Hasmot Ali
Continuous Monitoring of Large-Scale Generative AI via Deterministic Knowledge Graph Structures
Sep 04, 2025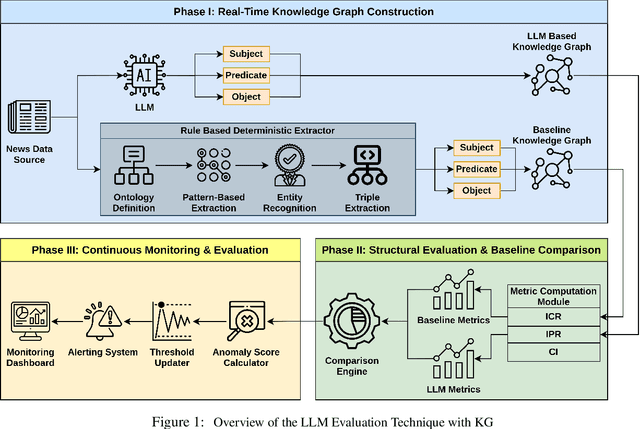

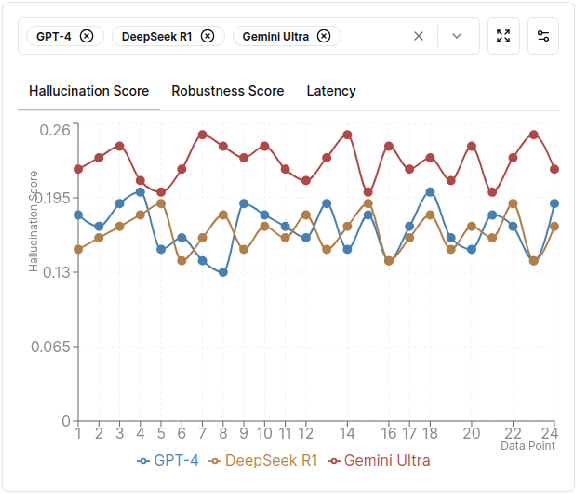

Abstract:Generative AI (GEN AI) models have revolutionized diverse application domains but present substantial challenges due to reliability concerns, including hallucinations, semantic drift, and inherent biases. These models typically operate as black-boxes, complicating transparent and objective evaluation. Current evaluation methods primarily depend on subjective human assessment, limiting scalability, transparency, and effectiveness. This research proposes a systematic methodology using deterministic and Large Language Model (LLM)-generated Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to continuously monitor and evaluate GEN AI reliability. We construct two parallel KGs: (i) a deterministic KG built using explicit rule-based methods, predefined ontologies, domain-specific dictionaries, and structured entity-relation extraction rules, and (ii) an LLM-generated KG dynamically derived from real-time textual data streams such as live news articles. Utilizing real-time news streams ensures authenticity, mitigates biases from repetitive training, and prevents adaptive LLMs from bypassing predefined benchmarks through feedback memorization. To quantify structural deviations and semantic discrepancies, we employ several established KG metrics, including Instantiated Class Ratio (ICR), Instantiated Property Ratio (IPR), and Class Instantiation (CI). An automated real-time monitoring framework continuously computes deviations between deterministic and LLM-generated KGs. By establishing dynamic anomaly thresholds based on historical structural metric distributions, our method proactively identifies and flags significant deviations, thus promptly detecting semantic anomalies or hallucinations. This structured, metric-driven comparison between deterministic and dynamically generated KGs delivers a robust and scalable evaluation framework.
Advanced Tool Learning and Selection System (ATLASS): A Closed-Loop Framework Using LLM
Mar 13, 2025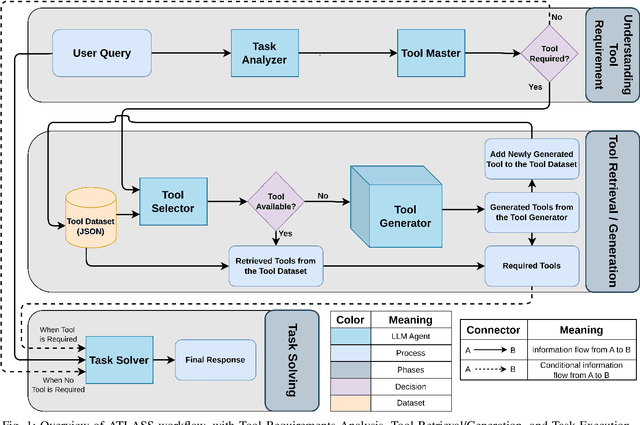
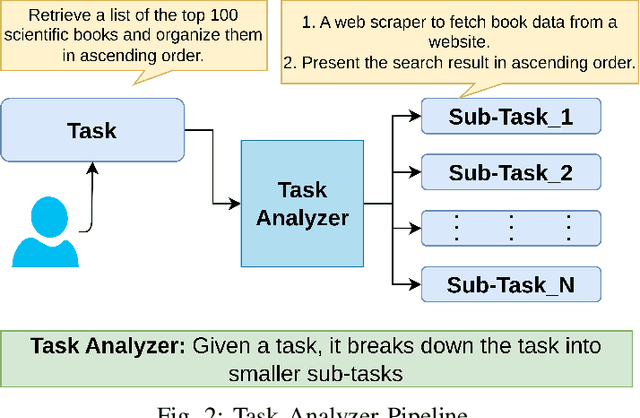
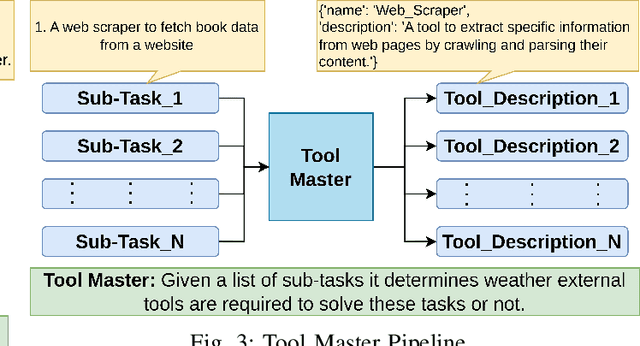
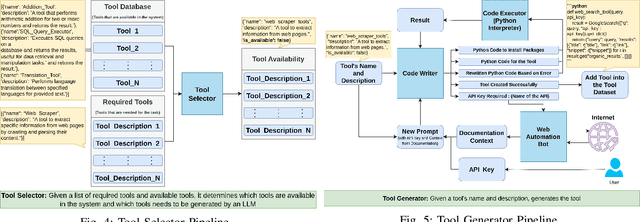
Abstract:The combination of LLM agents with external tools enables models to solve complex tasks beyond their knowledge base. Human-designed tools are inflexible and restricted to solutions within the scope of pre-existing tools created by experts. To address this problem, we propose ATLASS, an advanced tool learning and selection system designed as a closed-loop framework. It enables the LLM to solve problems by dynamically generating external tools on demand. In this framework, agents play a crucial role in orchestrating tool selection, execution, and refinement, ensuring adaptive problem-solving capabilities. The operation of ATLASS follows three phases: The first phase, Understanding Tool Requirements, involves the Agents determining whether tools are required and specifying their functionality; the second phase, Tool Retrieval/Generation, involves the Agents retrieving or generating tools based on their availability; and the third phase, Task Solving, involves combining all the component tools necessary to complete the initial task. The Tool Dataset stores the generated tools, ensuring reusability and minimizing inference cost. Current LLM-based tool generation systems have difficulty creating complex tools that need APIs or external packages. In ATLASS, we solve the problem by automatically setting up the environment, fetching relevant API documentation online, and using a Python interpreter to create a reliable, versatile tool that works in a wider range of situations. OpenAI GPT-4.0 is used as the LLM agent, and safety and ethical concerns are handled through human feedback before executing generated code. By addressing the limitations of predefined toolsets and enhancing adaptability, ATLASS serves as a real-world solution that empowers users with dynamically generated tools for complex problem-solving.
Artificial Neural Networks to Recognize Speakers Division from Continuous Bengali Speech
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Voice based applications are ruling over the era of automation because speech has a lot of factors that determine a speakers information as well as speech. Modern Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is a blessing in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) for efficient communication among humans and devices using Artificial Intelligence technology. Speech is one of the easiest mediums of communication because it has a lot of identical features for different speakers. Nowadays it is possible to determine speakers and their identity using their speech in terms of speaker recognition. In this paper, we presented a method that will provide a speakers geographical identity in a certain region using continuous Bengali speech. We consider eight different divisions of Bangladesh as the geographical region. We applied the Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) and Delta features on an Artificial Neural Network to classify speakers division. We performed some preprocessing tasks like noise reduction and 8-10 second segmentation of raw audio before feature extraction. We used our dataset of more than 45 hours of audio data from 633 individual male and female speakers. We recorded the highest accuracy of 85.44%.
Enhancement of Bengali OCR by Specialized Models and Advanced Techniques for Diverse Document Types
Feb 07, 2024
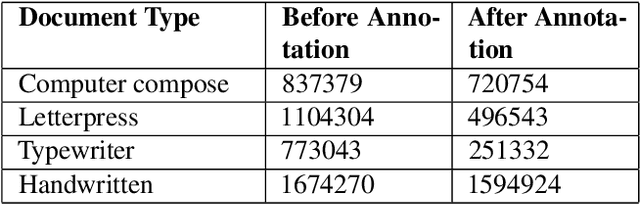
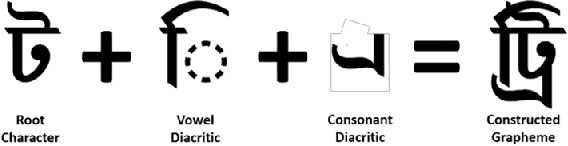
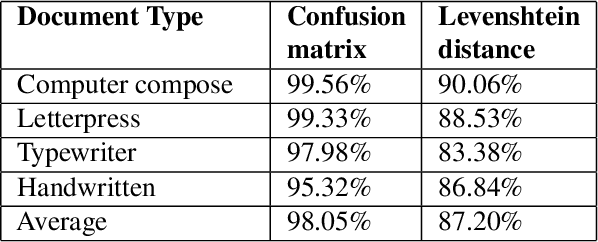
Abstract:This research paper presents a unique Bengali OCR system with some capabilities. The system excels in reconstructing document layouts while preserving structure, alignment, and images. It incorporates advanced image and signature detection for accurate extraction. Specialized models for word segmentation cater to diverse document types, including computer-composed, letterpress, typewriter, and handwritten documents. The system handles static and dynamic handwritten inputs, recognizing various writing styles. Furthermore, it has the ability to recognize compound characters in Bengali. Extensive data collection efforts provide a diverse corpus, while advanced technical components optimize character and word recognition. Additional contributions include image, logo, signature and table recognition, perspective correction, layout reconstruction, and a queuing module for efficient and scalable processing. The system demonstrates outstanding performance in efficient and accurate text extraction and analysis.
* 8 pages, 7 figures, 4 table Link of the paper https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/WACV2024W/WVLL/html/Rabby_Enhancement_of_Bengali_OCR_by_Specialized_Models_and_Advanced_Techniques_WACVW_2024_paper.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge