Helena Williams
DEEPBEAS3D: Deep Learning and B-Spline Explicit Active Surfaces
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:Deep learning-based automatic segmentation methods have become state-of-the-art. However, they are often not robust enough for direct clinical application, as domain shifts between training and testing data affect their performance. Failure in automatic segmentation can cause sub-optimal results that require correction. To address these problems, we propose a novel 3D extension of an interactive segmentation framework that represents a segmentation from a convolutional neural network (CNN) as a B-spline explicit active surface (BEAS). BEAS ensures segmentations are smooth in 3D space, increasing anatomical plausibility, while allowing the user to precisely edit the 3D surface. We apply this framework to the task of 3D segmentation of the anal sphincter complex (AS) from transperineal ultrasound (TPUS) images, and compare it to the clinical tool used in the pelvic floor disorder clinic (4D View VOCAL, GE Healthcare; Zipf, Austria). Experimental results show that: 1) the proposed framework gives the user explicit control of the surface contour; 2) the perceived workload calculated via the NASA-TLX index was reduced by 30% compared to VOCAL; and 3) it required 7 0% (170 seconds) less user time than VOCAL (p< 0.00001)
Adaptive Multi-scale Online Likelihood Network for AI-assisted Interactive Segmentation
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:Existing interactive segmentation methods leverage automatic segmentation and user interactions for label refinement, significantly reducing the annotation workload compared to manual annotation. However, these methods lack quick adaptability to ambiguous and noisy data, which is a challenge in CT volumes containing lung lesions from COVID-19 patients. In this work, we propose an adaptive multi-scale online likelihood network (MONet) that adaptively learns in a data-efficient online setting from both an initial automatic segmentation and user interactions providing corrections. We achieve adaptive learning by proposing an adaptive loss that extends the influence of user-provided interaction to neighboring regions with similar features. In addition, we propose a data-efficient probability-guided pruning method that discards uncertain and redundant labels in the initial segmentation to enable efficient online training and inference. Our proposed method was evaluated by an expert in a blinded comparative study on COVID-19 lung lesion annotation task in CT. Our approach achieved 5.86% higher Dice score with 24.67% less perceived NASA-TLX workload score than the state-of-the-art. Source code is available at: https://github.com/masadcv/MONet-MONAILabel
Interactive Segmentation via Deep Learning and B-Spline Explicit Active Surfaces
Oct 25, 2021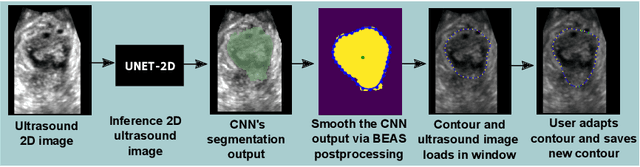
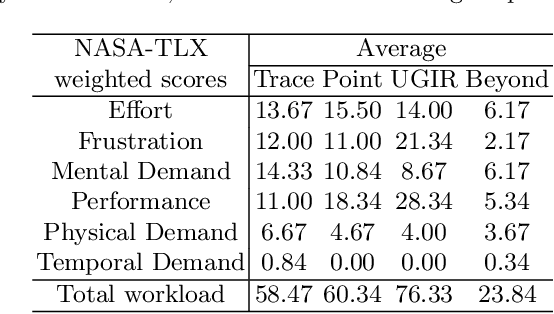
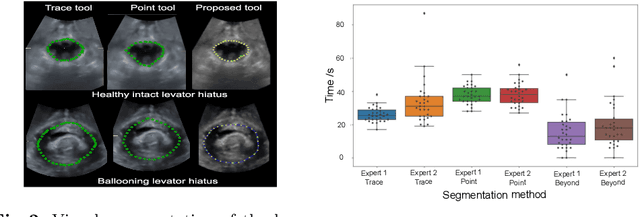
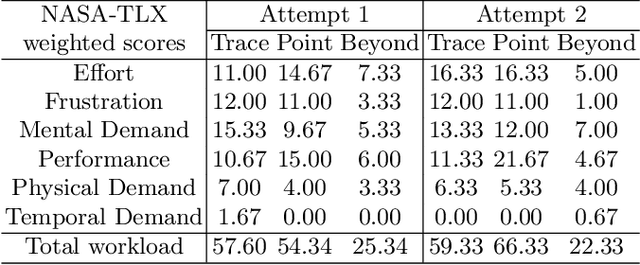
Abstract:Automatic medical image segmentation via convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has shown promising results. However, they may not always be robust enough for clinical use. Sub-optimal segmentation would require clinician's to manually delineate the target object, causing frustration. To address this problem, a novel interactive CNN-based segmentation framework is proposed in this work. The aim is to represent the CNN segmentation contour as B-splines by utilising B-spline explicit active surfaces (BEAS). The interactive element of the framework allows the user to precisely edit the contour in real-time, and by utilising BEAS it ensures the final contour is smooth and anatomically plausible. This framework was applied to the task of 2D segmentation of the levator hiatus from 2D ultrasound (US) images, and compared to the current clinical tools used in pelvic floor disorder clinic (4DView, GE Healthcare; Zipf, Austria). Experimental results show that: 1) the proposed framework is more robust than current state-of-the-art CNNs; 2) the perceived workload calculated via the NASA-TLX index was reduced more than half for the proposed approach in comparison to current clinical tools; and 3) the proposed tool requires at least 13 seconds less user time than the clinical tools, which was significant (p=0.001).
* 11 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge