Ibrahim Yildirim
Flip-KLJN: Random Resistance Flipping for Noise-Driven Secure Communication
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:The information-theoretically (unconditionally) secure Kirchhoff-law-Johnson-noise (KLJN) bit exchange protocol uses two identical resistor pairs with high (H) and low (L) resistance values, driven by Gaussian noise generators emulating Johnson noise with a high common temperature. The resulting mean-square noise voltage on the wire connecting Alice and Bob has three levels: low (L/L), intermediate (H/L or L/H), and high (H/H), and secure key sharing is achieved at the intermediate level (L/H or H/L). This paper introduces the Flip-KLJN scheme, where a pre-agreed intermediate level, such as H/L, triggers a flip of the bit map value during the bit exchange period. For Eve, the bit map flips appear random. Thus, the formerly discarded H/H and L/L situations can also have a pre-agreed bit value mapping, which flips together with the original bit mapping. Thus, Flip-KLJN doubles the key rate and ensures that all three levels on the wire are indistinguishable for Eve. Bit error probabilities are addressed through analytic calculations and computer simulations.
Angular-Based Hybrid Beamforming for Wideband THz Massive MIMO Systems: Mitigating Beam Split by Leveraging Angular Spread
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Beam split is a critical challenge in wideband THz massive MIMO systems, arising from frequency-dependent beam misalignment that degrades communication performance, particularly in scenarios with narrow beamwidths and large arrays. This work proposes an angular-based hybrid beamforming framework that leverages angular spread to mitigate the beam split effect. Instead of relying on precise angular spread modeling, we utilize coarse angular information to guide the design of subcarrier-specific beams, effectively reducing misalignment across subcarriers. By broadening the effective beamwidth through angular spread, the proposed method enhances user coverage and alleviates beam split without requiring complex time-delay units or hardware-intensive solutions. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves significant improvements in spectral efficiency and beamforming accuracy while maintaining low computational and hardware complexity. This work provides a practical and efficient solution for addressing beam split in next-generation wideband THz communication systems.
Spider RIS: Mobilizing Intelligent Surfaces for Enhanced Wireless Communications
May 04, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we introduce Spider RIS technology, which offers an innovative solution to the challenges encountered in movable antennas (MAs) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-enabled communication systems. By combining the dynamic adaptation capability of MAs and the flexible location advantages of UAVs, this technology offers a dynamic and movable RIS, which can flexibly optimize physical locations within the two-dimensional movement platform. Spider RIS aims to enhance the communication efficiency and reliability of wireless networks, particularly in obstructive environments, by elevating the signal quality and achievable rate. The motivation of Spider RIS is based on the ability to fully exploit the spatial variability of wireless channels and maximize channel capacity even with a limited number of reflecting elements by overcoming the limitations of traditional fixed RIS and energy-intensive UAV systems. Considering the geometry-based millimeter wave channel model, we present the design of a three-stage angular-based hybrid beamforming system empowered by Spider RIS: First, analog beamformers are designed using angular information, followed by the generation of digital precoder/combiner based on the effective channel observed from baseband stage. Subsequently, the joint dynamic positioning with phase shift design of the Spider RIS is optimized using particle swarm optimization, maximizing the achievable rate of the systems.
Plug-In RIS: A Novel Approach to Fully Passive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Nov 16, 2023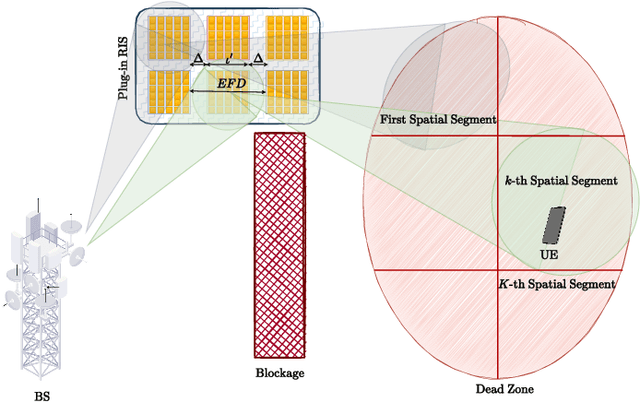
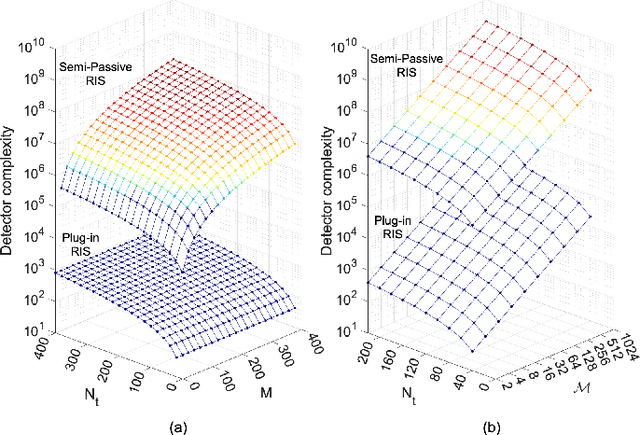
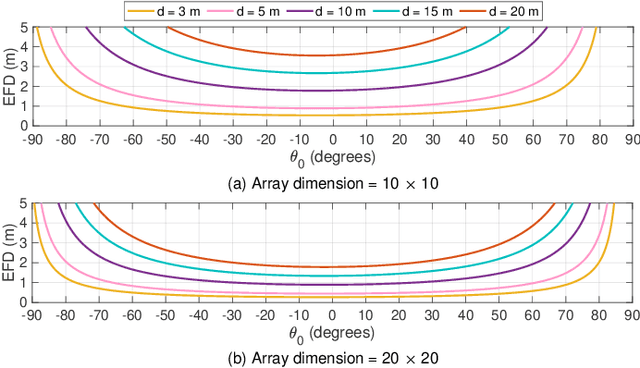
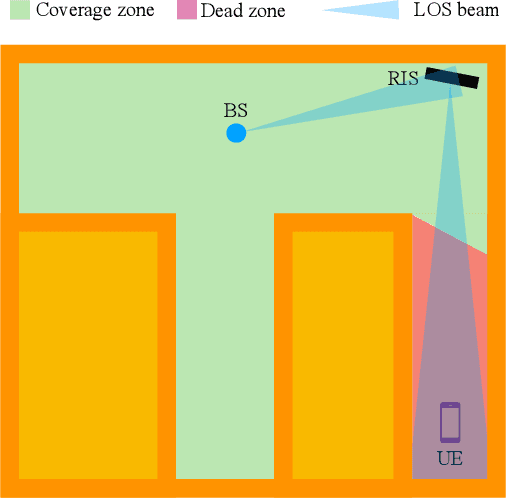
Abstract:This paper presents a promising design concept for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), named plug-in RIS, wherein the RIS is plugged into an appropriate position in the environment, adjusted once according to the location of both base station and blocked region, and operates with fixed beams to enhance the system performance. The plug-in RIS is a novel system design, streamlining RIS-assisted millimeter-wave (mmWave) communication without requiring decoupling two parts of the end-to-end channel, traditional control signal transmission, and online RIS configuration. In plug-in RIS-aided transmission, the transmitter efficiently activates specific regions of the divided large RIS by employing hybrid beamforming techniques, each with predetermined phase adjustments tailored to reflect signals to desired user locations. This user-centric approach enhances connectivity and overall user experience by dynamically illuminating the targeted user based on location. By introducing plug-in RIS's theoretical framework, design principles, and performance evaluation, we demonstrate its potential to revolutionize mmWave communications in limited channel state information (CSI) scenarios. Simulation results illustrate that plug-in RIS provides power/cost-efficient solutions to overcome blockage in the mmWave communication system and a striking convergence in average bit error rate and achievable rate performance with traditional full CSI-enabled RIS solutions.
Unleashing the Potential of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces in Martian Communication
Aug 10, 2023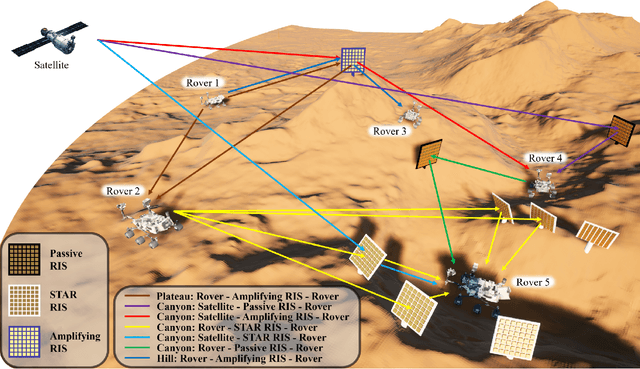
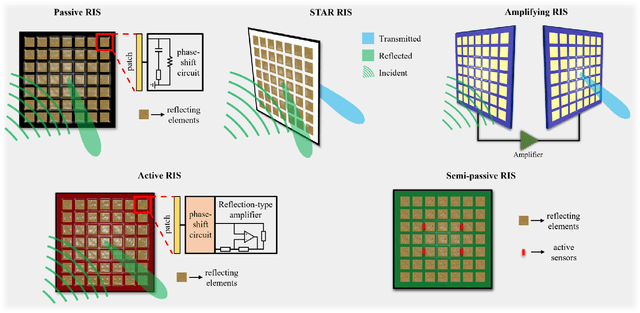
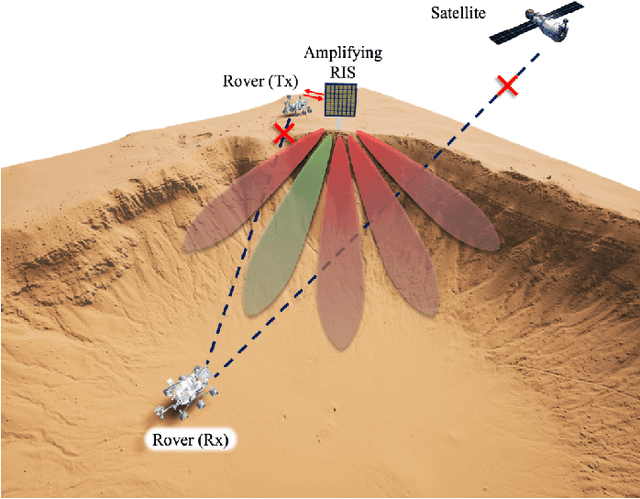
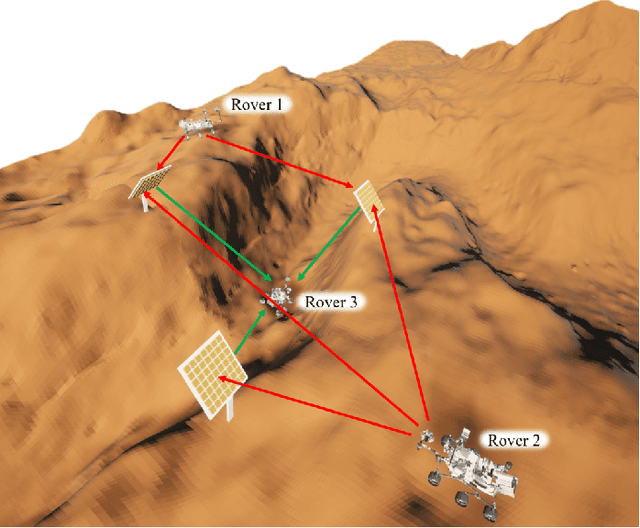
Abstract:Space exploration has witnessed a steady increase since the 1960s, with Mars playing a significant role in our quest for further knowledge. As the ambition to colonize Mars becomes a reality through the collaboration of private companies and space agencies, the need for reliable and robust communication infrastructures in the Martian environment becomes paramount. In this context, reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-empowered communication emerges as a promising technology to enhance the coverage and improve the communication quality. By considering various Martian scenarios such as canyons, craters, mountains, and plateaus, this article explores of the potential of RISs in increasing the coverage in Martian environments, thereby enabling future Mars missions to be more robust and reliable. The article also investigates the application of RIS-assisted localization in both line-of-sight (LOS) and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios, presenting a general framework for accurate user angle estimation in challenging Martian conditions. The findings and presented framework of this article provide a promising research direction for integrating RISs in deep space communication as well as paving the way for future improvements in interplanetary communication networks.
Practical Implementation of RIS-Aided Spectrum Sensing: A Deep Learning-Based Solution
Jul 27, 2023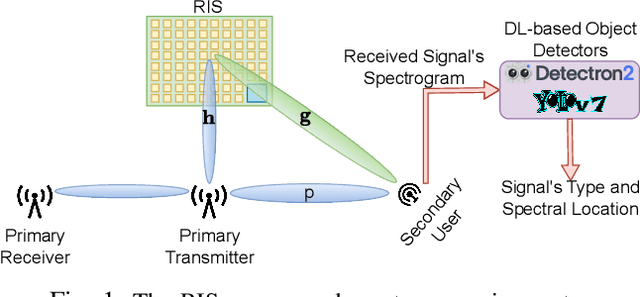
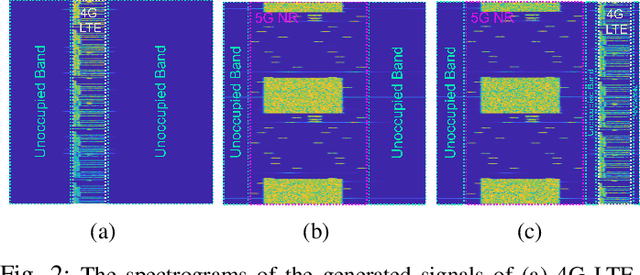
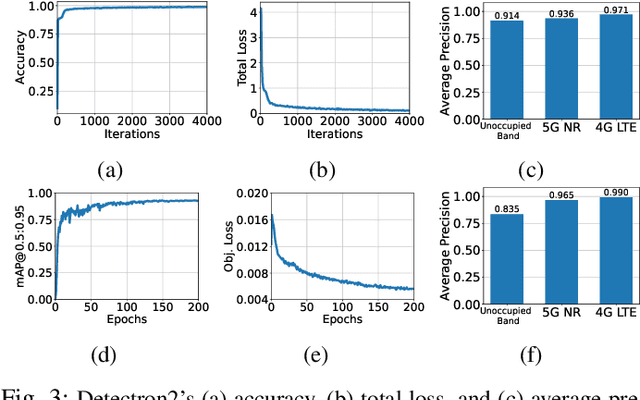
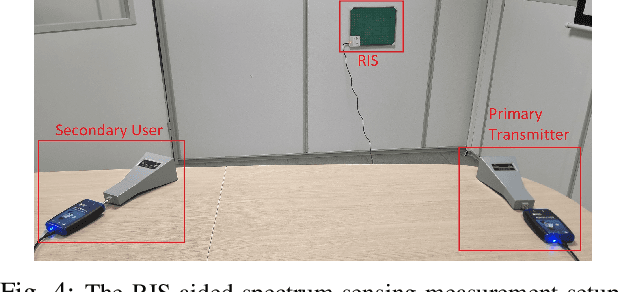
Abstract:This paper presents reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided deep learning (DL)-based spectrum sensing for next-generation cognitive radios. To that end, the secondary user (SU) monitors the primary transmitter (PT) signal, where the RIS plays a pivotal role in increasing the strength of the PT signal at the SU. The spectrograms of the synthesized dataset, including the 4G LTE and 5G NR signals, are mapped to images utilized for training the state-of-art object detection approaches, namely Detectron2 and YOLOv7. By conducting extensive experiments using a real RIS prototype, we demonstrate that the RIS can consistently and significantly improve the performance of the DL detectors to identify the PT signal type along with its time and frequency utilization. This study also paves the way for optimizing spectrum utilization through RIS-assisted CR application in next-generation wireless communication systems.
Antenna Array Structures for Enhanced Cluster Index Modulation
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:This paper investigates the effect of various antenna array structures, i.e., uniform linear array (ULA), uniform rectangular array (URA), uniform circular array (UCA), and concentric circular array (CCA), on cluster index modulation (CIM) enabled massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) millimeter-wave (mmWave) communications systems. As the CIM technique indexes spatial clusters to convey additional information bits, the different radiation characteristics caused by different array structures can significantly affect system performance. By analyzing the effects of array characteristics such as radiation pattern, array directivity, half-power beam width (HPBW), and radiation side lobes on bit error rate (BER) performance, we reveal that URA achieves better error performance than its counterparts in a CIM-enabled mmWave system. We demonstrate that narrower beams alone cannot guarantee better BER performance in a CIM-based system. Instead, other radiation characteristics, especially radiation side lobes, can significantly influence system performance by entailing extra interference in the non-intended directions. Illustrative results show that URA owes its superiority to its lower side lobes. We also propose an algorithm to implement fixed phase shifters (FPS) as a hardware-efficient (HE) analog network structure (beamformer/combiner) to reduce cost and energy consumption in mmWave systems and investigate the effect of a non-ideal analog network on the BER performance for different array structures. It is demonstrated that HE systems with a few FPSs can achieve similar BER performance compared to the optimum (OP) analog network structure.
Cluster Index Modulation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted mmWave Massive MIMO
Feb 08, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose a transmission mechanism for a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted millimeter wave (mmWave) system based on cluster index modulation (CIM), named best-gain optimized cluster selection CIM (BGCS-CIM). The proposed BGCS-CIM scheme considers effective cluster power gain and spatial diversity gain obtained by the additional paths within the indexed cluster to construct an efficient codebook. We also integrate the proposed scheme into a practical system model to create a virtual path between transmitter and receiver where the direct link has been blocked. Thanks to the designed whitening filter, a closed-form expression for the upper bound on the average bit error rate (ABER) is derived and used to validate the simulation results. It has been shown that the proposed BGCS-CIM scheme outperforms the existing benchmarks thanks to its higher effective cluster gain, spatial diversity of indexed clusters, and lower inter-cluster interference.
Indoor Coverage Enhancement for RIS-Assisted Communication Systems: Practical Measurements and Efficient Grouping
Nov 14, 2022



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-empowered communications represent exciting prospects as one of the promising technologies capable of meeting the requirements of the sixth generation networks such as low-latency, reliability, and dense connectivity. However, validation of test cases and real-world experiments of RISs are imperative to their practical viability. To this end, this paper presents a physical demonstration of an RIS-assisted communication system in an indoor environment in order to enhance the coverage by increasing the received signal power. We first analyze the performance of the RIS-assisted system for a set of different locations of the receiver and observe around 10 dB improvement in the received signal power by careful RIS phase adjustments. Then, we employ an efficient codebook design for RIS configurations to adjust the RIS states on the move without feedback channels. We also investigate the impact of an efficient grouping of RIS elements, whose objective is to reduce the training time needed to find the optimal RIS configuration. In our extensive experimental measurements, we demonstrate that with the proposed grouping scheme, training time is reduced from one-half to one-eighth by sacrificing only a few dBs in received signal power.
RIS-Aided Angular-Based Hybrid Beamforming Design in mmWave Massive MIMO Systems
Aug 13, 2022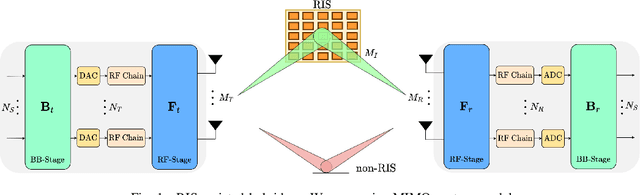
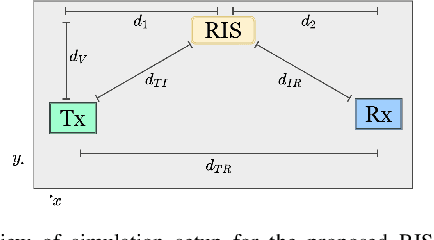
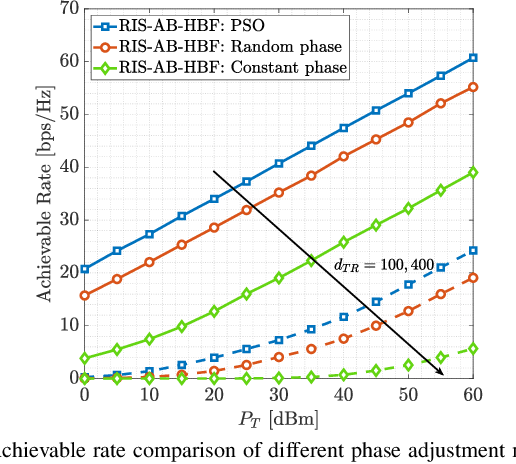
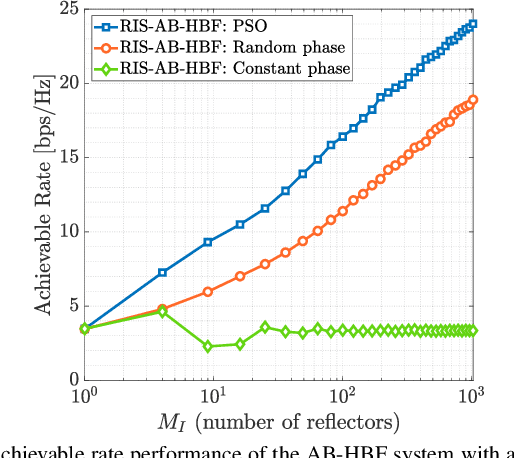
Abstract:This paper proposes a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided and angular-based hybrid beamforming (AB-HBF) technique for the millimeter wave (mmWave) massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The proposed RIS-AB-HBF architecture consists of three stages: (i) RF beamformer, (ii) baseband (BB) precoder/combiner, and (iii) RIS phase shift design. First, in order to reduce the number of RF chains and the channel estimation overhead, RF beamformers are designed based on the 3D geometry-based mmWave channel model using slow time-varying angular parameters of the channel. Second, a BB precoder/combiner is designed by exploiting the reduced-size effective channel seen from the BB stages. Then, the phase shifts of the RIS are adjusted to maximize the achievable rate of the system via the nature-inspired particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Illustrative simulation results demonstrate that the use of RISs in the AB-HBF systems has the potential to provide more promising advantages in terms of reliability and flexibility in system design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge