Helder Fontes
Vision-Radio Experimental Infrastructure Architecture Towards 6G
Feb 29, 2024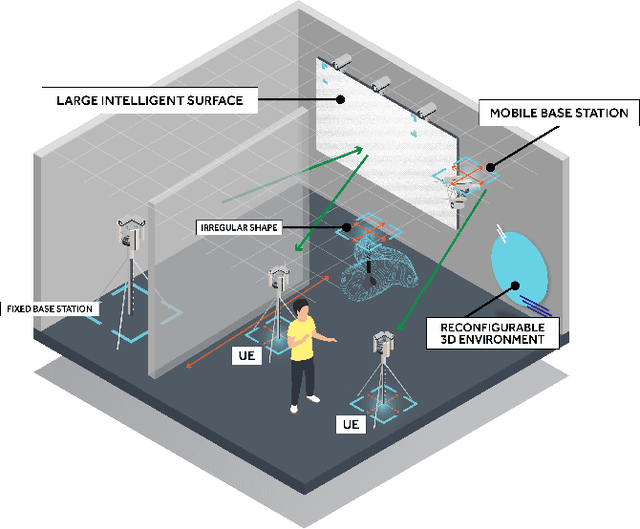
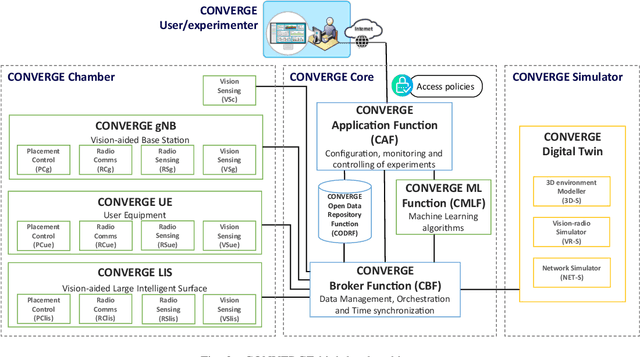
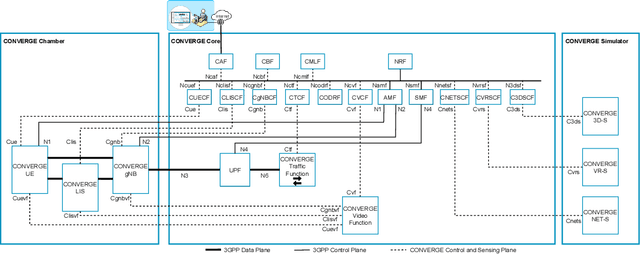
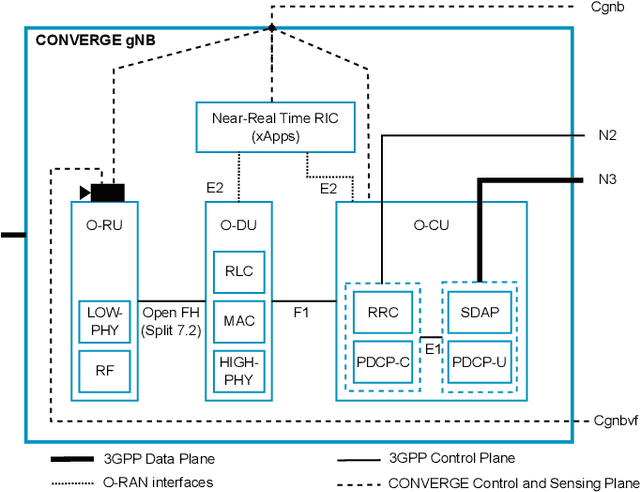
Abstract:Telecommunications and computer vision have evolved separately so far. Yet, with the shift to sub-terahertz (sub-THz) and terahertz (THz) radio communications, there is an opportunity to explore computer vision technologies together with radio communications, considering the dependency of both technologies on Line of Sight. The combination of radio sensing and computer vision can address challenges such as obstructions and poor lighting. Also, machine learning algorithms, capable of processing multimodal data, play a crucial role in deriving insights from raw and low-level sensing data, offering a new level of abstraction that can enhance various applications and use cases such as beamforming and terminal handovers. This paper introduces CONVERGE, a pioneering vision-radio paradigm that bridges this gap by leveraging Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) to facilitate a dual "View-to-Communicate, Communicate-to-View" approach. CONVERGE offers tools that merge wireless communications and computer vision, establishing a novel Research Infrastructure (RI) that will be open to the scientific community and capable of providing open datasets. This new infrastructure will support future research in 6G and beyond concerning multiple verticals, such as telecommunications, automotive, manufacturing, media, and health.
On the Analysis of Computational Delays in Reinforcement Learning-based Rate Adaptation Algorithms
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Several research works have applied Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms to solve the Rate Adaptation (RA) problem in Wi-Fi networks. The dynamic nature of the radio link requires the algorithms to be responsive to changes in link quality. Delays in the execution of the algorithm may be detrimental to its performance, which in turn may decrease network performance. This aspect has been overlooked in the state of the art. In this paper, we present an analysis of common computational delays in RL-based RA algorithms, and propose a methodology that may be applied to reduce these computational delays and increase the efficiency of this type of algorithms. We apply the proposed methodology to an existing RL-based RA algorithm. The obtained experimental results indicate a reduction of one order of magnitude in the execution time of the algorithm, improving its responsiveness to link quality changes.
UAV-Assisted Wireless Communications: An Experimental Analysis of Air-to-Ground and Ground-to-Air Channels in Open Environments
Mar 29, 2023

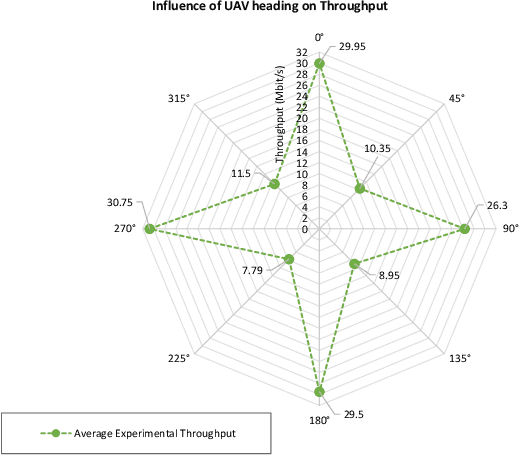
Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) offer promising potential as communications node carriers, providing on-demand wireless connectivity to users. While existing literature presents various channel models, they often overlook the impact of UAV heading. This paper experimentally characterizes Air-to-Ground (A2G) and Ground-to-Air (G2A) wireless channels in obstacle-free, interference-free open environments, accounting for distance and UAV heading. We analyze the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and TCP throughput between ground users and UAVs, covering distances between 50 m and 500 m, and considering different UAV headings. Our study offers a more accurate channel model characterization compared to deterministic models such as Friis and two-ray. Additionally, we characterize the antenna's radiation pattern based on UAV headings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge