Huiying Liu
Large Language Model Aided QoS Prediction for Service Recommendation
Aug 05, 2024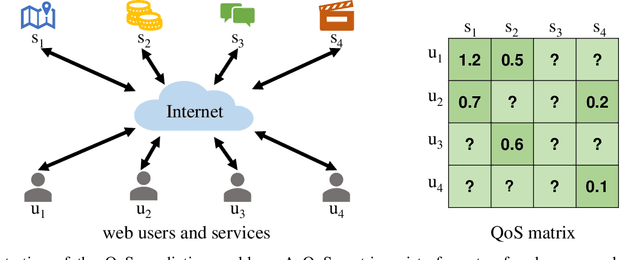
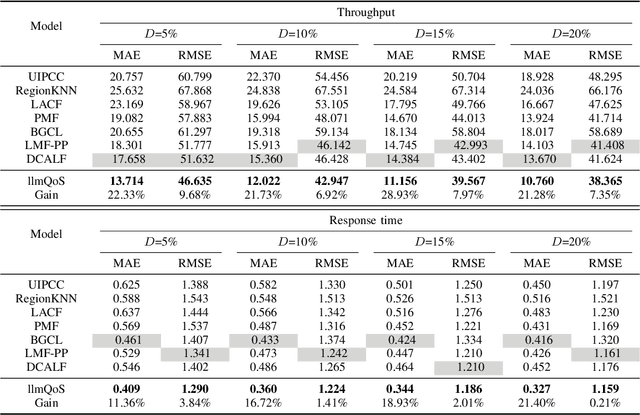
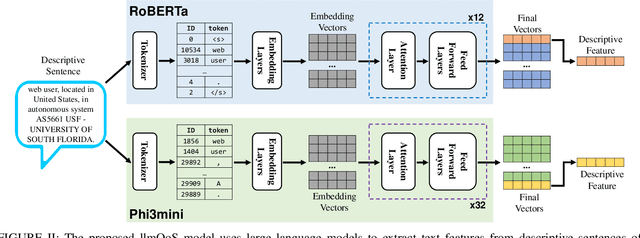
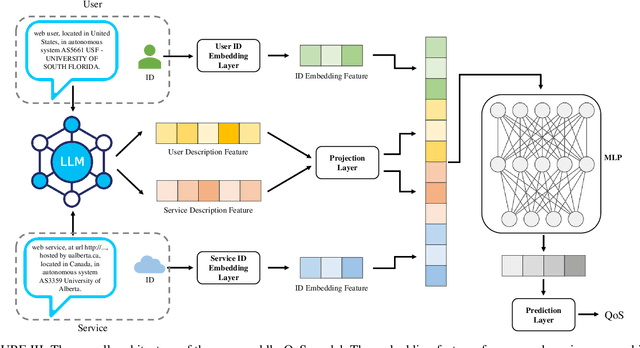
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have seen rapid improvement in the recent years, and are used in a wider range of applications. After being trained on large text corpus, LLMs obtain the capability of extracting rich features from textual data. Such capability is potentially useful for the web service recommendation task, where the web users and services have intrinsic attributes that can be described using natural language sentences and are useful for recommendation. In this paper, we explore the possibility and practicality of using LLMs for web service recommendation. We propose the large language model aided QoS prediction (llmQoS) model, which use LLMs to extract useful information from attributes of web users and services via descriptive sentences. This information is then used in combination with the QoS values of historical interactions of users and services, to predict QoS values for any given user-service pair. Our proposed model is shown to overcome the data sparsity issue for QoS prediction. We show that on the WSDream dataset, llmQoS outperforms comparable baseline models consistently.
Calibrate the inter-observer segmentation uncertainty via diagnosis-first principle
Aug 05, 2022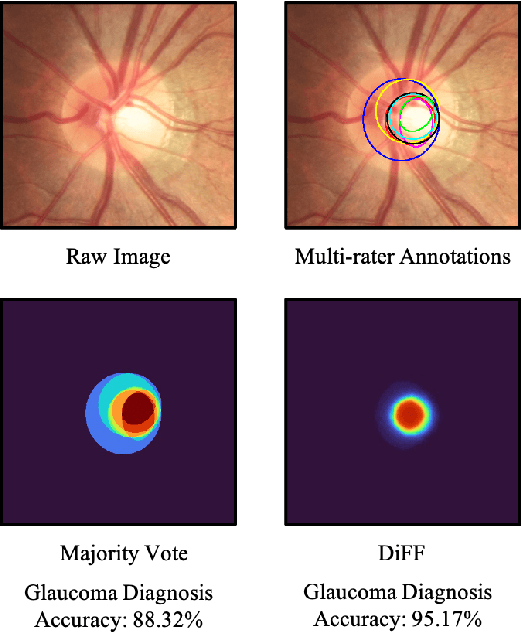
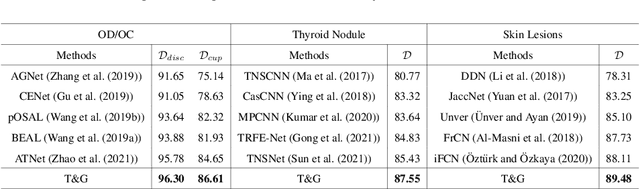
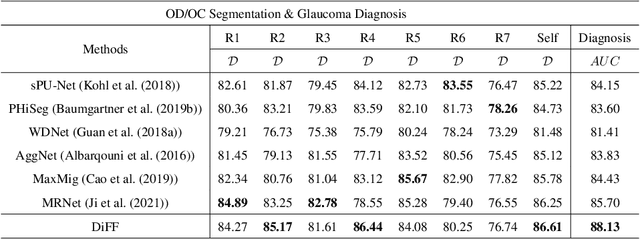
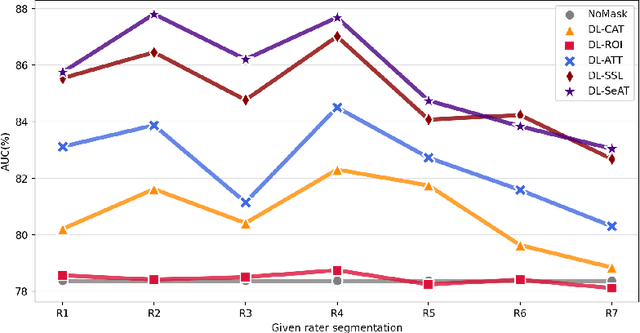
Abstract:On the medical images, many of the tissues/lesions may be ambiguous. That is why the medical segmentation is typically annotated by a group of clinical experts to mitigate the personal bias. However, this clinical routine also brings new challenges to the application of machine learning algorithms. Without a definite ground-truth, it will be difficult to train and evaluate the deep learning models. When the annotations are collected from different graders, a common choice is majority vote. However such a strategy ignores the difference between the grader expertness. In this paper, we consider the task of predicting the segmentation with the calibrated inter-observer uncertainty. We note that in clinical practice, the medical image segmentation is usually used to assist the disease diagnosis. Inspired by this observation, we propose diagnosis-first principle, which is to take disease diagnosis as the criterion to calibrate the inter-observer segmentation uncertainty. Following this idea, a framework named Diagnosis First segmentation Framework (DiFF) is proposed to estimate diagnosis-first segmentation from the raw images.Specifically, DiFF will first learn to fuse the multi-rater segmentation labels to a single ground-truth which could maximize the disease diagnosis performance. We dubbed the fused ground-truth as Diagnosis First Ground-truth (DF-GT).Then, we further propose Take and Give Modelto segment DF-GT from the raw image. We verify the effectiveness of DiFF on three different medical segmentation tasks: OD/OC segmentation on fundus images, thyroid nodule segmentation on ultrasound images, and skin lesion segmentation on dermoscopic images. Experimental results show that the proposed DiFF is able to significantly facilitate the corresponding disease diagnosis, which outperforms previous state-of-the-art multi-rater learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge