Jón F. Daðason
Semi-self-supervised Automated ICD Coding
May 20, 2022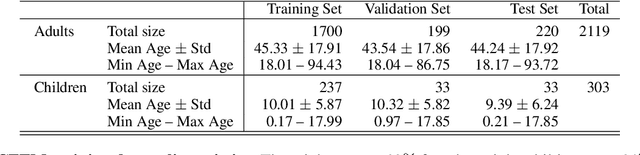
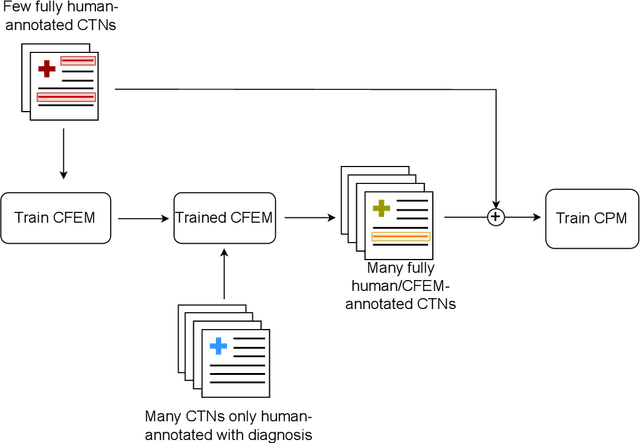
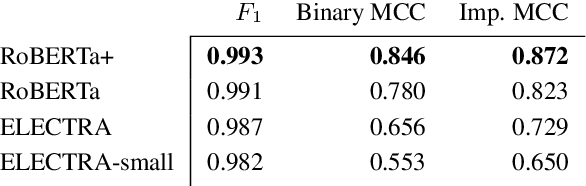
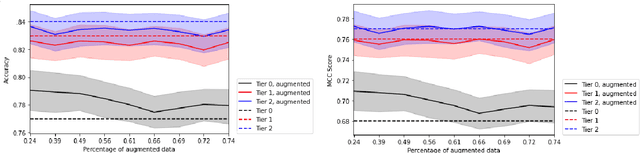
Abstract:Clinical Text Notes (CTNs) contain physicians' reasoning process, written in an unstructured free text format, as they examine and interview patients. In recent years, several studies have been published that provide evidence for the utility of machine learning for predicting doctors' diagnoses from CTNs, a task known as ICD coding. Data annotation is time consuming, particularly when a degree of specialization is needed, as is the case for medical data. This paper presents a method of augmenting a sparsely annotated dataset of Icelandic CTNs with a machine-learned imputation in a semi-self-supervised manner. We train a neural network on a small set of annotated CTNs and use it to extract clinical features from a set of un-annotated CTNs. These clinical features consist of answers to about a thousand potential questions that a physician might find the answers to during a consultation of a patient. The features are then used to train a classifier for the diagnosis of certain types of diseases. We report the results of an evaluation of this data augmentation method over three tiers of data availability to the physician. Our data augmentation method shows a significant positive effect which is diminished when clinical features from the examination of the patient and diagnostics are made available. We recommend our method for augmenting scarce datasets for systems that take decisions based on clinical features that do not include examinations or tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge