Heejae Chon
Eliciting Instruction-tuned Code Language Models' Capabilities to Utilize Auxiliary Function for Code Generation
Sep 20, 2024
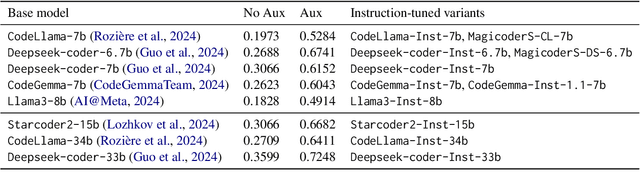
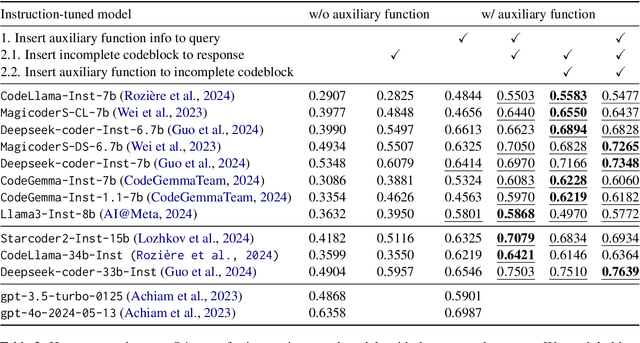
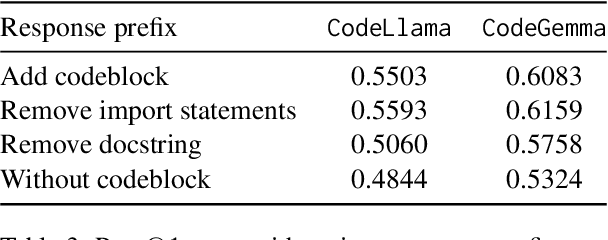
Abstract:We study the code generation behavior of instruction-tuned models built on top of code pre-trained language models when they could access an auxiliary function to implement a function. We design several ways to provide auxiliary functions to the models by adding them to the query or providing a response prefix to incorporate the ability to utilize auxiliary functions with the instruction-following capability. Our experimental results show the effectiveness of combining the base models' auxiliary function utilization ability with the instruction following ability. In particular, the performance of adopting our approaches with the open-sourced language models surpasses that of the recent powerful proprietary language models, i.e., gpt-4o.
Is Functional Correctness Enough to Evaluate Code Language Models? Exploring Diversity of Generated Codes
Aug 24, 2024Abstract:Language models (LMs) have exhibited impressive abilities in generating codes from natural language requirements. In this work, we highlight the diversity of code generated by LMs as a critical criterion for evaluating their code generation capabilities, in addition to functional correctness. Despite its practical implications, there is a lack of studies focused on assessing the diversity of generated code, which overlooks its importance in the development of code LMs. We propose a systematic approach to evaluate the diversity of generated code, utilizing various metrics for inter-code similarity as well as functional correctness. Specifically, we introduce a pairwise code similarity measure that leverages large LMs' capabilities in code understanding and reasoning, demonstrating the highest correlation with human judgment. We extensively investigate the impact of various factors on the quality of generated code, including model sizes, temperatures, training approaches, prompting strategies, and the difficulty of input problems. Our consistent observation of a positive correlation between the test pass score and the inter-code similarity score indicates that current LMs tend to produce functionally correct code with limited diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge