Jón Guðnason
Learning Emotional Representations from Imbalanced Speech Data for Speech Emotion Recognition and Emotional Text-to-Speech
Jun 09, 2023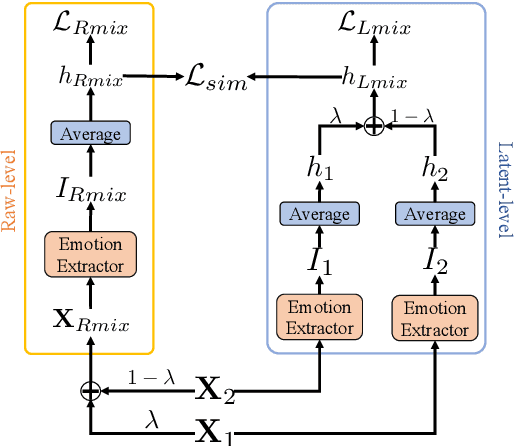
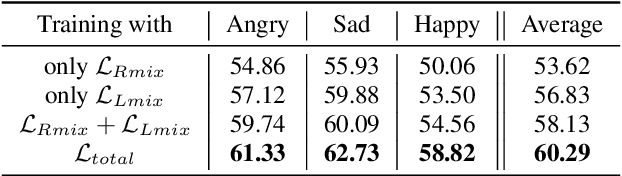
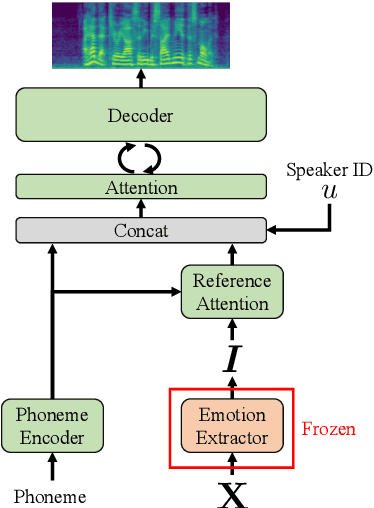
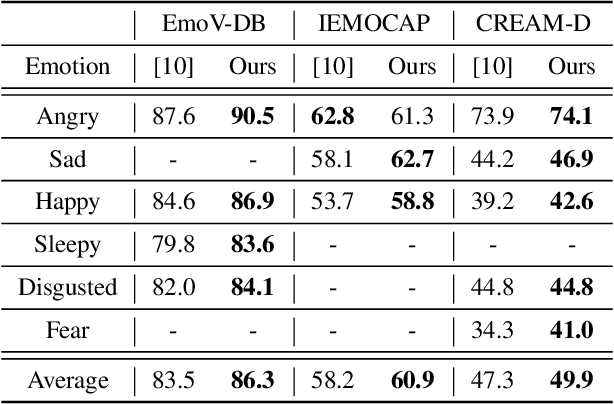
Abstract:Effective speech emotional representations play a key role in Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) and Emotional Text-To-Speech (TTS) tasks. However, emotional speech samples are more difficult and expensive to acquire compared with Neutral style speech, which causes one issue that most related works unfortunately neglect: imbalanced datasets. Models might overfit to the majority Neutral class and fail to produce robust and effective emotional representations. In this paper, we propose an Emotion Extractor to address this issue. We use augmentation approaches to train the model and enable it to extract effective and generalizable emotional representations from imbalanced datasets. Our empirical results show that (1) for the SER task, the proposed Emotion Extractor surpasses the state-of-the-art baseline on three imbalanced datasets; (2) the produced representations from our Emotion Extractor benefit the TTS model, and enable it to synthesize more expressive speech.
Fine-grained Emotional Control of Text-To-Speech: Learning To Rank Inter- And Intra-Class Emotion Intensities
Mar 11, 2023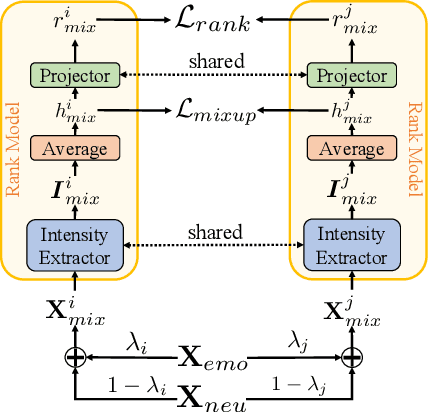
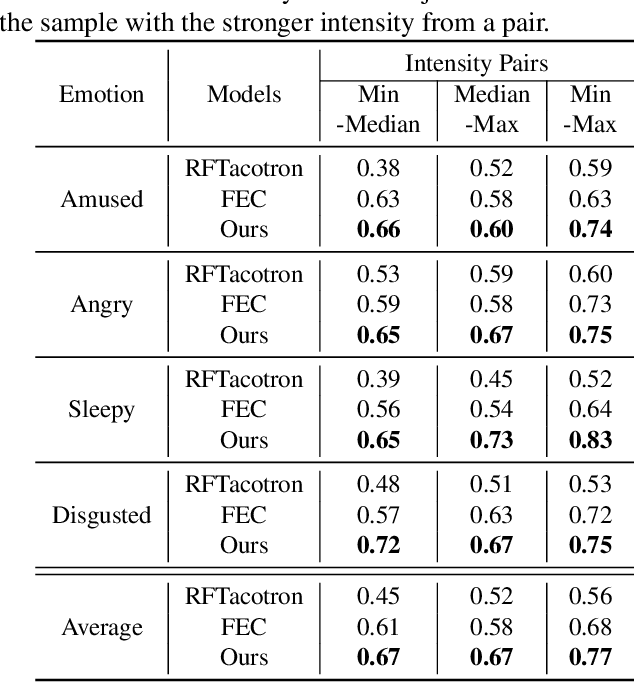
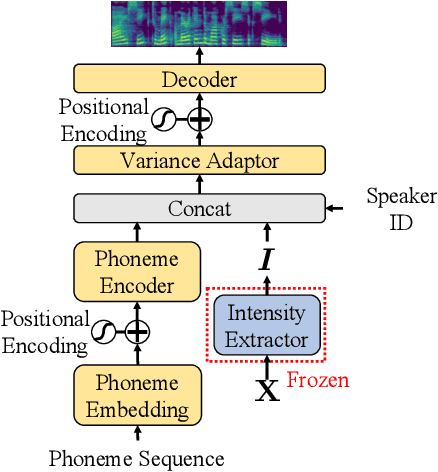
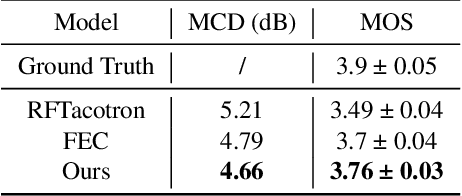
Abstract:State-of-the-art Text-To-Speech (TTS) models are capable of producing high-quality speech. The generated speech, however, is usually neutral in emotional expression, whereas very often one would want fine-grained emotional control of words or phonemes. Although still challenging, the first TTS models have been recently proposed that are able to control voice by manually assigning emotion intensity. Unfortunately, due to the neglect of intra-class distance, the intensity differences are often unrecognizable. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained controllable emotional TTS, that considers both inter- and intra-class distances and be able to synthesize speech with recognizable intensity difference. Our subjective and objective experiments demonstrate that our model exceeds two state-of-the-art controllable TTS models for controllability, emotion expressiveness and naturalness.
Generative Data Augmentation Guided by Triplet Loss for Speech Emotion Recognition
Aug 09, 2022
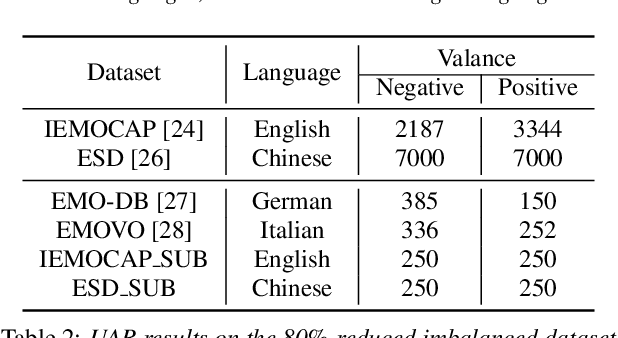
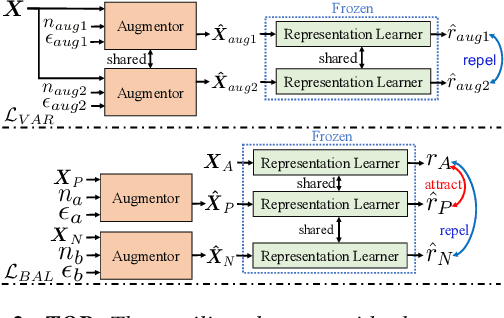
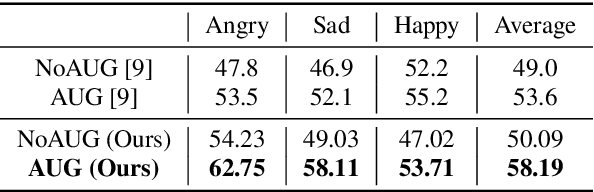
Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is crucial for human-computer interaction but still remains a challenging problem because of two major obstacles: data scarcity and imbalance. Many datasets for SER are substantially imbalanced, where data utterances of one class (most often Neutral) are much more frequent than those of other classes. Furthermore, only a few data resources are available for many existing spoken languages. To address these problems, we exploit a GAN-based augmentation model guided by a triplet network, to improve SER performance given imbalanced and insufficient training data. We conduct experiments and demonstrate: 1) With a highly imbalanced dataset, our augmentation strategy significantly improves the SER performance (+8% recall score compared with the baseline). 2) Moreover, in a cross-lingual benchmark, where we train a model with enough source language utterances but very few target language utterances (around 50 in our experiments), our augmentation strategy brings benefits for the SER performance of all three target languages.
Language Technology Programme for Icelandic 2019-2023
Mar 20, 2020
Abstract:In this paper, we describe a new national language technology programme for Icelandic. The programme, which spans a period of five years, aims at making Icelandic usable in communication and interactions in the digital world, by developing accessible, open-source language resources and software. The research and development work within the programme is carried out by a consortium of universities, institutions, and private companies, with a strong emphasis on cooperation between academia and industries. Five core projects will be the main content of the programme: language resources, speech recognition, speech synthesis, machine translation, and spell and grammar checking. We also describe other national language technology programmes and give an overview over the history of language technology in Iceland.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge