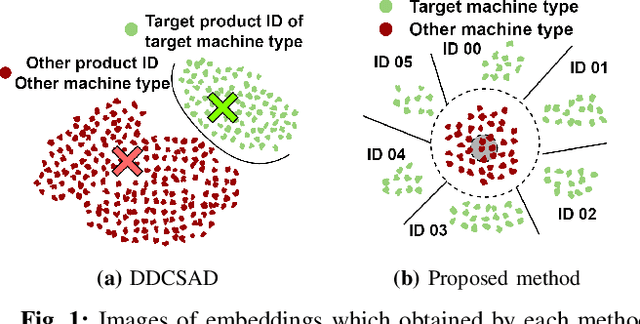
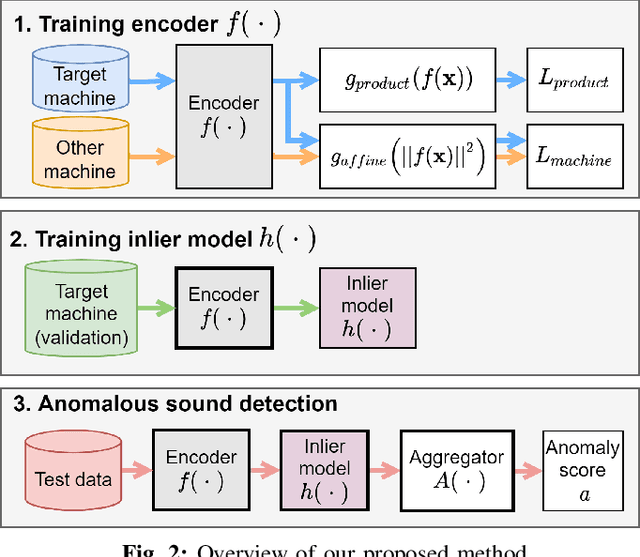
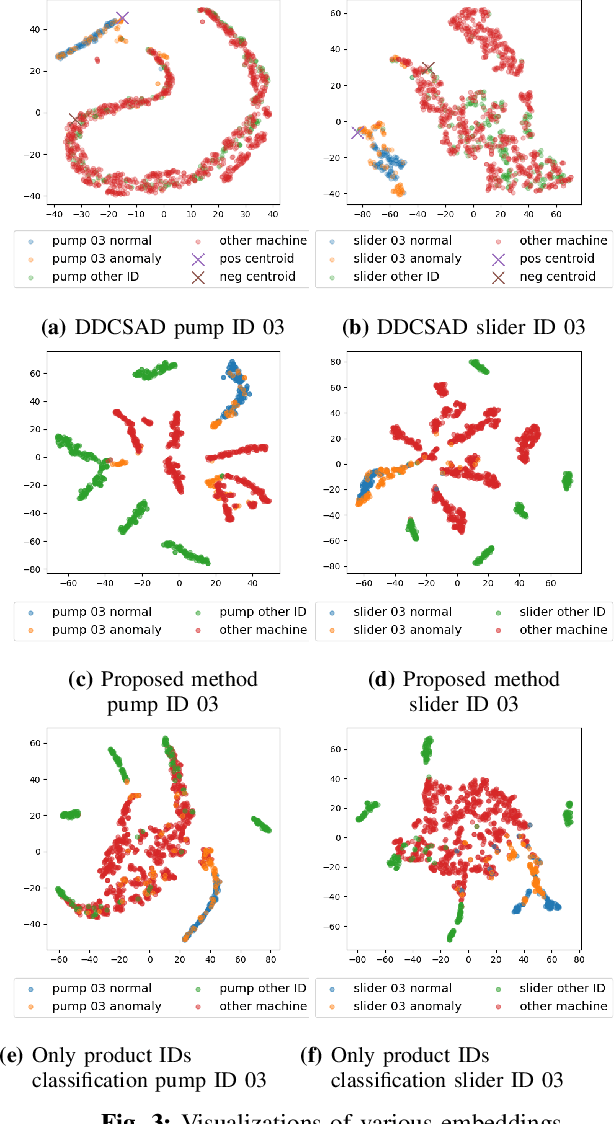
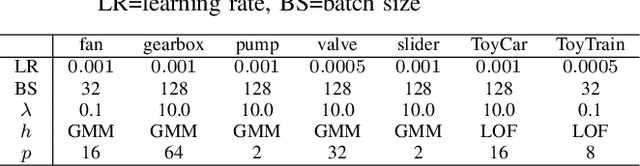
Abstract:Anomalous sound detection systems must detect unknown, atypical sounds using only normal audio data. Conventional methods use the serial method, a combination of outlier exposure (OE), which classifies normal and pseudo-anomalous data and obtains embedding, and inlier modeling (IM), which models the probability distribution of the embedding. Although the serial method shows high performance due to the powerful feature extraction of OE and the robustness of IM, OE still has a problem that doesn't work well when the normal and pseudo-anomalous data are too similar or too different. To explicitly distinguish these data, the proposed method uses multi-task learning of two binary cross-entropies when training OE. The first is a loss that classifies the sound of the target machine to which product it is emitted from, which deals with the case where the normal data and the pseudo-anomalous data are too similar. The second is a loss that identifies whether the sound is emitted from the target machine or not, which deals with the case where the normal data and the pseudo-anomalous data are too different. We perform our experiments with DCASE 2021 Task~2 dataset. Our proposed single-model method outperforms the top-ranked method, which combines multiple models, by 2.1% in AUC.
Anomalous Sound Detection Using a Binary Classification Model and Class Centroids
Jun 11, 2021


Abstract:An anomalous sound detection system to detect unknown anomalous sounds usually needs to be built using only normal sound data. Moreover, it is desirable to improve the system by effectively using a small amount of anomalous sound data, which will be accumulated through the system's operation. As one of the methods to meet these requirements, we focus on a binary classification model that is developed by using not only normal data but also outlier data in the other domains as pseudo-anomalous sound data, which can be easily updated by using anomalous data. In this paper, we implement a new loss function based on metric learning to learn the distance relationship from each class centroid in feature space for the binary classification model. The proposed multi-task learning of the binary classification and the metric learning makes it possible to build the feature space where the within-class variance is minimized and the between-class variance is maximized while keeping normal and anomalous classes linearly separable. We also investigate the effectiveness of additionally using anomalous sound data for further improving the binary classification model. Our results showed that multi-task learning using binary classification and metric learning to consider the distance from each class centroid in the feature space is effective, and performance can be significantly improved by using even a small amount of anomalous data during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge