Heeja Kim
Explainable Product Classification for Customs
Nov 18, 2023Abstract:The task of assigning internationally accepted commodity codes (aka HS codes) to traded goods is a critical function of customs offices. Like court decisions made by judges, this task follows the doctrine of precedent and can be nontrivial even for experienced officers. Together with the Korea Customs Service (KCS), we propose a first-ever explainable decision supporting model that suggests the most likely subheadings (i.e., the first six digits) of the HS code. The model also provides reasoning for its suggestion in the form of a document that is interpretable by customs officers. We evaluated the model using 5,000 cases that recently received a classification request. The results showed that the top-3 suggestions made by our model had an accuracy of 93.9\% when classifying 925 challenging subheadings. A user study with 32 customs experts further confirmed that our algorithmic suggestions accompanied by explainable reasonings, can substantially reduce the time and effort taken by customs officers for classification reviews.
Classification of Goods Using Text Descriptions With Sentences Retrieval
Nov 02, 2021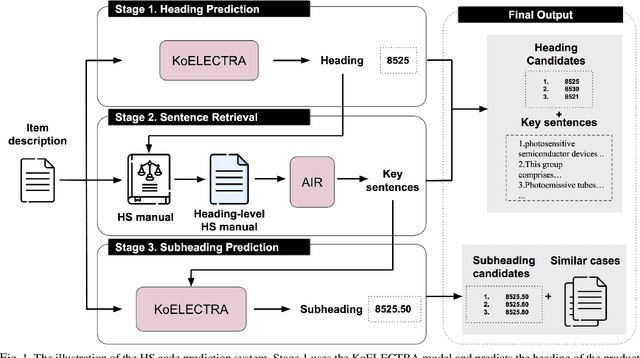
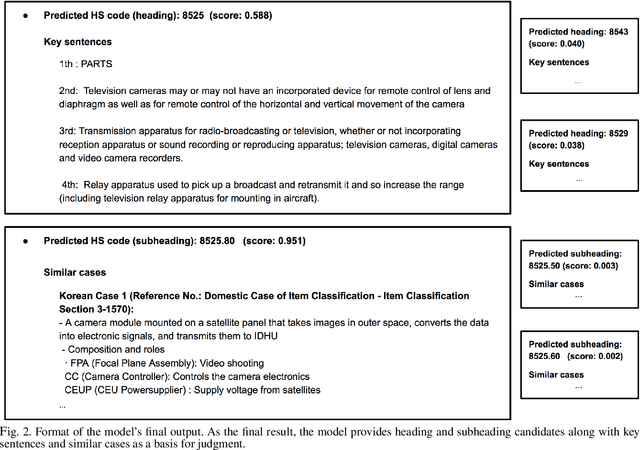
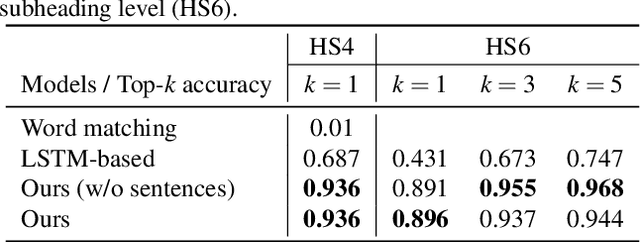

Abstract:The task of assigning and validating internationally accepted commodity code (HS code) to traded goods is one of the critical functions at the customs office. This decision is crucial to importers and exporters, as it determines the tariff rate. However, similar to court decisions made by judges, the task can be non-trivial even for experienced customs officers. The current paper proposes a deep learning model to assist this seemingly challenging HS code classification. Together with Korea Customs Service, we built a decision model based on KoELECTRA that suggests the most likely heading and subheadings (i.e., the first four and six digits) of the HS code. Evaluation on 129,084 past cases shows that the top-3 suggestions made by our model have an accuracy of 95.5% in classifying 265 subheadings. This promising result implies algorithms may reduce the time and effort taken by customs officers substantially by assisting the HS code classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge