Huishu Yuan
A multimodal vision foundation model for generalizable knee pathology
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Musculoskeletal disorders represent a leading cause of global disability, creating an urgent demand for precise interpretation of medical imaging. Current artificial intelligence (AI) approaches in orthopedics predominantly rely on task-specific, supervised learning paradigms. These methods are inherently fragmented, require extensive annotated datasets, and often lack generalizability across different modalities and clinical scenarios. The development of foundation models in this field has been constrained by the scarcity of large-scale, curated, and open-source musculoskeletal datasets. To address these challenges, we introduce OrthoFoundation, a multimodal vision foundation model optimized for musculoskeletal pathology. We constructed a pre-training dataset of 1.2 million unlabeled knee X-ray and MRI images from internal and public databases. Utilizing a Dinov3 backbone, the model was trained via self-supervised contrastive learning to capture robust radiological representations. OrthoFoundation achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across 14 downstream tasks. It attained superior accuracy in X-ray osteoarthritis diagnosis and ranked first in MRI structural injury detection. The model demonstrated remarkable label efficiency, matching supervised baselines using only 50% of labeled data. Furthermore, despite being pre-trained on knee images, OrthoFoundation exhibited exceptional cross-anatomy generalization to the hip, shoulder, and ankle. OrthoFoundation represents a significant advancement toward general-purpose AI for musculoskeletal imaging. By learning fundamental, joint-agnostic radiological semantics from large-scale multimodal data, it overcomes the limitations of conventional models, which provides a robust framework for reducing annotation burdens and enhancing diagnostic accuracy in clinical practice.
Coarse-Fine View Attention Alignment-Based GAN for CT Reconstruction from Biplanar X-Rays
Aug 19, 2024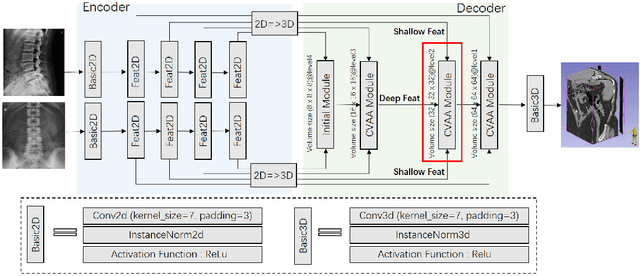
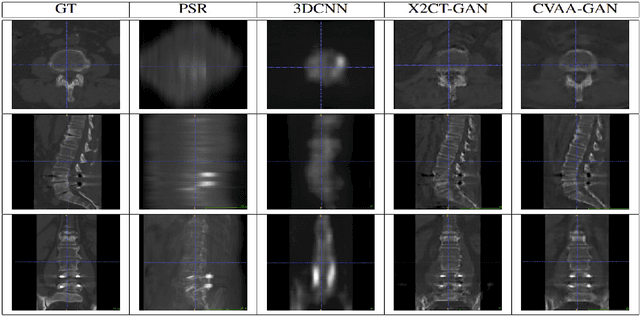
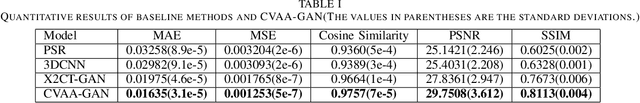
Abstract:For surgical planning and intra-operation imaging, CT reconstruction using X-ray images can potentially be an important alternative when CT imaging is not available or not feasible. In this paper, we aim to use biplanar X-rays to reconstruct a 3D CT image, because biplanar X-rays convey richer information than single-view X-rays and are more commonly used by surgeons. Different from previous studies in which the two X-ray views were treated indifferently when fusing the cross-view data, we propose a novel attention-informed coarse-to-fine cross-view fusion method to combine the features extracted from the orthogonal biplanar views. This method consists of a view attention alignment sub-module and a fine-distillation sub-module that are designed to work together to highlight the unique or complementary information from each of the views. Experiments have demonstrated the superiority of our proposed method over the SOTA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge