Huiyou Chang
Non-Local Context Encoder: Robust Biomedical Image Segmentation against Adversarial Attacks
Apr 27, 2019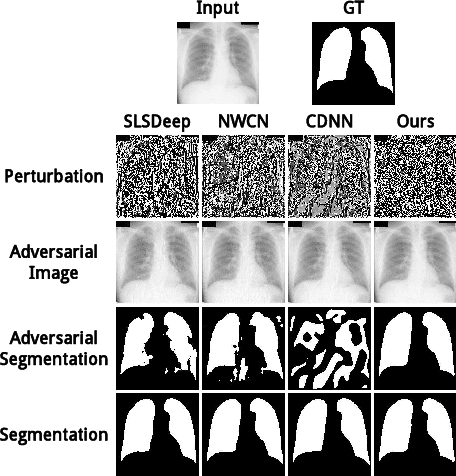
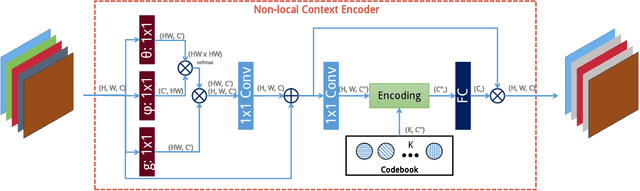
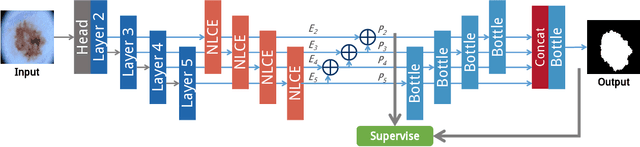
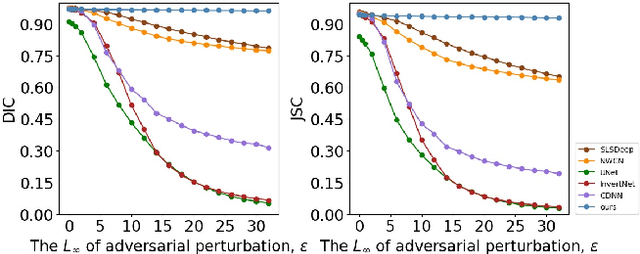
Abstract:Recent progress in biomedical image segmentation based on deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has drawn much attention. However, its vulnerability towards adversarial samples cannot be overlooked. This paper is the first one that discovers that all the CNN-based state-of-the-art biomedical image segmentation models are sensitive to adversarial perturbations. This limits the deployment of these methods in safety-critical biomedical fields. In this paper, we discover that global spatial dependencies and global contextual information in a biomedical image can be exploited to defend against adversarial attacks. To this end, non-local context encoder (NLCE) is proposed to model short- and long range spatial dependencies and encode global contexts for strengthening feature activations by channel-wise attention. The NLCE modules enhance the robustness and accuracy of the non-local context encoding network (NLCEN), which learns robust enhanced pyramid feature representations with NLCE modules, and then integrates the information across different levels. Experiments on both lung and skin lesion segmentation datasets have demonstrated that NLCEN outperforms any other state-of-the-art biomedical image segmentation methods against adversarial attacks. In addition, NLCE modules can be applied to improve the robustness of other CNN-based biomedical image segmentation methods.
Non-locally Enhanced Encoder-Decoder Network for Single Image De-raining
Aug 04, 2018
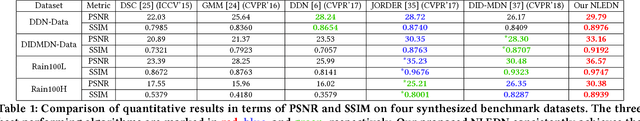
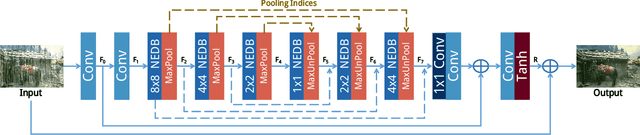
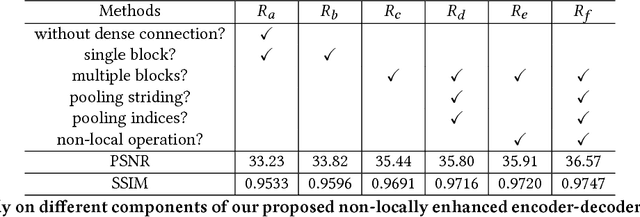
Abstract:Single image rain streaks removal has recently witnessed substantial progress due to the development of deep convolutional neural networks. However, existing deep learning based methods either focus on the entrance and exit of the network by decomposing the input image into high and low frequency information and employing residual learning to reduce the mapping range, or focus on the introduction of cascaded learning scheme to decompose the task of rain streaks removal into multi-stages. These methods treat the convolutional neural network as an encapsulated end-to-end mapping module without deepening into the rationality and superiority of neural network design. In this paper, we delve into an effective end-to-end neural network structure for stronger feature expression and spatial correlation learning. Specifically, we propose a non-locally enhanced encoder-decoder network framework, which consists of a pooling indices embedded encoder-decoder network to efficiently learn increasingly abstract feature representation for more accurate rain streaks modeling while perfectly preserving the image detail. The proposed encoder-decoder framework is composed of a series of non-locally enhanced dense blocks that are designed to not only fully exploit hierarchical features from all the convolutional layers but also well capture the long-distance dependencies and structural information. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively remove rain-streaks on rainy image of various densities while well preserving the image details, which achieves significant improvements over the recent state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge