Hehao Niu
Double Intelligent Reflecting Surface-assisted Multi-User MIMO mmWave Systems with Hybrid Precoding
Nov 26, 2021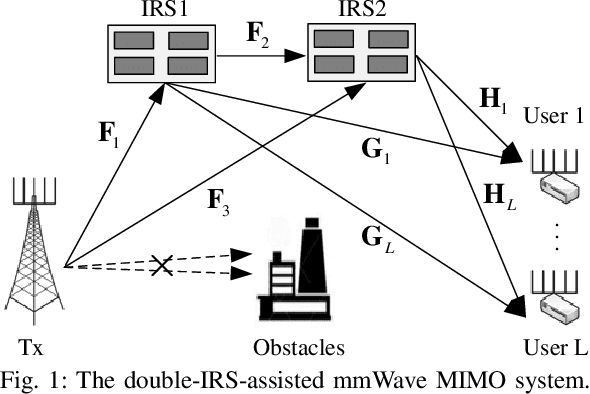
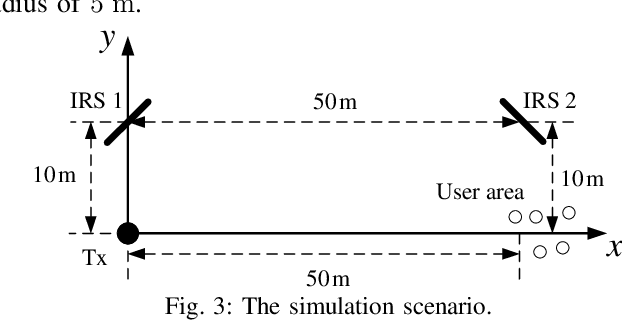
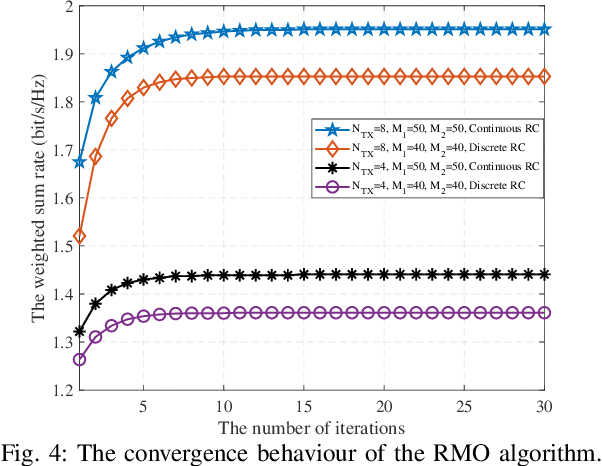
Abstract:This work investigates the effect of double intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) in improving the spectrum efficient of multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) network operating in the millimeter wave (mmWave) band. Specifically, we aim to solve a weighted sum rate maximization problem by jointly optimizing the digital precoding at the transmitter and the analog phase shifters at the IRS, subject to the minimum achievable rate constraint. To facilitate the design of an efficient solution, we first reformulate the original problem into a tractable one by exploiting the majorization-minimization (MM) method. Then, a block coordinate descent (BCD) method is proposed to obtain a suboptimal solution, where the precoding matrices and the phase shifters are alternately optimized. Specifically, the digital precoding matrix design problem is solved by the quadratically constrained quadratic programming (QCQP), while the analog phase shift optimization is solved by the Riemannian manifold optimization (RMO). The convergence and computational complexity are analyzed. Finally, simulation results are provided to verify the performance of the proposed design, as well as the effectiveness of double-IRS in improving the spectral efficiency.
Simultaneous Transmission and Reflection Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted MIMO Systems
Jun 17, 2021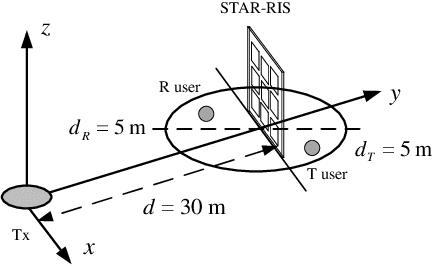
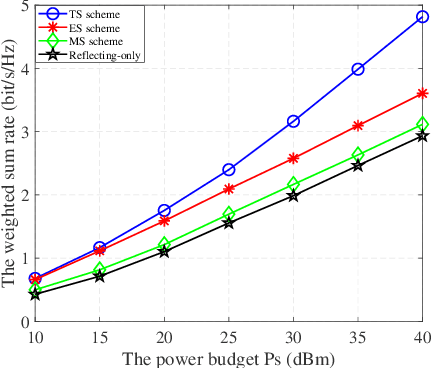
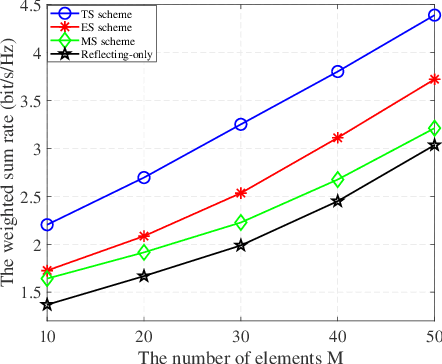
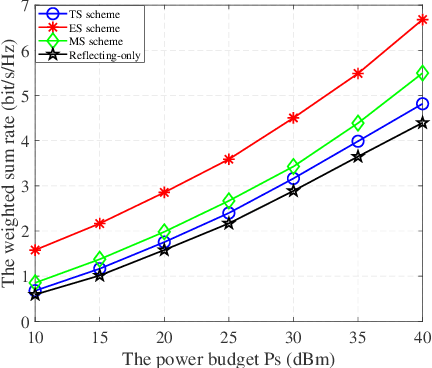
Abstract:In this work, we investigate a novel simultaneous transmission and reflection reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted multiple-input multiple-output downlink system, where three practical transmission protocols, namely, energy splitting (ES), mode selection (MS), and time splitting (TS), are studied. For the system under consideration, we maximize the weighted sum rate with multiple coupled variables. To solve this optimization problem, a block coordinate descent algorithm is proposed to reformulate this problem and design the precoding matrices and the transmitting and reflecting coefficients (TARCs) in an alternate manner. Specifically, for the ES scheme, the precoding matrices are solved using the Lagrange dual method, while the TARCs are obtained using the penalty concave-convex method. Additionally, the proposed method is extended to the MS scheme by solving a mixed-integer problem. Moreover, we solve the formulated problem for the TS scheme using a one-dimensional search and the Majorization-Minimization technique. Our simulation results reveal that: 1) Simultaneous transmission and reflection RIS (STAR-RIS) can achieve better performance than reflecting-only RIS; 2) In unicast communication, TS scheme outperforms the ES and MS schemes, while in broadcast communication, ES scheme outperforms the TS and MS schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge