Roy George
Lite VLA: Efficient Vision-Language-Action Control on CPU-Bound Edge Robots
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:The deployment of artificial intelligence models at the edge is increasingly critical for autonomous robots operating in GPS-denied environments where local, resource-efficient reasoning is essential. This work demonstrates the feasibility of deploying small Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on mobile robots to achieve real-time scene understanding and reasoning under strict computational constraints. Unlike prior approaches that separate perception from mobility, the proposed framework enables simultaneous movement and reasoning in dynamic environments using only on-board hardware. The system integrates a compact VLM with multimodal perception to perform contextual interpretation directly on embedded hardware, eliminating reliance on cloud connectivity. Experimental validation highlights the balance between computational efficiency, task accuracy, and system responsiveness. Implementation on a mobile robot confirms one of the first successful deployments of small VLMs for concurrent reasoning and mobility at the edge. This work establishes a foundation for scalable, assured autonomy in applications such as service robotics, disaster response, and defense operations.
Advanced Tool Learning and Selection System (ATLASS): A Closed-Loop Framework Using LLM
Mar 13, 2025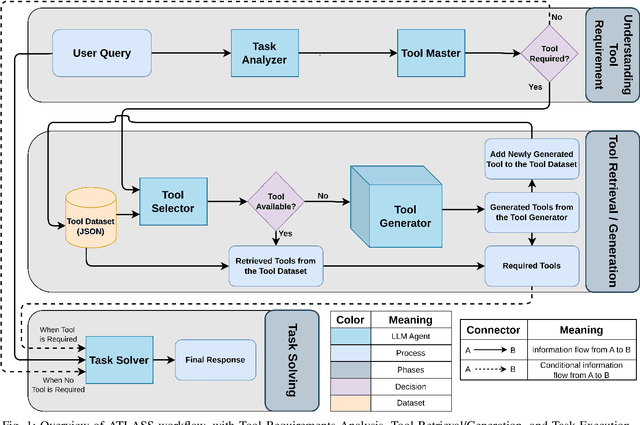
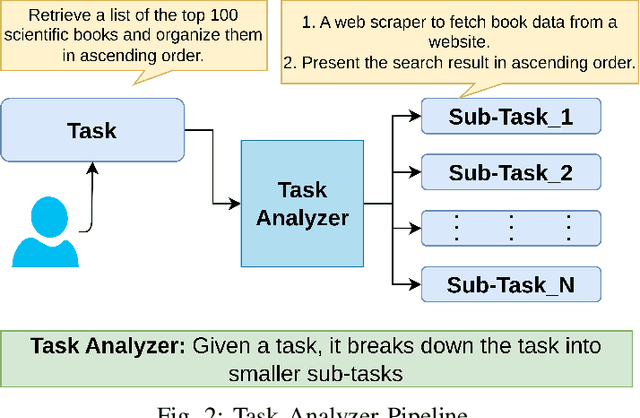
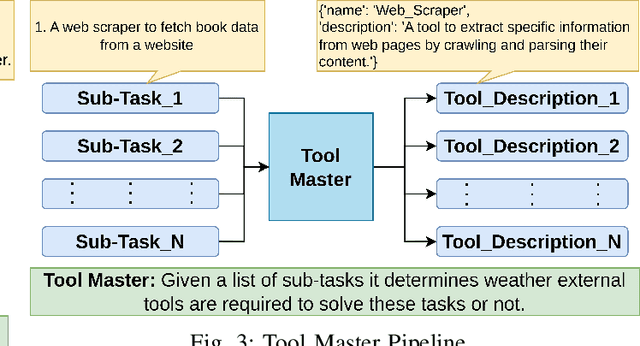
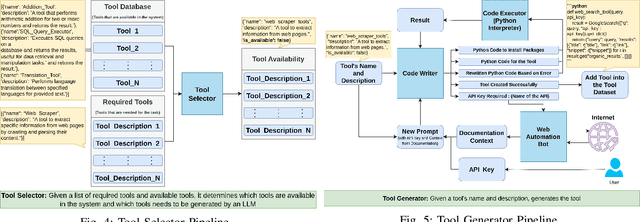
Abstract:The combination of LLM agents with external tools enables models to solve complex tasks beyond their knowledge base. Human-designed tools are inflexible and restricted to solutions within the scope of pre-existing tools created by experts. To address this problem, we propose ATLASS, an advanced tool learning and selection system designed as a closed-loop framework. It enables the LLM to solve problems by dynamically generating external tools on demand. In this framework, agents play a crucial role in orchestrating tool selection, execution, and refinement, ensuring adaptive problem-solving capabilities. The operation of ATLASS follows three phases: The first phase, Understanding Tool Requirements, involves the Agents determining whether tools are required and specifying their functionality; the second phase, Tool Retrieval/Generation, involves the Agents retrieving or generating tools based on their availability; and the third phase, Task Solving, involves combining all the component tools necessary to complete the initial task. The Tool Dataset stores the generated tools, ensuring reusability and minimizing inference cost. Current LLM-based tool generation systems have difficulty creating complex tools that need APIs or external packages. In ATLASS, we solve the problem by automatically setting up the environment, fetching relevant API documentation online, and using a Python interpreter to create a reliable, versatile tool that works in a wider range of situations. OpenAI GPT-4.0 is used as the LLM agent, and safety and ethical concerns are handled through human feedback before executing generated code. By addressing the limitations of predefined toolsets and enhancing adaptability, ATLASS serves as a real-world solution that empowers users with dynamically generated tools for complex problem-solving.
Physical Rule-Guided Convolutional Neural Network
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:The black-box nature of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and their reliance on large datasets limit their use in complex domains with limited labeled data. Physics-Guided Neural Networks (PGNNs) have emerged to address these limitations by integrating scientific principles and real-world knowledge, enhancing model interpretability and efficiency. This paper proposes a novel Physics-Guided CNN (PGCNN) architecture that incorporates dynamic, trainable, and automated LLM-generated, widely recognized rules integrated into the model as custom layers to address challenges like limited data and low confidence scores. The PGCNN is evaluated on multiple datasets, demonstrating superior performance compared to a baseline CNN model. Key improvements include a significant reduction in false positives and enhanced confidence scores for true detection. The results highlight the potential of PGCNNs to improve CNN performance for broader application areas.
Deep Learning for Automated Wound Classification And Segmentation
Aug 10, 2024
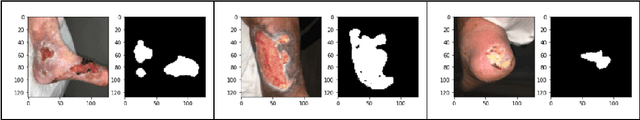


Abstract:Wounds, such as foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, leg ulcers, and infected wounds, come up with substantial problems for healthcare professionals. Prompt and accurate segmentation is crucial for effective treatment. However, contemporary methods need an exhaustive model that is qualified for both classification and segmentation, especially lightweight ones. In this work, we tackle this issue by presenting a new architecture that incorporates U-Net, which is optimized for both wound classification and effective segmentation. We curated four extensive and diverse collections of wound images, utilizing the publicly available Medetec Dataset, and supplemented with additional data sourced from the Internet. Our model performed exceptionally well, with an F1 score of 0.929, a Dice score of 0.931 in segmentation, and an accuracy of 0.915 in classification, proving its effectiveness in both classification and segmentation work. This accomplishment highlights the potential of our approach to automating wound care management.
Securing the Diagnosis of Medical Imaging: An In-depth Analysis of AI-Resistant Attacks
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning (ML) is a rapidly developing area of medicine that uses significant resources to apply computer science and statistics to medical issues. ML's proponents laud its capacity to handle vast, complicated, and erratic medical data. It's common knowledge that attackers might cause misclassification by deliberately creating inputs for machine learning classifiers. Research on adversarial examples has been extensively conducted in the field of computer vision applications. Healthcare systems are thought to be highly difficult because of the security and life-or-death considerations they include, and performance accuracy is very important. Recent arguments have suggested that adversarial attacks could be made against medical image analysis (MedIA) technologies because of the accompanying technology infrastructure and powerful financial incentives. Since the diagnosis will be the basis for important decisions, it is essential to assess how strong medical DNN tasks are against adversarial attacks. Simple adversarial attacks have been taken into account in several earlier studies. However, DNNs are susceptible to more risky and realistic attacks. The present paper covers recent proposed adversarial attack strategies against DNNs for medical imaging as well as countermeasures. In this study, we review current techniques for adversarial imaging attacks, detections. It also encompasses various facets of these techniques and offers suggestions for the robustness of neural networks to be improved in the future.
AI-Driven Approaches for Optimizing Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Survey
Jun 22, 2024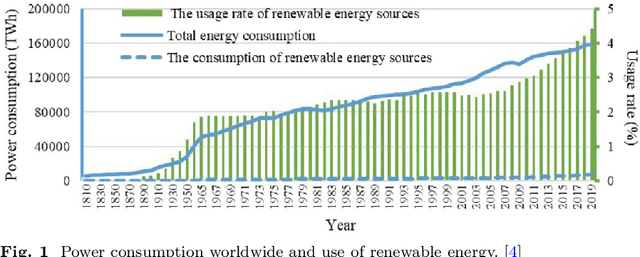
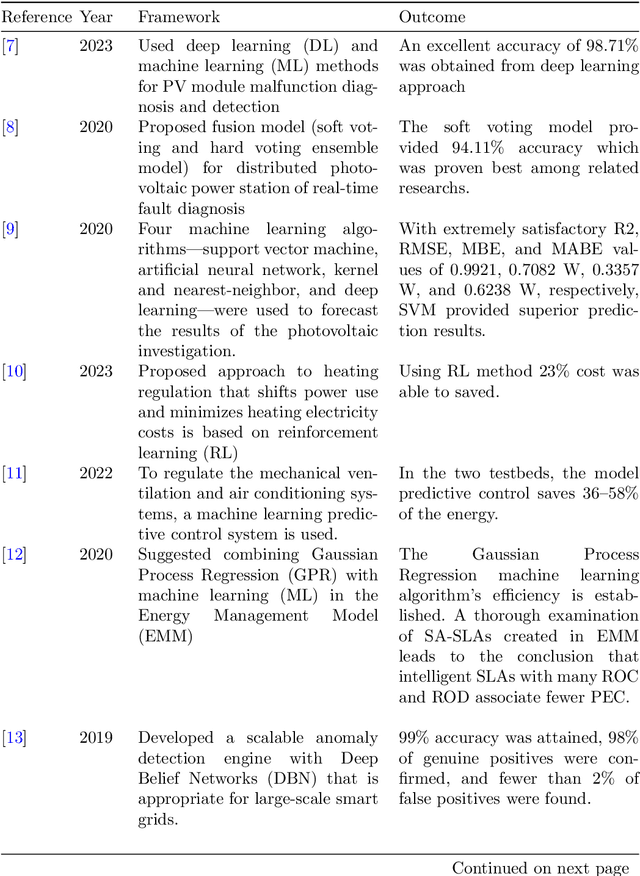
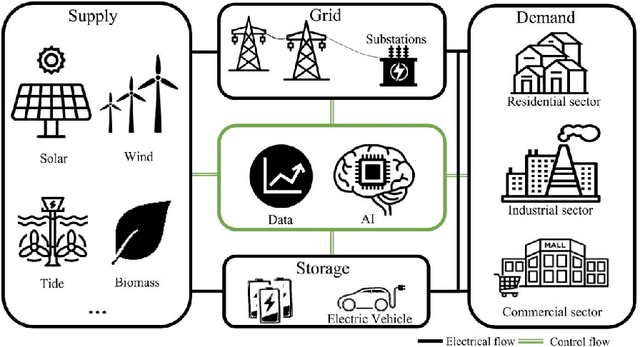
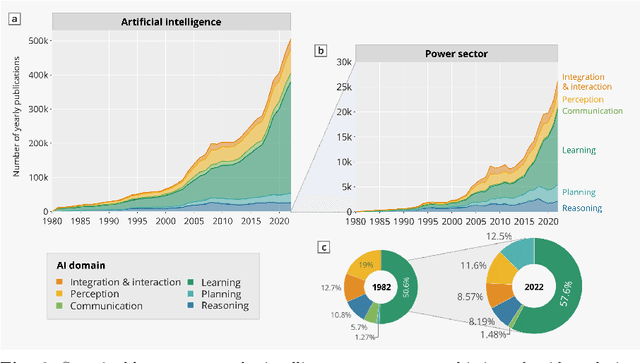
Abstract:Reduced environmental effect, lower operating costs, and a stable and sustainable energy supply for current and future generations are the main reasons why power optimization is important. Power optimization makes ensuring that energy is used more effectively, cutting down on waste and optimizing the utilization of resources.In today's world, power optimization and artificial intelligence (AI) integration are essential to changing the way energy is produced, used, and distributed. Real-time monitoring and analysis of power usage trends is made possible by AI-driven algorithms and predictive analytics, which enable dynamic modifications to effectively satisfy demand. Efficiency and sustainability are increased when power consumption is optimized in different sectors thanks to the use of intelligent systems. This survey paper comprises an extensive review of the several AI techniques used for power optimization as well as a methodical analysis of the literature for the study of various intelligent system application domains across different disciplines of power consumption.This literature review identifies the performance and outcomes of 17 different research methods by assessing them, and it aims to distill valuable insights into their strengths and limitations. Furthermore, this article outlines future directions in the integration of AI for power consumption optimization.
Present and Future of AI in Renewable Energy Domain : A Comprehensive Survey
Jun 22, 2024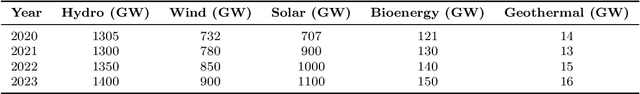
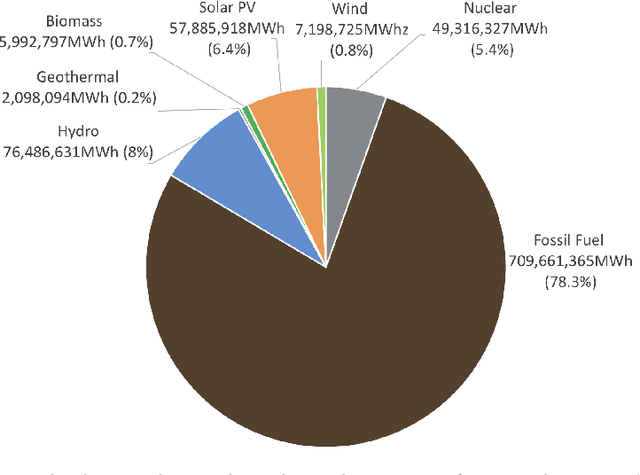
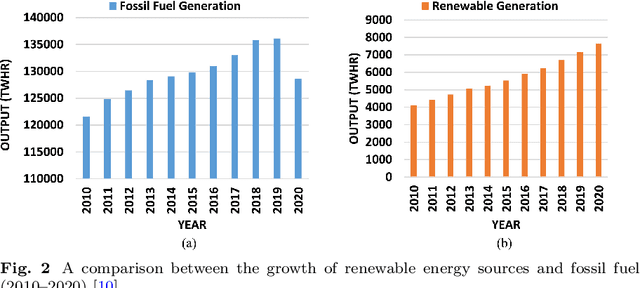

Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a crucial instrument for streamlining processes in various industries, including electrical power systems, as a result of recent digitalization. Algorithms for artificial intelligence are data-driven models that are based on statistical learning theory and are used as a tool to take use of the data that the power system and its users generate. Initially, we perform a thorough literature analysis of artificial intelligence (AI) applications related to renewable energy (RE). Next, we present a thorough analysis of renewable energy factories and assess their suitability, along with a list of the most widely used and appropriate AI algorithms. Nine AI-based strategies are identified here to assist Renewable Energy (RE) in contemporary power systems. This survey paper comprises an extensive review of the several AI techniques used for renewable energy as well as a methodical analysis of the literature for the study of various intelligent system application domains across different disciplines of renewable energy. This literature review identifies the performance and outcomes of nine different research methods by assessing them, and it aims to distill valuable insights into their strengths and limitations. This study also addressed three main topics: using AI technology for renewable power generation, utilizing AI for renewable energy forecasting, and optimizing energy systems. Additionally, it explored AI's superiority over conventional models in controllability, data handling, cyberattack prevention, smart grid implementation, robotics- AI's significance in shaping the future of the energy industry. Furthermore, this article outlines future directions in the integration of AI for renewable energy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge