Hrafn Loftsson
Aligning Language Models for Icelandic Legal Text Summarization
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:The integration of language models in the legal domain holds considerable promise for streamlining processes and improving efficiency in managing extensive workloads. However, the specialized terminology, nuanced language, and formal style of legal texts can present substantial challenges. This study examines whether preference-based training techniques, specifically Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback and Direct Preference Optimization, can enhance models' performance in generating Icelandic legal summaries that align with domain-specific language standards and user preferences. We compare models fine-tuned with preference training to those using conventional supervised learning. Results indicate that preference training improves the legal accuracy of generated summaries over standard fine-tuning but does not significantly enhance the overall quality of Icelandic language usage. Discrepancies between automated metrics and human evaluations further underscore the importance of qualitative assessment in developing language models for the legal domain.
* Published at NoDaLiDa 2025
SentAlign: Accurate and Scalable Sentence Alignment
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:We present SentAlign, an accurate sentence alignment tool designed to handle very large parallel document pairs. Given user-defined parameters, the alignment algorithm evaluates all possible alignment paths in fairly large documents of thousands of sentences and uses a divide-and-conquer approach to align documents containing tens of thousands of sentences. The scoring function is based on LaBSE bilingual sentence representations. SentAlign outperforms five other sentence alignment tools when evaluated on two different evaluation sets, German-French and English-Icelandic, and on a downstream machine translation task.
Building an Icelandic Entity Linking Corpus
Jun 10, 2022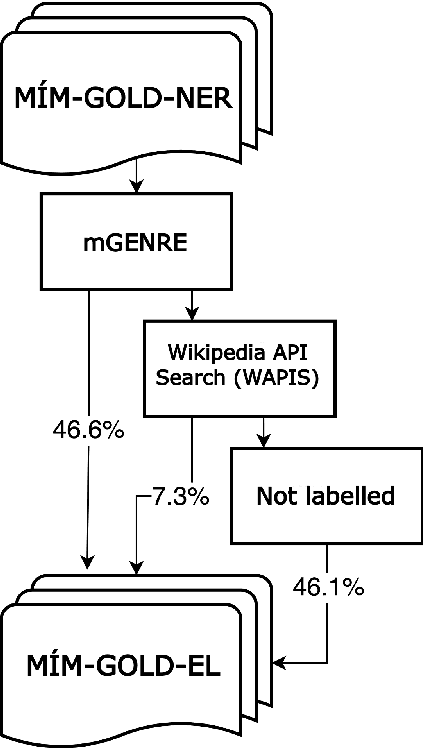
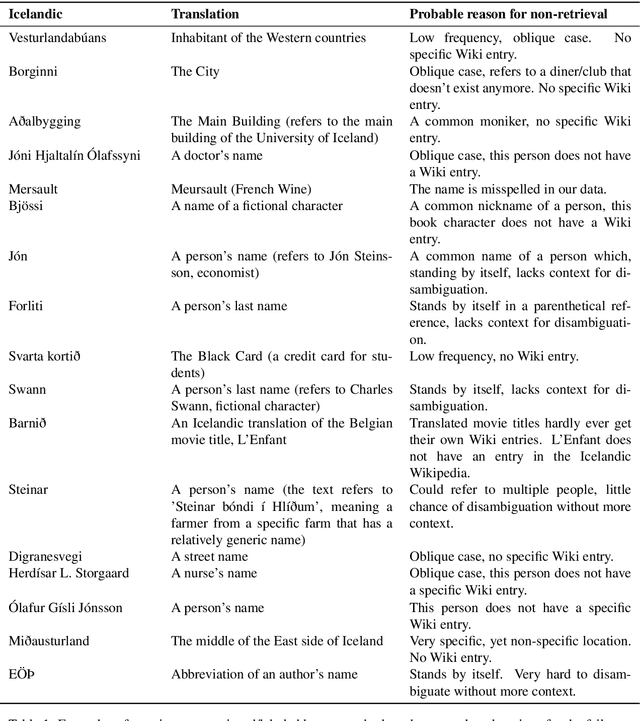
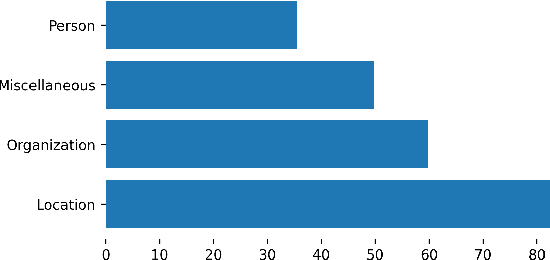
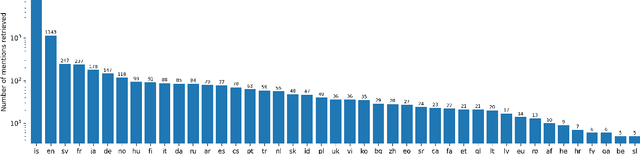
Abstract:In this paper, we present the first Entity Linking corpus for Icelandic. We describe our approach of using a multilingual entity linking model (mGENRE) in combination with Wikipedia API Search (WAPIS) to label our data and compare it to an approach using WAPIS only. We find that our combined method reaches 53.9% coverage on our corpus, compared to 30.9% using only WAPIS. We analyze our results and explain the value of using a multilingual system when working with Icelandic. Additionally, we analyze the data that remain unlabeled, identify patterns and discuss why they may be more difficult to annotate.
Semi-self-supervised Automated ICD Coding
May 20, 2022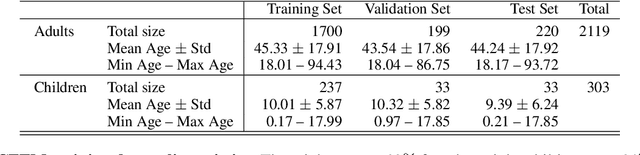
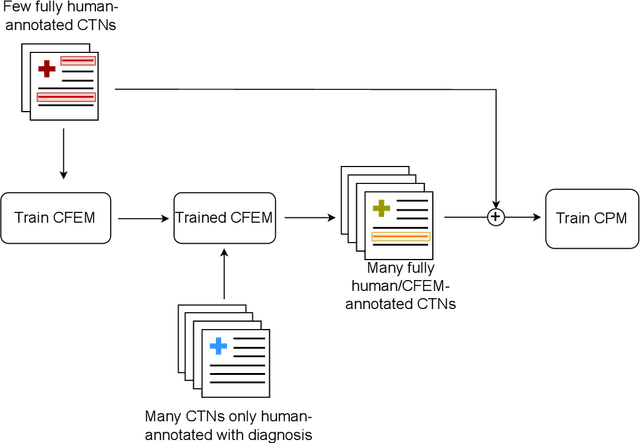
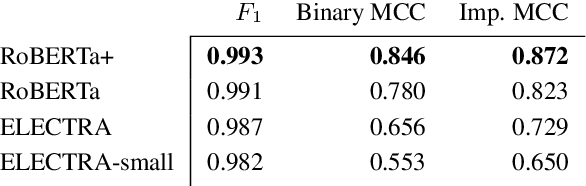
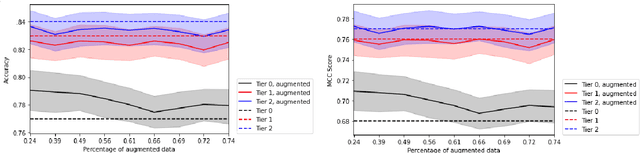
Abstract:Clinical Text Notes (CTNs) contain physicians' reasoning process, written in an unstructured free text format, as they examine and interview patients. In recent years, several studies have been published that provide evidence for the utility of machine learning for predicting doctors' diagnoses from CTNs, a task known as ICD coding. Data annotation is time consuming, particularly when a degree of specialization is needed, as is the case for medical data. This paper presents a method of augmenting a sparsely annotated dataset of Icelandic CTNs with a machine-learned imputation in a semi-self-supervised manner. We train a neural network on a small set of annotated CTNs and use it to extract clinical features from a set of un-annotated CTNs. These clinical features consist of answers to about a thousand potential questions that a physician might find the answers to during a consultation of a patient. The features are then used to train a classifier for the diagnosis of certain types of diseases. We report the results of an evaluation of this data augmentation method over three tiers of data availability to the physician. Our data augmentation method shows a significant positive effect which is diminished when clinical features from the examination of the patient and diagnostics are made available. We recommend our method for augmenting scarce datasets for systems that take decisions based on clinical features that do not include examinations or tests.
Kvistur 2.0: a BiLSTM Compound Splitter for Icelandic
Apr 16, 2020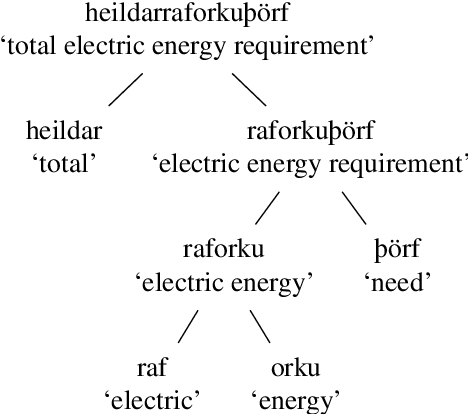
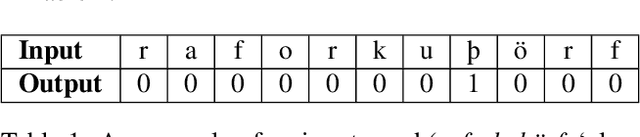
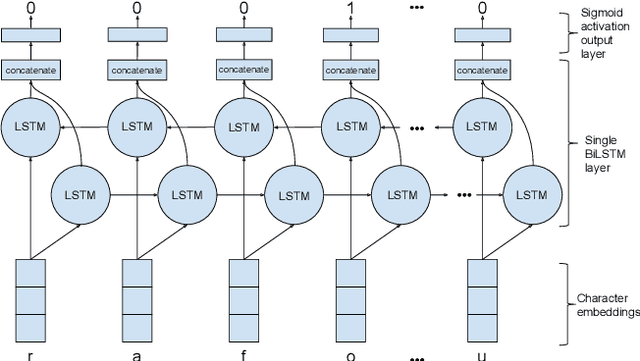
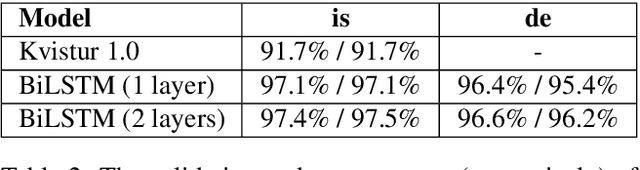
Abstract:In this paper, we present a character-based BiLSTM model for splitting Icelandic compound words, and show how varying amounts of training data affects the performance of the model. Compounding is highly productive in Icelandic, and new compounds are constantly being created. This results in a large number of out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words, negatively impacting the performance of many NLP tools. Our model is trained on a dataset of 2.9 million unique word forms and their constituent structures from the Database of Icelandic Morphology. The model learns how to split compound words into two parts and can be used to derive the constituent structure of any word form. Knowing the constituent structure of a word form makes it possible to generate the optimal split for a given task, e.g., a full split for subword tokenization, or, in the case of part-of-speech tagging, splitting an OOV word until the largest known morphological head is found. The model outperforms other previously published methods when evaluated on a corpus of manually split word forms. This method has been integrated into Kvistur, an Icelandic compound word analyzer.
Language Technology Programme for Icelandic 2019-2023
Mar 20, 2020
Abstract:In this paper, we describe a new national language technology programme for Icelandic. The programme, which spans a period of five years, aims at making Icelandic usable in communication and interactions in the digital world, by developing accessible, open-source language resources and software. The research and development work within the programme is carried out by a consortium of universities, institutions, and private companies, with a strong emphasis on cooperation between academia and industries. Five core projects will be the main content of the programme: language resources, speech recognition, speech synthesis, machine translation, and spell and grammar checking. We also describe other national language technology programmes and give an overview over the history of language technology in Iceland.
Nefnir: A high accuracy lemmatizer for Icelandic
Jul 27, 2019
Abstract:Lemmatization, finding the basic morphological form of a word in a corpus, is an important step in many natural language processing tasks when working with morphologically rich languages. We describe and evaluate Nefnir, a new open source lemmatizer for Icelandic. Nefnir uses suffix substitution rules, derived from a large morphological database, to lemmatize tagged text. Evaluation shows that for correctly tagged text, Nefnir obtains an accuracy of 99.55%, and for text tagged with a PoS tagger, the accuracy obtained is 96.88%.
Augmenting a BiLSTM tagger with a Morphological Lexicon and a Lexical Category Identification Step
Jul 21, 2019
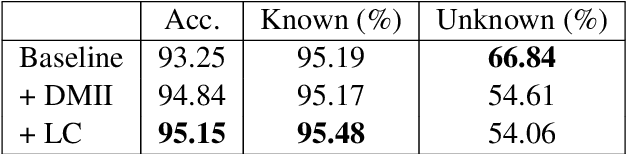
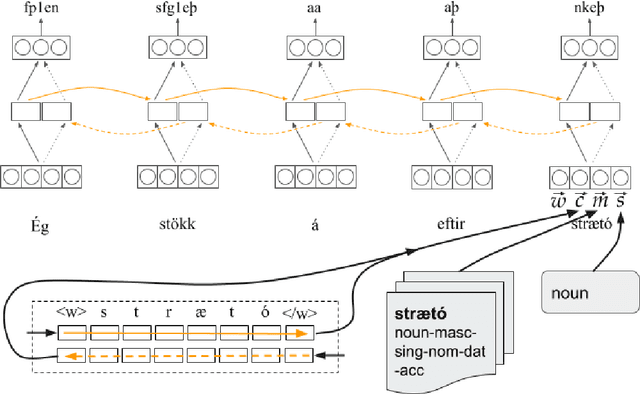
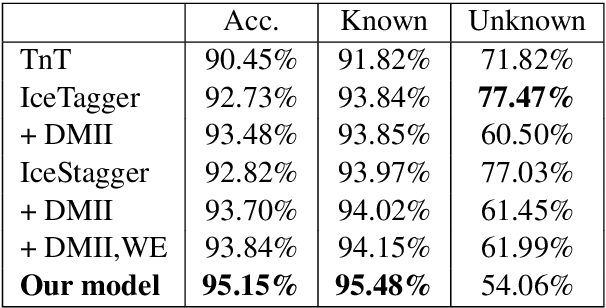
Abstract:Previous work on using BiLSTM models for PoS tagging has primarily focused on small tagsets. We evaluate BiLSTM models for tagging Icelandic, a morphologically rich language, using a relatively large tagset. Our baseline BiLSTM model achieves higher accuracy than any previously published tagger not taking advantage of a morphological lexicon. When we extend the model by incorporating such data, we outperform previous state-of-the-art results by a significant margin. We also report on work in progress that attempts to address the problem of data sparsity inherent in morphologically detailed, fine-grained tagsets. We experiment with training a separate model on only the lexical category and using the coarse-grained output tag as an input for the main model. This method further increases the accuracy and reduces the tagging errors by 21.3% compared to previous state-of-the-art results. Finally, we train and test our tagger on a new gold standard for Icelandic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge