Heather Whalley
Examining the Role of Mood Patterns in Predicting Self-Reported Depressive symptoms
Jun 14, 2020



Abstract:Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide. Initial efforts to detect depression signals from social media posts have shown promising results. Given the high internal validity, results from such analyses are potentially beneficial to clinical judgment. The existing models for automatic detection of depressive symptoms learn proxy diagnostic signals from social media data, such as help-seeking behavior for mental health or medication names. However, in reality, individuals with depression typically experience depressed mood, loss of pleasure nearly in all the activities, feeling of worthlessness or guilt, and diminished ability to think. Therefore, a lot of the proxy signals used in these models lack the theoretical underpinnings for depressive symptoms. It is also reported that social media posts from many patients in the clinical setting do not contain these signals. Based on this research gap, we propose to monitor a type of signal that is well-established as a class of symptoms in affective disorders -- mood. The mood is an experience of feeling that can last for hours, days, or even weeks. In this work, we attempt to enrich current technology for detecting symptoms of potential depression by constructing a 'mood profile' for social media users.
Named Entity Recognition for Electronic Health Records: A Comparison of Rule-based and Machine Learning Approaches
Mar 10, 2019
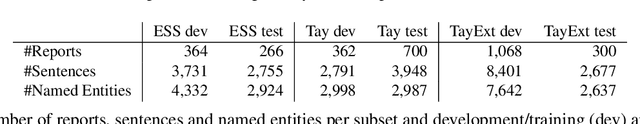
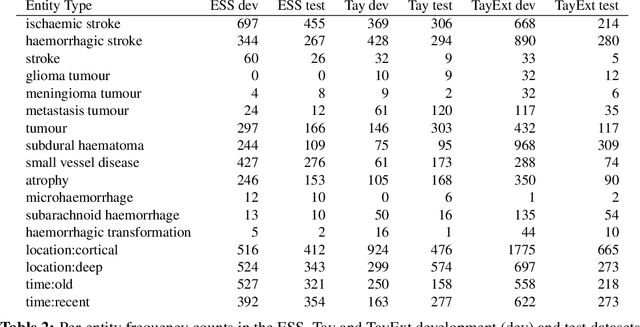
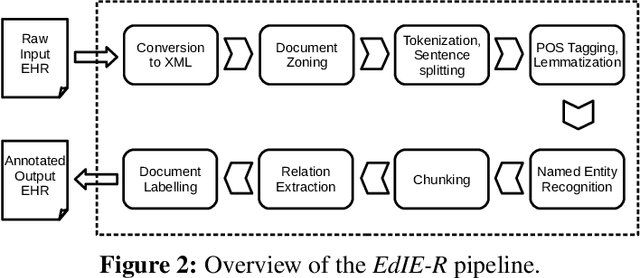
Abstract:This work investigates multiple approaches to Named Entity Recognition (NER) for text in Electronic Health Record (EHR) data. In particular, we look into the application of (i) rule-based, (ii) deep learning and (iii) transfer learning systems for the task of NER on brain imaging reports with a focus on records from patients with stroke. We explore the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, develop rules and train on a common dataset, and evaluate each system's performance on common test sets of Scottish radiology reports from two sources (brain imaging reports in ESS -- Edinburgh Stroke Study data collected by NHS Lothian as well as radiology reports created in NHS Tayside). Our comparison shows that a hand-crafted system is the most accurate way to automatically label EHR, but machine learning approaches can provide a feasible alternative where resources for a manual system are not readily available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge