Hoonrae Kim
Mirror: Multimodal Cognitive Reframing Therapy for Rolling with Resistance
Apr 16, 2025
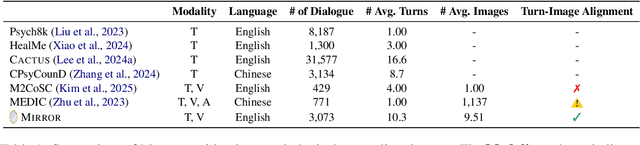
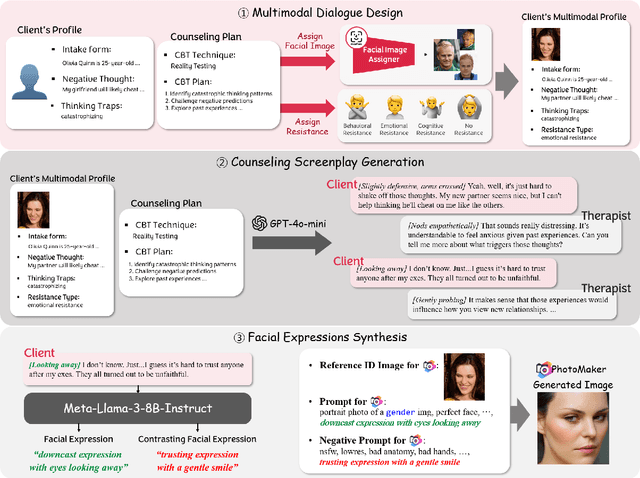
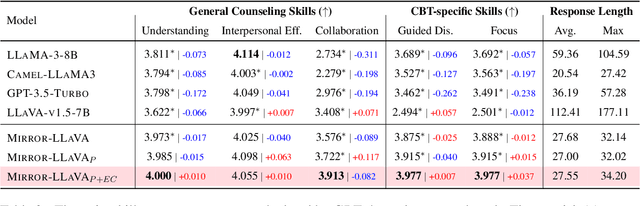
Abstract:Recent studies have explored the use of large language models (LLMs) in psychotherapy; however, text-based cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) models often struggle with client resistance, which can weaken therapeutic alliance. To address this, we propose a multimodal approach that incorporates nonverbal cues, allowing the AI therapist to better align its responses with the client's negative emotional state. Specifically, we introduce a new synthetic dataset, Multimodal Interactive Rolling with Resistance (Mirror), which is a novel synthetic dataset that pairs client statements with corresponding facial images. Using this dataset, we train baseline Vision-Language Models (VLMs) that can analyze facial cues, infer emotions, and generate empathetic responses to effectively manage resistance. They are then evaluated in terms of both the therapist's counseling skills and the strength of the therapeutic alliance in the presence of client resistance. Our results demonstrate that Mirror significantly enhances the AI therapist's ability to handle resistance, which outperforms existing text-based CBT approaches.
Multimodal Cognitive Reframing Therapy via Multi-hop Psychotherapeutic Reasoning
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Previous research has revealed the potential of large language models (LLMs) to support cognitive reframing therapy; however, their focus was primarily on text-based methods, often overlooking the importance of non-verbal evidence crucial in real-life therapy. To alleviate this gap, we extend the textual cognitive reframing to multimodality, incorporating visual clues. Specifically, we present a new dataset called Multi Modal-Cognitive Support Conversation (M2CoSC), which pairs each GPT-4-generated dialogue with an image that reflects the virtual client's facial expressions. To better mirror real psychotherapy, where facial expressions lead to interpreting implicit emotional evidence, we propose a multi-hop psychotherapeutic reasoning approach that explicitly identifies and incorporates subtle evidence. Our comprehensive experiments with both LLMs and vision-language models (VLMs) demonstrate that the VLMs' performance as psychotherapists is significantly improved with the M2CoSC dataset. Furthermore, the multi-hop psychotherapeutic reasoning method enables VLMs to provide more thoughtful and empathetic suggestions, outperforming standard prompting methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge