Huiqiang Wang
Dynamic Degradation Decomposition Network for All-in-One Image Restoration
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Currently, restoring clean images from a variety of degradation types using a single model is still a challenging task. Existing all-in-one image restoration approaches struggle with addressing complex and ambiguously defined degradation types. In this paper, we introduce a dynamic degradation decomposition network for all-in-one image restoration, named D$^3$Net. D$^3$Net achieves degradation-adaptive image restoration with guided prompt through cross-domain interaction and dynamic degradation decomposition. Concretely, in D$^3$Net, the proposed Cross-Domain Degradation Analyzer (CDDA) engages in deep interaction between frequency domain degradation characteristics and spatial domain image features to identify and model variations of different degradation types on the image manifold, generating degradation correction prompt and strategy prompt, which guide the following decomposition process. Furthermore, the prompt-based Dynamic Decomposition Mechanism (DDM) for progressive degradation decomposition, that encourages the network to adaptively select restoration strategies utilizing the two-level prompt generated by CDDA. Thanks to the synergistic cooperation between CDDA and DDM, D$^3$Net achieves superior flexibility and scalability in handling unknown degradation, while effectively reducing unnecessary computational overhead. Extensive experiments on multiple image restoration tasks demonstrate that D$^3$Net significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, especially improving PSNR by 5.47dB and 3.30dB on the SOTS-Outdoor and GoPro datasets, respectively.
Split Time Series into Patches: Rethinking Long-term Series Forecasting with Dateformer
Jul 12, 2022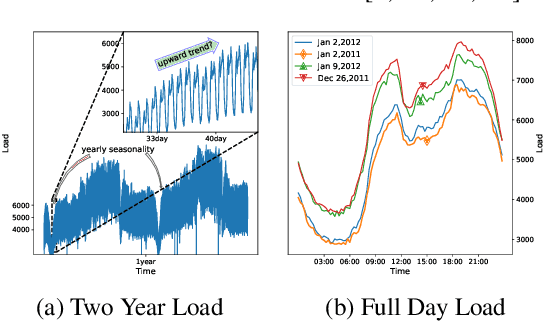
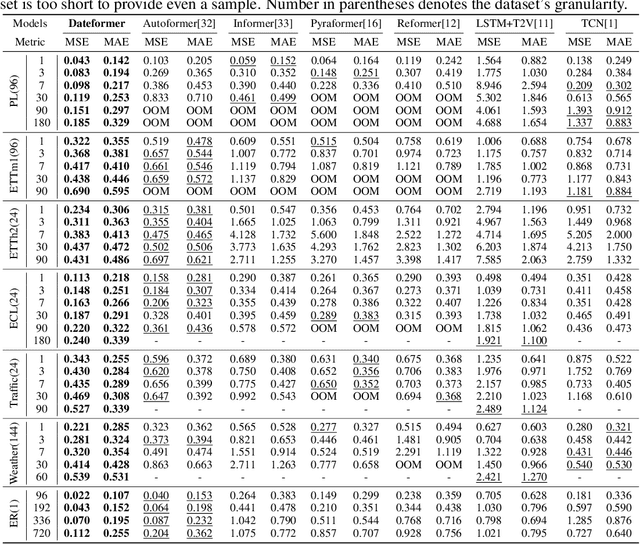

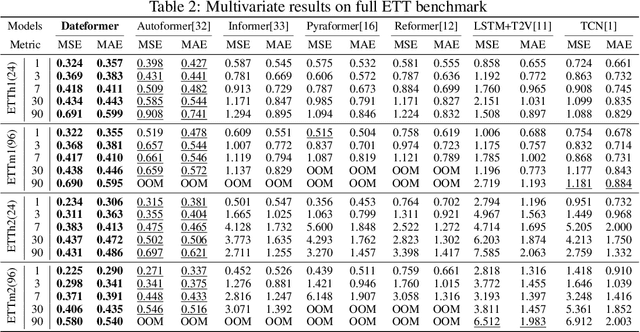
Abstract:Time is one of the most significant characteristics of time-series, yet has received insufficient attention. Prior time-series forecasting research has mainly focused on mapping a past subseries (lookback window) to a future series (forecast window), and time of series often just play an auxiliary role even completely ignored in most cases. Due to the point-wise processing within these windows, extrapolating series to longer-term future is tough in the pattern. To overcome this barrier, we propose a brand-new time-series forecasting framework named Dateformer who turns attention to modeling time instead of following the above practice. Specifically, time-series are first split into patches by day to supervise the learning of dynamic date-representations with Date Encoder Representations from Transformers (DERT). These representations are then fed into a simple decoder to produce a coarser (or global) prediction, and used to help the model seek valuable information from the lookback window to learn a refined (or local) prediction. Dateformer obtains the final result by summing the above two parts. Our empirical studies on seven benchmarks show that the time-modeling method is more efficient for long-term series forecasting compared with sequence modeling methods. Dateformer yields state-of-the-art accuracy with a 40% remarkable relative improvement, and broadens the maximum credible forecasting range to a half-yearly level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge