Hsiu-Yu Yang
Implicit Affordance Acquisition via Causal Action-Effect Modeling in the Video Domain
Dec 18, 2023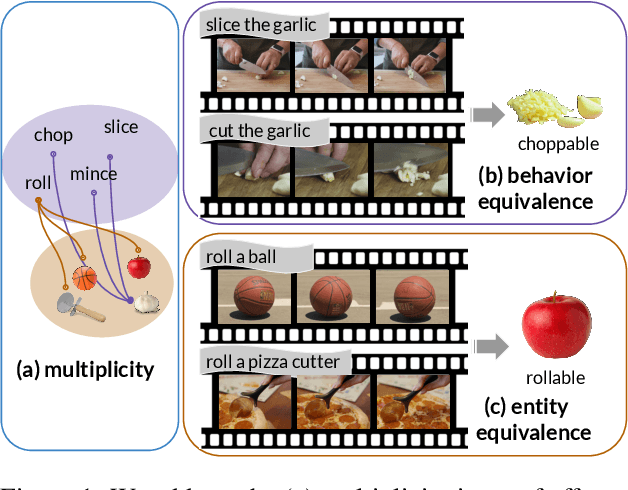
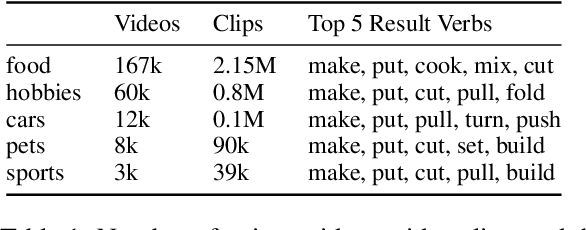

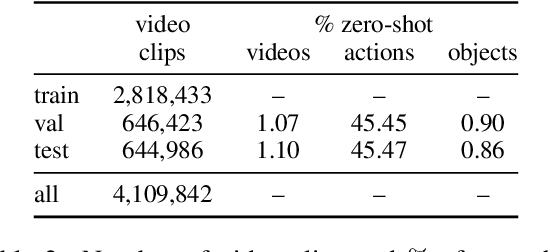
Abstract:Affordance knowledge is a fundamental aspect of commonsense knowledge. Recent findings indicate that world knowledge emerges through large-scale self-supervised pretraining, motivating our exploration of acquiring affordance knowledge from the visual domain. To this end, we augment an existing instructional video resource to create the new Causal Action-Effect (CAE) dataset and design two novel pretraining tasks -- Masked Action Modeling (MAM) and Masked Effect Modeling (MEM) -- promoting the acquisition of two affordance properties in models: behavior and entity equivalence, respectively. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods in learning affordance properties. Furthermore, we show that a model pretrained on both tasks outperforms a strong image-based visual-linguistic foundation model (FLAVA) as well as pure linguistic models on a zero-shot physical reasoning probing task.
Does External Knowledge Help Explainable Natural Language Inference? Automatic Evaluation vs. Human Ratings
Oct 13, 2021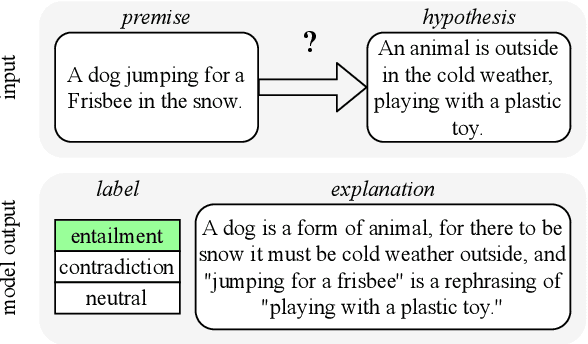
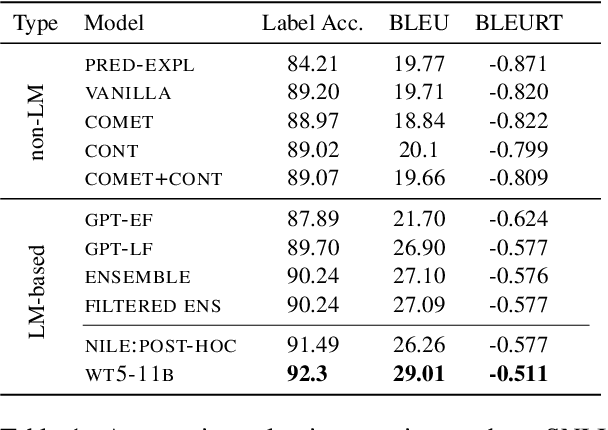
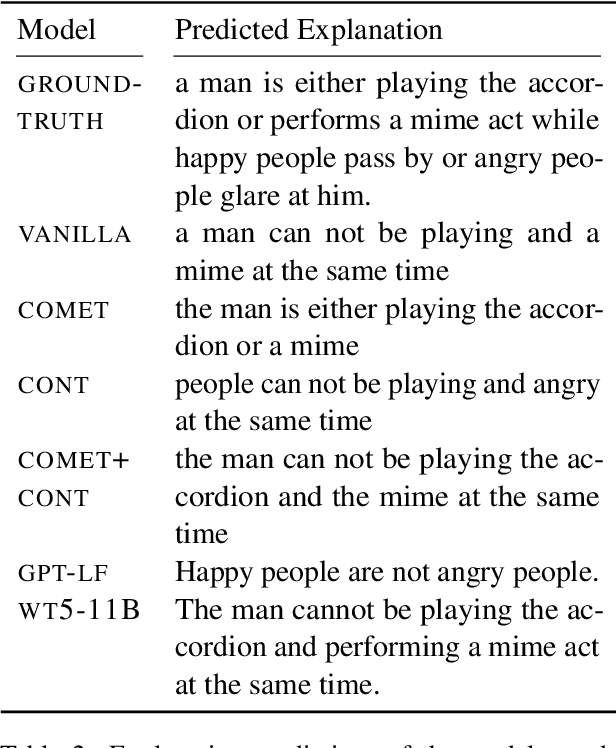
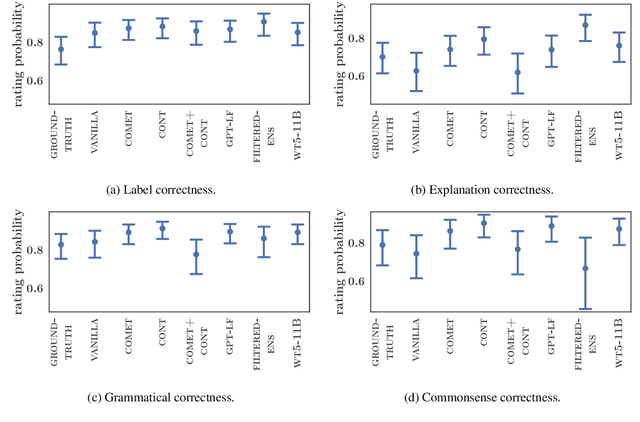
Abstract:Natural language inference (NLI) requires models to learn and apply commonsense knowledge. These reasoning abilities are particularly important for explainable NLI systems that generate a natural language explanation in addition to their label prediction. The integration of external knowledge has been shown to improve NLI systems, here we investigate whether it can also improve their explanation capabilities. For this, we investigate different sources of external knowledge and evaluate the performance of our models on in-domain data as well as on special transfer datasets that are designed to assess fine-grained reasoning capabilities. We find that different sources of knowledge have a different effect on reasoning abilities, for example, implicit knowledge stored in language models can hinder reasoning on numbers and negations. Finally, we conduct the largest and most fine-grained explainable NLI crowdsourcing study to date. It reveals that even large differences in automatic performance scores do neither reflect in human ratings of label, explanation, commonsense nor grammar correctness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge